标签:des style blog http color io os 使用 ar
一、贴源码
源码存放的目录是src->core->Class.js

1 L.Class = function () {}; 2 3 L.Class.extend = function (props) { 4 5 // extended class with the new prototype 6 var NewClass = function () { 7 8 // call the constructor 9 if (this.initialize) { 10 this.initialize.apply(this, arguments); 11 } 12 13 // call all constructor hooks 14 if (this._initHooks.length) { 15 this.callInitHooks(); 16 } 17 }; 18 19 // jshint camelcase: false 20 var parentProto = NewClass.__super__ = this.prototype; 21 22 var proto = L.Util.create(parentProto); 23 proto.constructor = NewClass; 24 25 NewClass.prototype = proto; 26 27 //inherit parent‘s statics 28 for (var i in this) { 29 if (this.hasOwnProperty(i) && i !== ‘prototype‘) { 30 NewClass[i] = this[i]; 31 } 32 } 33 34 // mix static properties into the class 35 if (props.statics) { 36 L.extend(NewClass, props.statics); 37 delete props.statics; 38 } 39 40 // mix includes into the prototype 41 if (props.includes) { 42 L.Util.extend.apply(null, [proto].concat(props.includes)); 43 delete props.includes; 44 } 45 46 // merge options 47 if (proto.options) { 48 props.options = L.Util.extend(L.Util.create(proto.options), props.options); 49 } 50 51 // mix given properties into the prototype 52 L.extend(proto, props); 53 54 proto._initHooks = []; 55 56 // add method for calling all hooks 57 proto.callInitHooks = function () { 58 59 if (this._initHooksCalled) { return; } 60 61 if (parentProto.callInitHooks) { 62 parentProto.callInitHooks.call(this); 63 } 64 65 this._initHooksCalled = true; 66 67 for (var i = 0, len = proto._initHooks.length; i < len; i++) { 68 proto._initHooks[i].call(this); 69 } 70 }; 71 72 return NewClass; 73 }; 74 75 76 // method for adding properties to prototype 77 L.Class.include = function (props) { 78 L.extend(this.prototype, props); 79 }; 80 81 // merge new default options to the Class 82 L.Class.mergeOptions = function (options) { 83 L.extend(this.prototype.options, options); 84 }; 85 86 // add a constructor hook 87 L.Class.addInitHook = function (fn) { // (Function) || (String, args...) 88 var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1); 89 90 var init = typeof fn === ‘function‘ ? fn : function () { 91 this[fn].apply(this, args); 92 }; 93 94 this.prototype._initHooks = this.prototype._initHooks || []; 95 this.prototype._initHooks.push(init); 96 };
二、代码分析
(1)在L的命名空间下,定义Class对象,以构造函数的形式给出。
L.Class = function () {};
(2)分别给Class对象添加静态方法extend 、include、mergeOptions、addInitHook。
1 var L = {}; 2 L.Class = function(){}; 3 4 5 /* 6 * 作用:扩展该类的prototype,继承父类的静态函数、静态属性等 7 * 8 * */ 9 L.Class.extend = function(props){}; 10 /* 11 * 作用:添加属性到原型 12 * */ 13 L.Class.include = function (props) {}; 14 /* 15 * 作用:合并默认的options到Class 16 * */ 17 L.Class.mergeOptions = function (options) {}; 18 /* 19 * 作用:添加一个构造函数的钩子 20 * */ 21 L.Class.addInitHook = function (fn){};
(3)分析L.Class.extend函数
贴上L.Class.extend函数的源码:

1 L.Class.extend = function (props) { 2 3 // extended class with the new prototype 4 var NewClass = function () { 5 6 // call the constructor 7 if (this.initialize) { 8 this.initialize.apply(this, arguments); 9 } 10 11 // call all constructor hooks 12 if (this._initHooks.length) { 13 this.callInitHooks(); 14 } 15 }; 16 17 // jshint camelcase: false 18 var parentProto = NewClass.__super__ = this.prototype; 19 20 var proto = L.Util.create(parentProto); 21 proto.constructor = NewClass; 22 23 NewClass.prototype = proto; 24 25 //inherit parent‘s statics 26 for (var i in this) { 27 if (this.hasOwnProperty(i) && i !