标签:little contain 返回结果 on() app ndt pre ima @class
简单来说,Beautiful Soup是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据。官方解释如下:
Beautiful Soup提供一些简单的、python式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。
它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。
Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Beautiful Soup会帮你节省数小时甚至数天的工作时间.你可能在寻找 Beautiful Soup3 的文档,Beautiful Soup 3 目前已经停止开发,官网推荐在现在的项目中使用Beautiful Soup 4。
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
Beautiful Soup支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器,如果我们不安装它,则 Python 会使用 Python默认的解析器,lxml 解析器更加强大,速度更快,推荐安装。
pip3 install lxml
另一个可供选择的解析器是纯Python实现的 html5lib , html5lib的解析方式与浏览器相同,可以选择下列方法来安装html5lib:
pip install html5lib
解析器对比:
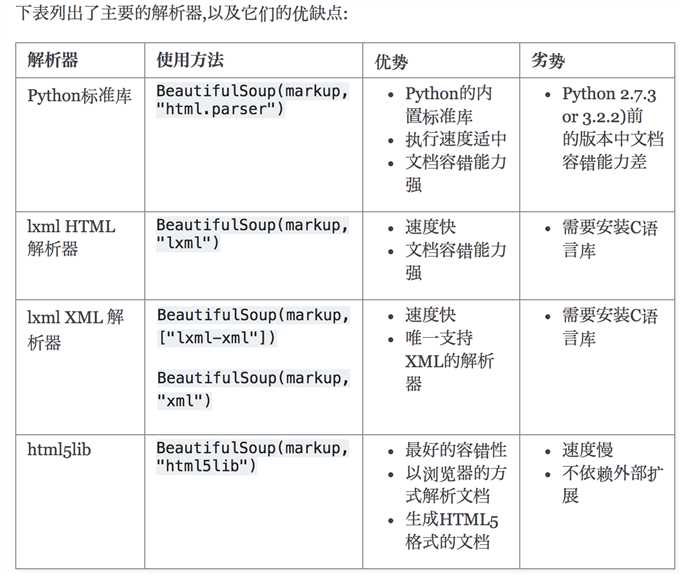
下面的一段HTML代码将作为例子被多次用到.这是 爱丽丝梦游仙境的 的一段内容(以后内容中简称为 爱丽丝 的文档):
html_doc = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse‘s story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse‘s story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """
使用BeautifulSoup解析这段代码,能够得到一个 BeautifulSoup 的对象
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "html.parser") print(soup.head) # 获取head标签 print(soup.head.title) # 获取head标签中title标签 print(soup.a) # 注意:获取的是第一个a标签
从文档中找到所有<a>标签的链接:
for link in soup.find_all("a"): print(link.get("href"))
从文档中获取所有文字内容:
print(soup.get_text())
通俗点讲就是 HTML 中的一个个标签,Tag 对象与XML或HTML原生文档中的tag相同:
soup = BeautifulSoup(‘<b class="boldest">Extremely bold</b>‘) tag = soup.b type(tag) # <class ‘bs4.element.Tag‘>
soup对象再以爱丽丝梦游仙境的html_doc为例,操作文档树最简单的方法就是告诉它你想获取的tag的name.如果想获取 <head> 标签,只要用 soup.head :
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "html.parser") # 获取soup对象 print(soup.find_all("a")) # 获取a标签对象,(是标签不是单独的一个a) print(soup.find_all("p")) # 获取p标签对象
for link in soup.find_all("a"): print(link.name) # 获取html中的所有a标签 (a)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup for link in soup.find_all("a"): """link是一个a标签对象,使用a标签.获取标签中的其他数据""" # print(link.name) # 获取html中的所有a标签 (a) print(link.get("id")) print(link.get("class")) print(link.get("href")) # 获取方法1 print(link["href"]) # 获取方法2 print(link.attrs) # {"class":"sister","id":"link1"}
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "html.parser") for link in soup.find_all("a"): print(link.text) # 获取文本方法1 print(link.string) # 获取文本 print(link.get_text()) # 获取文本方法2
print(soup.p.text) # 取到p下所有的文本内容 print(soup.p.string) # p下的文本只为一个可以取到,否则为None
嵌套选择(就是“点出想要的数据”)
print(soup.head.title.string) print(soup.body.a.string)
子节点、子孙节点
