标签:初始 vat name 命中率 lin 9.png 不刷新 getch www
上一篇[MyBatis框架原理2:SqlSession运行过程][1]介绍了MyBatis的工作流程,其中涉及到了MyBatis缓存的使用,首先回顾一下工作流程图:
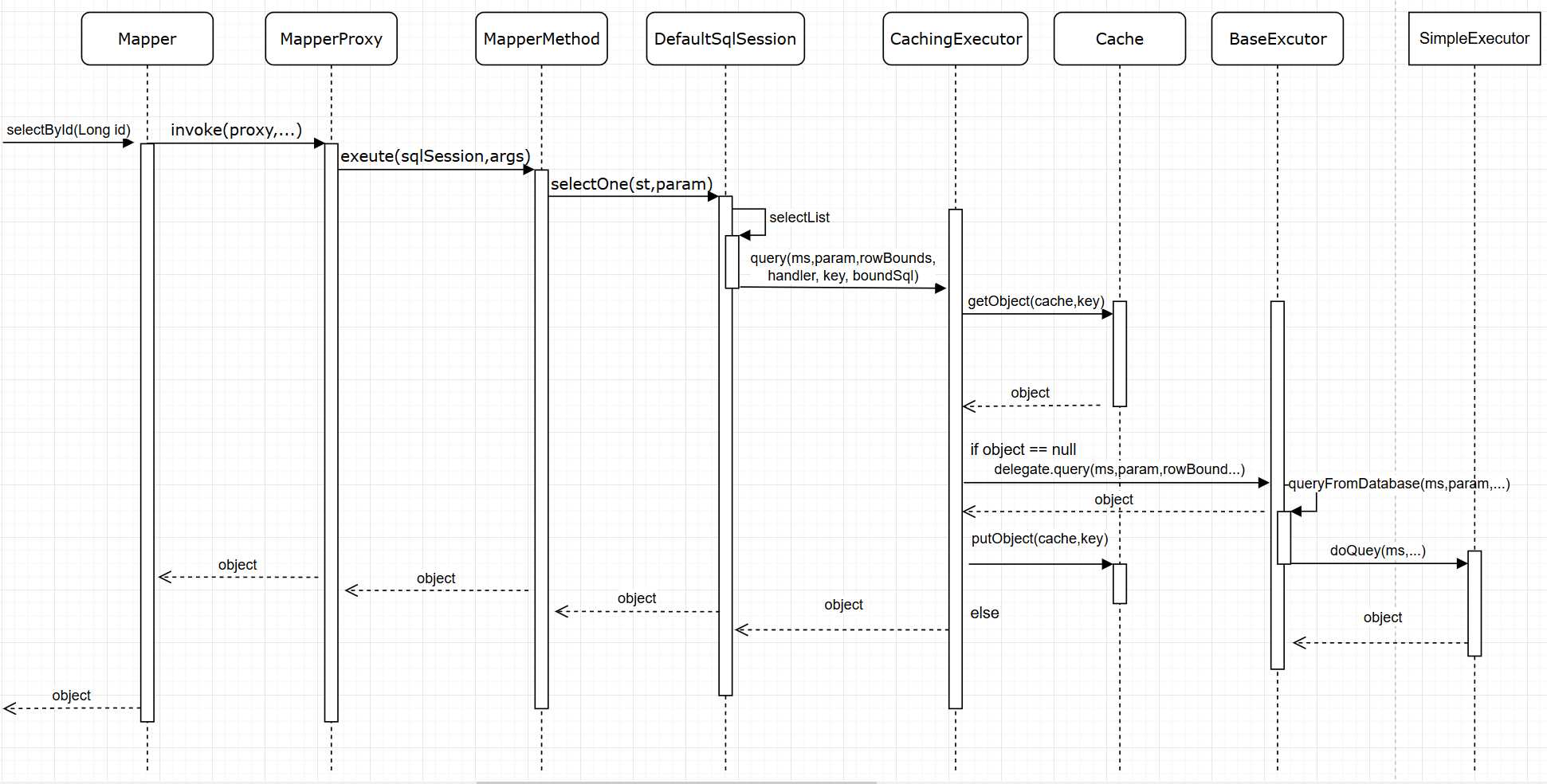
如果开启了二级缓存,数据查询执行过程就是首先从二级缓存中查询,如果未命中则从一级缓存中查询,如果也未命中则从数据库中查询。MyBatis的一级和二级缓存都是基于Cache接口的实现,下面先来看看Cache接口和其各种实现类。
public interface Cache {
String getId();
//缓存中添加数据,key为生成的CacheKey,value为查询结果
void putObject(Object key, Object value);
//查询
Object getObject(Object key);
//删除
Object removeObject(Object key);
//清空缓存
void clear();
//获取缓存数量
int getSize();
//获取读写锁
ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock();
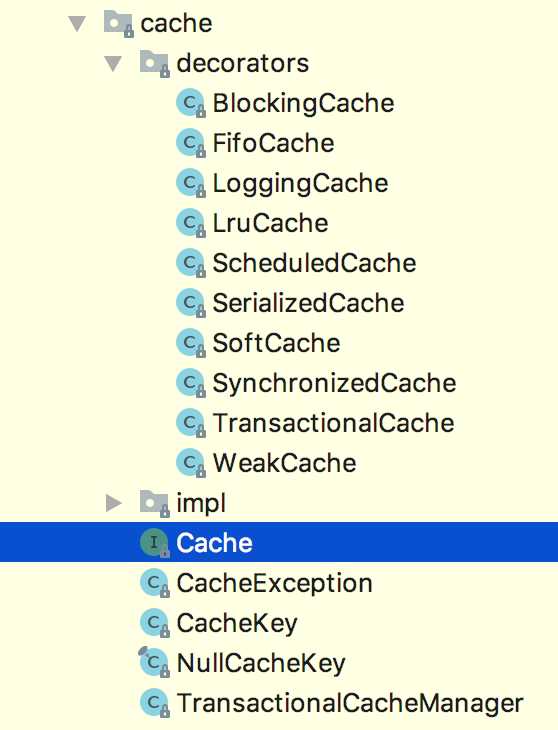
}Cache接口位于MyBatis的cache包下,定义了缓存的基本方法,其实现类采用了装饰器模式,通过实现类的组装,可以实现操控缓存的功能。cache包结构如下:
public class BlockingCache implements Cache {
//阻塞时长
private long timeout;
private final Cache delegate;
//key和ReentrantLock对象一一对应
private final ConcurrentHashMap<Object, ReentrantLock> locks;
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
//获取key的锁
acquireLock(key);
//根据key查询
Object value = delegate.getObject(key);
//如果命中缓存,释放锁,未命中则继续持有锁
if (value != null) {
releaseLock(key);
}
return value;
}
@Override
//从数据库获取结果后,将结果放入BlockingCache,然后释放锁
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
try {
delegate.putObject(key, value);
} finally {
releaseLock(key);
}
}
...CacheKey对象是用来确认缓存项的唯一标识,由其内部ArrayList添加的所有对象来确认两个CacheKey是否相同,通常ArrayList内将添加MappedStatement的id,SQL语句,用户传递给SQL语句的参数以及查询结果集范围RowBounds等,CacheKey源码如下:
