标签:lin center span target arc split void repo 算法
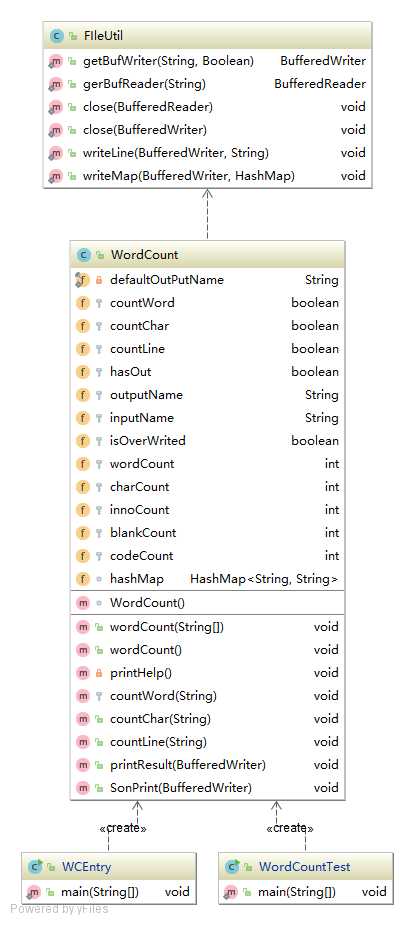
1. 字符统计
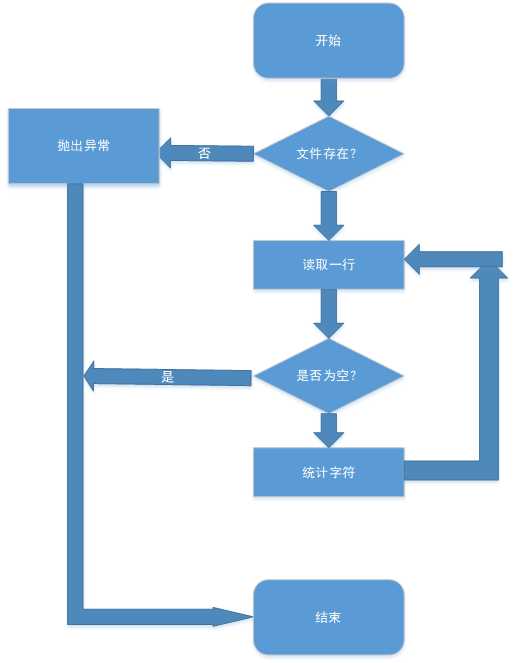
2. 单词统计
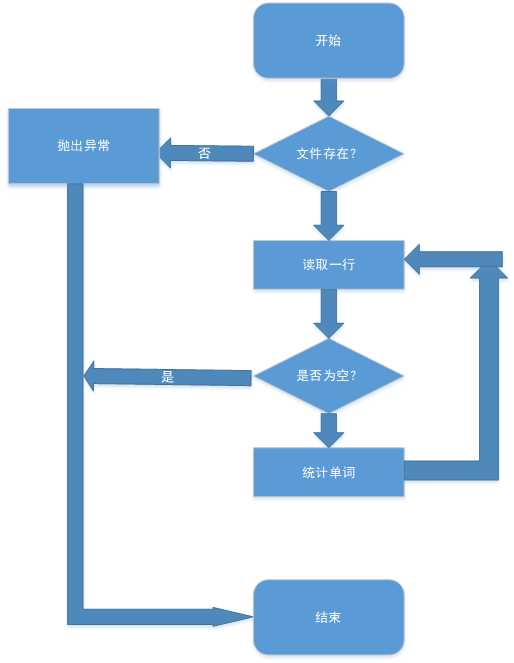
3.统计行数
逻辑差不多,与上面类似
考虑到扩展性,利用反射机制和钩子方法实现子类对父类功能的复用和扩展。
public void printResult(BufferedWriter bw){
if (countWord) {
FIleUtil.writeLine(bw, outputName+",单词数:"+wordCount+"\n");
}
if (countLine){
FIleUtil.writeLine(bw, outputName+",代码行/空行/注释行:"+codeCount+"/"+blankCount+"/"+innoCount+"\n");
}
if (countChar) {
FIleUtil.writeLine(bw, outputName+",字符数:"+charCount+"\n");
}
if (isOverWrited){
SonPrint(bw);
}
}
public void wordCount(){
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = FIleUtil.getBufWriter(outputName, true);
Set<String> keys = hashMap.keySet();
keys.remove("-o");
try {
br = FIleUtil.gerBufReader(inputName);
String s = br.readLine();
while (s != null) {
for (String key : keys) {
Field field = this.getClass().getDeclaredField(hashMap.get(key));
if ((boolean)field.get(this) == true) {
Method method = this.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(hashMap.get(key),String.class);
method.invoke(this,s);
}
}
s = br.readLine();
}
printResult(bw);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
FIleUtil.close(br);
FIleUtil.close(bw);
}
}
/**
* 统计单词
*/
protected void countWord(String s){
if (s != null ) {
String[] split = null;
split = s.split("\\s{1,}|,");
if (split != null) {
for (String word : split) {
if (!"".equals(word)) {
wordCount++;
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 统计字符数,如果制定文件 则输入到制定文件
* 没有则输出到 result.txt 路径为当前目录
*/
public void countChar(String s){
if(s != null){
charCount++; //回车
charCount += s.length();
}
}
/**
* 统计行数
*/
public void countLine(String s){
BufferedWriter bw = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
if (s.contains("//")) {
innoCount++;
} else if ("".equals(s)){
blankCount++;
} else {
codeCount++;
}
}
public class WordCountTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
//不存在的文件 黑盒
String[] param_noFIle = {"-w", "no.txt", };
new WordCount().wordCount(param_noFIle);
//不存在的参数 黑盒
String[] param_no = {"-n", "no.txt", };
new WordCount().wordCount(param_no);