# 获取子节点 print(soup.p.contents) # p下所有子节点 print(soup.p.childern) # 得到一个迭代器,包含p下所有子节点,使用for循环遍历 for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.children): print(i, child) # 获取子孙节点 print(soup.p.descendants) # 获取子孙节点,p下所有的标签都会选择出来 for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.descendants): print(i, child)
父节点、祖先节点
print(soup.a.parent) # 获取a标签的父节点 print(soup.a.parents) # 找到a标签所有的祖先节点,父亲的父亲,父亲的父亲的父亲... # 迭代器 for循环遍历 for i in soup.p.parents: print(i)
兄弟节点
print(soup.a.next_sibling) # 下一个兄弟 print("----", soup.a.previous_sibling) # 上一个兄弟 print(list(soup.a.next_sibling)) # 下面的兄弟们 -->生成器对象 print(soup.a.previous_siblings) # 上面的兄弟们 --> 生成器对象 for i in soup.a.previous_siblings: print(i)
BeautifulSoup定义了很多搜索方法,这里着重介绍2个: find() 和 find_all() .其它方法的参数和用法类似
字符串:即标签名
print(soup.find_all(name="a")) # 结果为一个列表中包含所有的a标签
正则表达式:结果 & 字符串一样
import re reg = re.compile("^b") ret = soup.find_all(name=reg) # #找出b开头的标签,结果有body和b标签 print(ret)
列表:查找列表中的标签
ret = soup.find_all(name=["a", "b"]) # 有几个找几个标签对象 print(ret)
第四种和第五种方法配合使用(不常用)
def has_class_but_no_id(tag): return tag.has_attr("class") and not tag.has_attr("id") for tag in soup.find_all(name=has_class_but_no_id): print(tag)
import re soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, "html.parser") # keyword: key=value的形式,value可以是过滤器:字符串 , 正则表达式 , 列表, True . print(soup.find_all(name=re.compile("^t"))) # 以字符匹配标签 print(soup.find_all(id=re.compile("link1"))) # id匹配 print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile("http"), id=re.compile(""))) # 或的关系, print(soup.find_all(id=True)) # 查找有di属性的标签 # 按照类名查找,注意关键字是class_,class_=value,value可以是五种选择器之一 print(soup.find_all("a", class_="sister")) # 查找类为sister的a标签 print(soup.find_all("a", class_="sister ssss")) # 查找类为sister和sss的a标签,顺序错误也匹配不成功 print(soup.find_all(class_=re.compile("^sis"))) # 查找类为sister的所有标签 # sttrs:字典查找 print(soup.find_all("p", attrs={"class": "story"})) # text: 值可以是:字符,列表,True,正则 print(soup.find_all(text="Elsie")) print(soup.find_all("a", text="Elsie")) # limit参数:如果文档树很大那么搜索会很慢.如果我们不需要全部结果,可以使用 limit # 参数限制返回结果的数量.效果与SQL中的limit关键字类似,当搜索到的结果数量达到 # limit 的限制时,就停止搜索返回结果 print(soup.find_all("a", limit=2)) # limit参数是限制返回的条数 # recursive:调用tag的 find_all() 方法时,Beautiful Soup会检索当前tag的所有子孙节点, # 如果只想搜索tag的直接子节点,可以使用参数 recursive=False 。 print(soup.html.find_all("a")) print(soup.html.find_all("a", recursive=False))
简单使用
像调用 find_all() 一样调用tagfind_all() 几乎是Beautiful Soup中最常用的搜索方法,所以我们定义了它的简写方法. BeautifulSoup
对象和 tag 对象可以被当作一个方法来使用,这个方法的执行结果与调用这个对象的 find_all() 方法相同,下面两行代码是等价的:
print(soup.find_all("a")) print(soup("a")) # 同样的效果 print(soup.title.find_all(text=True)) print(soup.title(text=True))
#3、find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs ) find_all() 方法将返回文档中符合条件的所有tag,尽管有时候我们只想得到一个结果.比如文档中只有一个<body>标签,那么使用 find_all() 方法来查找<body>标签就不太合适, 使用 find_all 方法并设置 limit=1 参数不如直接使用 find() 方法.下面两行代码是等价的: soup.find_all(‘title‘, limit=1) # [<title>The Dormouse‘s story</title>] soup.find(‘title‘) # <title>The Dormouse‘s story</title> 唯一的区别是 find_all() 方法的返回结果是值包含一个元素的列表,而 find() 方法直接返回结果. find_all() 方法没有找到目标是返回空列表, find() 方法找不到目标时,返回 None . print(soup.find("nosuchtag")) # None soup.head.title 是 tag的名字 方法的简写.这个简写的原理就是多次调用当前tag的 find() 方法: soup.head.title # <title>The Dormouse‘s story</title> soup.find("head").find("title") # <title>The Dormouse‘s story</title>
4、其他方法
见官网:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html#find-parents-find-parent
我们在写 CSS 时,标签名不加任何修饰,类名前加点,id名前加 #,在这里我们也可以利用类似的方法来筛选元素,用到的方法是 soup.select(),返回类型是 list
(1)通过标签名查找
print(soup.select("title")) #[<title>The Dormouse‘s story</title>] print(soup.select("b")) #[<b>The Dormouse‘s story</b>]
(2)通过类名查找
print(soup.select(".sister")) ‘‘‘ [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] ‘‘‘
(3)通过 id 名查找
print(soup.select("#link1")) # [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>]
(4)组合查找
组合查找即和写 class 文件时,标签名与类名、id名进行的组合原理是一样的,例如查找 p 标签中,id 等于 link1的内容,二者需要用空格分开
print(soup.select("p #link2")) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
直接子标签查找
print(soup.select("p > #link2")) # [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
(5)属性查找
查找时还可以加入属性元素,属性需要用中括号括起来,注意属性和标签属于同一节点,所以中间不能加空格,否则会无法匹配到。
print(soup.select("a[href=‘http://example.com/tillie‘]")) #[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
select 方法返回的结果都是列表形式,可以遍历形式输出,然后用 get_text() 方法来获取它的内容:
for title in soup.select(‘a‘): print (title.get_text()) ‘‘‘ Elsie Lacie Tillie ‘‘‘
选取节点
nodename 选取nodename节点的所有子节点 xpath(‘//div’) 选取了所有div节点 / 从根节点选取 xpath(‘/div’) 从根节点上选取div节点 // 选取所有的当前节点,不考虑他们的位置 xpath(‘//div’) 选取所有的div节点 . 选取当前节点 xpath(‘./div’) 选取当前节点下的div节点 .. 选取当前节点的父节点 xpath(‘..’) 回到上一个节点 @ 选取属性 xpath(’//@calss’) 选取所有的class属性
ret=selector.xpath("//div") ret=selector.xpath("/div") ret=selector.xpath("./div") ret=selector.xpath("//p[@id=‘p1‘]") ret=selector.xpath("//div[@class=‘d1‘]/div/p[@class=‘story‘]")
谓语
表达式 结果 xpath(‘/body/div[1]’) 选取body下的第一个div节点 xpath(‘/body/div[last()]’) 选取body下最后一个div节点 xpath(‘/body/div[last()-1]’) 选取body下倒数第二个div节点 xpath(‘/body/div[positon()<3]’) 选取body下前两个div节点 xpath(‘/body/div[@class]’) 选取body下带有class属性的div节点 xpath(‘/body/div[@class=”main”]’) 选取body下class属性为main的div节点 xpath(‘/body/div[@price>35.00]’) 选取body下price元素值大于35的div节点