public class CacheKey implements Cloneable, Serializable {
...
private final int multiplier;
private int hashcode;
private long checksum;
private int count;
private List<Object> updateList;
public CacheKey() {
this.hashcode = DEFAULT_HASHCODE;
this.multiplier = DEFAULT_MULTIPLYER;
this.count = 0;
this.updateList = new ArrayList<Object>();
}
//向updateLis中添加对象
public void update(Object object) {
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : ArrayUtil.hashCode(object);
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
updateList.add(object);
}
@Override
//重写equals方法判断CacheKey是否相同
public boolean equals(Object object) {
if (this == object) {
return true;
}
if (!(object instanceof CacheKey)) {
return false;
}
final CacheKey cacheKey = (CacheKey) object;
if (hashcode != cacheKey.hashcode) {
return false;
}
if (checksum != cacheKey.checksum) {
return false;
}
if (count != cacheKey.count) {
return false;
}
//比较updateList中每一项
for (int i = 0; i < updateList.size(); i++) {
Object thisObject = updateList.get(i);
Object thatObject = cacheKey.updateList.get(i);
if (!ArrayUtil.equals(thisObject, thatObject)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
一级缓存是session级别缓存,只存在当前会话中,在没有任何配置下,MyBatis默认开启一级缓存,当一个SqlSession第一次执行SQL语句和参数查询时,将生成的CacheKey和查询结果放入缓存中,下一次通过相同的SQL语句和参数查询时,就会从缓存中获取,当进行更新或者插入操作时,一级缓存会进行清空。在上一篇中说到,MayBatis进行一级缓存查询和写入是由BaseExecutor执行的,源码如下:
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
...