== ‘prototype‘) { 28 NewClass[i] = this[i]; 29 } 30 } 31 32 // mix static properties into the class 33 if (props.statics) { 34 L.extend(NewClass, props.statics); 35 delete props.statics; 36 } 37 38 // mix includes into the prototype 39 if (props.includes) { 40 L.Util.extend.apply(null, [proto].concat(props.includes)); 41 delete props.includes; 42 } 43 44 // merge options 45 if (proto.options) { 46 props.options = L.Util.extend(L.Util.create(proto.options), props.options); 47 } 48 49 // mix given properties into the prototype 50 L.extend(proto, props); 51 52 proto._initHooks = []; 53 54 // add method for calling all hooks 55 proto.callInitHooks = function () { 56 57 if (this._initHooksCalled) { return; } 58 59 if (parentProto.callInitHooks) { 60 parentProto.callInitHooks.call(this); 61 } 62 63 this._initHooksCalled = true; 64 65 for (var i = 0, len = proto._initHooks.length; i < len; i++) { 66 proto._initHooks[i].call(this); 67 } 68 }; 69 70 return NewClass; 71 };
现在,来看NewClass对象,NewClass对象就是创建一个新的内部对象,所有父类的属性和方法都基于此方法。this.initialize就是构造函数。
1 // extended class with the new prototype 2 var NewClass = function () { 3 4 // call the constructor 5 if (this.initialize) { 6 this.initialize.apply(this, arguments); 7 } 8 9 // call all constructor hooks 10 if (this._initHooks.length) { 11 this.callInitHooks(); 12 } 13 };
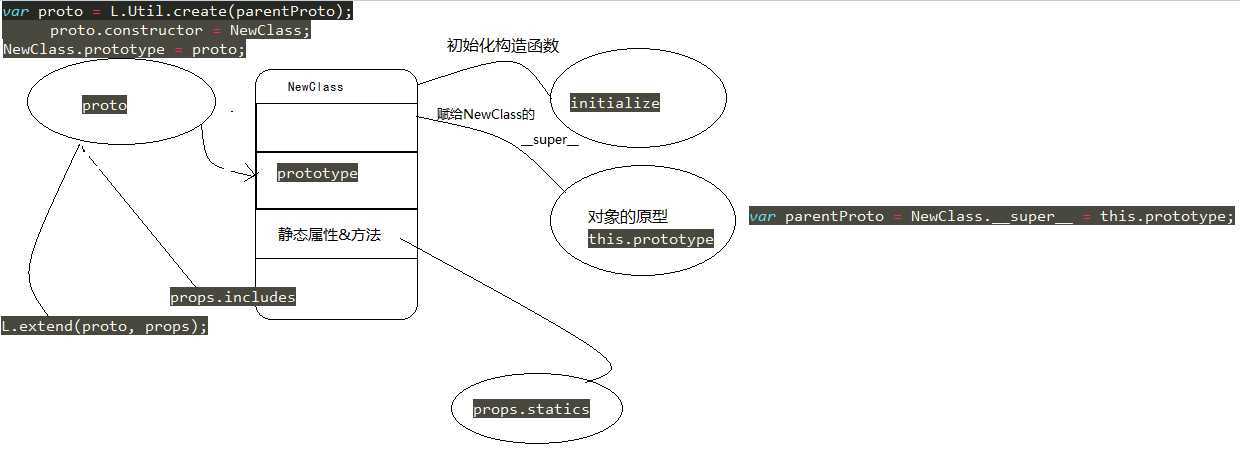
var parentProto = NewClass.__super__ = this.prototype; 将原型赋给NewClass的_super_属性,并赋值给parentProto。
var proto = L.Util.create(parentProto); //在LeafLet中有个Util.js,该工具类的方法的create方法的作用是:基于给定原型构建对象 proto.constructor = NewClass; //对象proto的构造函数指向NewClass NewClass.prototype = proto; //NewClass的原型指向proto,这个大家可以看看原型链的继承方式
附:L.Util.create代码:
// create an object from a given prototype create: Object.create || (function () { function F() {} return function (proto) { F.prototype = proto; return new F(); }; })()
接着往下看:
//inherit parent‘s statics for (var i in this) { if (this.hasOwnProperty(i) && i !== ‘prototype‘) { //继承父类的静态属性和方法,hasOwnProperty只会遍历自定义属性和方法,不会遍历原型 NewClass[i] = this[i]; } }
再接着往下看:
// mix static properties into the class if (props.statics) { L.extend(NewClass, props.statics); //L.extend == L.Util.extend,在Util.js中便可找到,作用是扩展属性,这里是将props.statics的属性给了NewClass delete props.statics; //删除该属性 } // mix includes into the prototype if (props.includes) { L.Util.extend.apply(null, [proto].concat(props.includes)); //apply这里巧妙的使用了null, 主要是为了使用extend的功能,将includes和proto的原型结合,连接成一个数组。 delete props.includes; //删除该属性 }
附:L.Util.extend源码
extend: function (dest) { var i, j, len, src; for (j = 1, len = arguments.length; j < len; j++) { src = arguments[j]; for (i in src) { dest[i] = src[i]; } } return dest; },
接着往下看:
// merge options if (proto.options) { props.options = L.Util.extend(L.Util.create(proto.options), props.options); //将options属性合并 } // mix given properties into the prototype L.extend(proto, props); //将props的扩展属性,包括原型给proto proto._initHooks = []; //初始化空的钩子数组
接着往下看:
// add method for calling all hooks
// 增加一个方法,调用所有的钩子 proto.callInitHooks = function () { if (this._initHooksCalled) { return; } //如果已经调用,直接return if (parentProto.callInitHooks) { //如果父类的原型中存在callInitHooks,则调用父类的callInitHooks parentProto.callInitHooks.call(this); } this._initHooksCalled = true; //设置调用后状态 for (var i = 0, len = proto._initHooks.length; i < len; i++) { proto._initHooks[i].call(this); //调用钩子的数组中的方法 } };
最后一步了,返回对象:
return NewClass;
(4)include:
// method for adding properties to prototype L.Class.include = function (props) { L.extend(this.prototype, props); };
(5)mergeOptions:
// merge new default options to the Class L.Class.mergeOptions = function (options) { L.extend(this.prototype.options, options); };
(6)addInitHook:
// add a constructor hook L.Class.addInitHook = function (fn) { // (Function) || (String, args...) var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1); var init = typeof fn === ‘function‘ ? fn : function () { this[fn].apply(this, args); }; this.prototype._initHooks = this.prototype._initHooks || []; this.prototype._initHooks.push(init); };
三、用图来理理extend函数
上一篇:Leaflet开源地图库源码研读(三)——浏览器&移动设备判断(browser.js)(by vczero)
leaflet开源地图库源码研读(四)——OOP的基础构建(by vczero)
标签:des style blog http color io os 使用 ar
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/vczero/p/leaflet_4.html