//黑盒
String[] param_nothing = {};
new WordCount().wordCount(param_nothing);
//黑盒
String[] params3 = {"-l"};
new WordCount().wordCount(params3);
//白盒测试 -w bug 多个回车空行导致的空串被统计
String[] param = {"-w", "aaa.txt", };
new WordCount().wordCount(param);
//白盒测试 -c
String[] param_c = {"-c", "bbb.txt", };
new WordCount().wordCount(param_c);
//白盒测试 -l
String[] param_l = {"-l","ccc.txt"};
new WordCount().wordCount(param_l);
//白盒 -c -o
String[] params = {"-c", "aaa.txt","-o", "bbb.txt"};
new WordCount().wordCount(params);
//白盒 -c -w -l -o
String[] params4 = {"-c", "-w","-l","src/cn/blankspace/WordCount.java","-o", "output.txt"};
new WordCount().wordCount(params4);
}
}
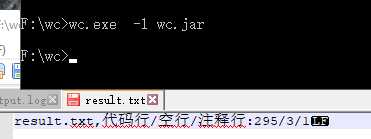
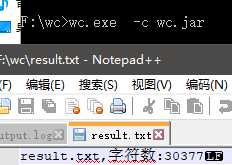
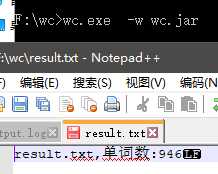
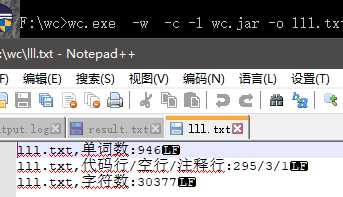
边界测试
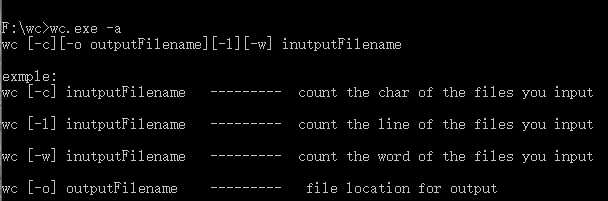



白盒测试
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 (分钟) |
实际耗时 (分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
10 |
5 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
10 |
5 |
|
Development |
开发 |
235 |
|
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
60 |
30 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
30 |
0 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 |
0 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
20 |
40 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
60 |
300 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
15 |
0 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
10 |
30 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
55 |
0 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
0 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
10 |
5 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
15 |
10 |
|
|
合计 |
295 |
435 |
我大部分的时间都花在了写代码上,因为我的方法是先写一个可运行的版本,然后再去重构它。所以编码花的时间要多一些。与以往不同的是,我花了一些时间去设计类图和算法流程图,这是我以前不愿意去干的,先花一些时间去建立模型,理清处编码的编码的思路,反而在一定程度上能加快编码的速度。对于新技术的学习,git是我一直在用的没有花什么学习成本。把jar打包成exe,如果想一口气把教程看完,再来做的确很难。但是通过一步步的跟着做,其实就很简单。
标签:lin center span target arc split void repo 算法
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/mrblankspace/p/9692364.html