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
protected int queryStack;
private boolean closed;
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad>();
//一级缓存初始化
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache");
this.closed = false;
this.configuration = configuration;
this.wrapper = this;
}
...public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//缓存中放入CacheKey和占位符
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//在数据库中查询操作
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//缓存中放入CacheKey和结果集
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
//返回结果
return list;
}public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//从缓存获取结果
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//未命中缓存,则从数据库查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
} public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//清空缓存
clearLocalCache();
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
通过以下代码验证下,分别开两个session进行相同的查询,第一个session查询两次:
public void testSelect() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("findUserById", 1);
System.out.println(user);
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("findUserById", 1);
System.out.println(user2);
sqlSession.close();
System.out.println("sqlSession closed!===================================");
//新建会话
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user3 = sqlSession2.selectOne("findUserById", 1);
System.out.println(user3);
sqlSession2.close();
}把日志设置为DEBUG级别得到运行日志:
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
User [id=1, username=小明, birthday=null, sex=1, address=四川成都]
User [id=1, username=小明, birthday=null, sex=1, address=四川成都]
DEBUG [main] - Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16022d9d]
DEBUG [main] - Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16022d9d]
DEBUG [main] - Returned connection 369241501 to pool.
sqlSession closed!===================================
DEBUG [main] - Opening JDBC Connection
DEBUG [main] - Checked out connection 369241501 from pool.
DEBUG [main] - Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16022d9d]
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
User [id=1, username=小明, birthday=null, sex=1, address=四川成都]
DEBUG [main] - Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16022d9d]
DEBUG [main] - Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16022d9d]
DEBUG [main] - Returned connection 369241501 to pool.
第一次会话中,虽然查询了两次id为1的用户,但是只执行了一次SQL,关闭会话后开启一次新的会话,再次查询id为1的用户,SQL再次执行,说明了一级缓存只存在SqlSession中,不同SqlSession不能共享。
二级缓存是Mapper级别缓存,也就是同一Mapper下不同的session共享二级缓存区域。
只需要在XML映射文件中增加cache标签或cache-ref标签标签就可以开启二级缓存,cache-ref标签配置的是共享其指定Mapper的二级缓存区域。具体配置信息如下:
二级缓存是在MyBatis的解析配置文件时初始化,在XMLMapperBuilder中将缓存配置解析:
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//指定默认类型为PerpetualCache
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
//默认缓存策略为LruCache
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//委托builderAssistant构建二级缓存
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}构建过程:
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
//设置缓存类型,默认为PerpetualCache
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
//设置缓存策略,默认使用LruCache装饰器
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
//设置刷新时间
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
//设置大小
.size(size)
//设置是否只读
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}最终得到默认的二级缓存对象结构为:

CachingExecutor将初始化的Cache对象用TransactionalCache包装后放入TransactionalCacheManager的Map中,下面代码中的tcm就是TransactionalCacheManager对象,CachingExecutor执行二级缓存操作过程:
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//从Configuration的MappedStatement中获取二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
//判断是否需要刷新缓存,SELECT不刷新,INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE刷新缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//从二级缓存中获取数据
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
//委托BaseExecutor查询
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//查询结果放入二级缓存
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}通过之前一级缓存的例子验证二级缓存,只需要在UserMapper映射文件中加入cache标签,并且让相关POJO类实现java.io.Serializable接口,运行得到日志:
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
User [id=1, username=小明, birthday=null, sex=1, address=四川成都]
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [com.kkb.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.0
User [id=1, username=小明, birthday=null, sex=1, address=四川成都]
DEBUG [main] - Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@5c072e3f]
DEBUG [main] - Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@5c072e3f]
DEBUG [main] - Returned connection 1543974463 to pool.
sqlSession closed!===================================
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [com.kkb.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper]: 0.3333333333333333
User [id=1, username=小明, birthday=null, sex=1, address=四川成都]
不同session查询同一条记录时,总共只执行了一次SQL语句,并且日志打印出了缓存的命中率,这时候不同session已经共享了二级缓存区域。
[1]: https://www.cnblogs.com/abcboy/p/9656302.html
标签:初始 vat name 命中率 lin 9.png 不刷新 getch www
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/abcboy/p/9688961.html