ret=selector.xpath("//p[@class=‘story‘]//a[2]") ret=selector.xpath("//p[@class=‘story‘]//a[last()]")
通配符 Xpath通过通配符来选取未知的XML元素
表达式 结果 xpath(’/div/*’) 选取div下的所有子节点 xpath(‘/div[@*]’) 选取所有带属性的div节点
ret=selector.xpath("//p[@class=‘story‘]/*") ret=selector.xpath("//p[@class=‘story‘]/a[@class]")
取多个路径 使用“|”运算符可以选取多个路径
表达式 结果
xpath(‘//div|//table’) 选取所有的div和table节点
ret=selector.xpath("//p[@class=‘story‘]/a[@class]|//div[@class=‘d3‘]") print(ret)
Xpath轴
轴可以定义相对于当前节点的节点集
轴名称 表达式 描述 ancestor xpath(‘./ancestor::*’) 选取当前节点的所有先辈节点(父、祖父) ancestor-or-self xpath(‘./ancestor-or-self::*’) 选取当前节点的所有先辈节点以及节点本身 attribute xpath(‘./attribute::*’) 选取当前节点的所有属性 child xpath(‘./child::*’) 返回当前节点的所有子节点 descendant xpath(‘./descendant::*’) 返回当前节点的所有后代节点(子节点、孙节点) following xpath(‘./following::*’) 选取文档中当前节点结束标签后的所有节点 following-sibing xpath(‘./following-sibing::*’) 选取当前节点之后的兄弟节点 parent xpath(‘./parent::*’) 选取当前节点的父节点 preceding xpath(‘./preceding::*’) 选取文档中当前节点开始标签前的所有节点 preceding-sibling xpath(‘./preceding-sibling::*’) 选取当前节点之前的兄弟节点 self xpath(‘./self::*’) 选取当前节点
功能函数
使用功能函数能够更好的进行模糊搜索
函数 用法 解释 starts-with xpath(‘//div[starts-with(@id,”ma”)]‘) 选取id值以ma开头的div节点 contains xpath(‘//div[contains(@id,”ma”)]‘) 选取id值包含ma的div节点 and xpath(‘//div[contains(@id,”ma”) and contains(@id,”in”)]‘) 选取id值包含ma和in的div节点 text() xpath(‘//div[contains(text(),”ma”)]‘) 选取节点文本包含ma的div节点
from lxml.etree import _Element for obj in ret: print(obj) print(type(obj)) # from lxml.etree import _Element ‘‘‘ Element对象 class xml.etree.ElementTree.Element(tag, attrib={}, **extra) tag:string,元素代表的数据种类。 text:string,元素的内容。 tail:string,元素的尾形。 attrib:dictionary,元素的属性字典。 #针对属性的操作 clear():清空元素的后代、属性、text和tail也设置为None。 get(key, default=None):获取key对应的属性值,如该属性不存在则返回default值。 items():根据属性字典返回一个列表,列表元素为(key, value)。 keys():返回包含所有元素属性键的列表。 set(key, value):设置新的属性键与值。 #针对后代的操作 append(subelement):添加直系子元素。 extend(subelements):增加一串元素对象作为子元素。#python2.7新特性 find(match):寻找第一个匹配子元素,匹配对象可以为tag或path。 findall(match):寻找所有匹配子元素,匹配对象可以为tag或path。 findtext(match):寻找第一个匹配子元素,返回其text值。匹配对象可以为tag或path。 insert(index, element):在指定位置插入子元素。 iter(tag=None):生成遍历当前元素所有后代或者给定tag的后代的迭代器。#python2.7新特性 iterfind(match):根据tag或path查找所有的后代。 itertext():遍历所有后代并返回text值。 remove(subelement):删除子元素。 ‘‘‘
标签:little contain 返回结果 on() app ndt pre ima @class
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaohei001/p/9720704.html