标签:pop push stack inf path sum pre val add continue
一、题目
1、审题
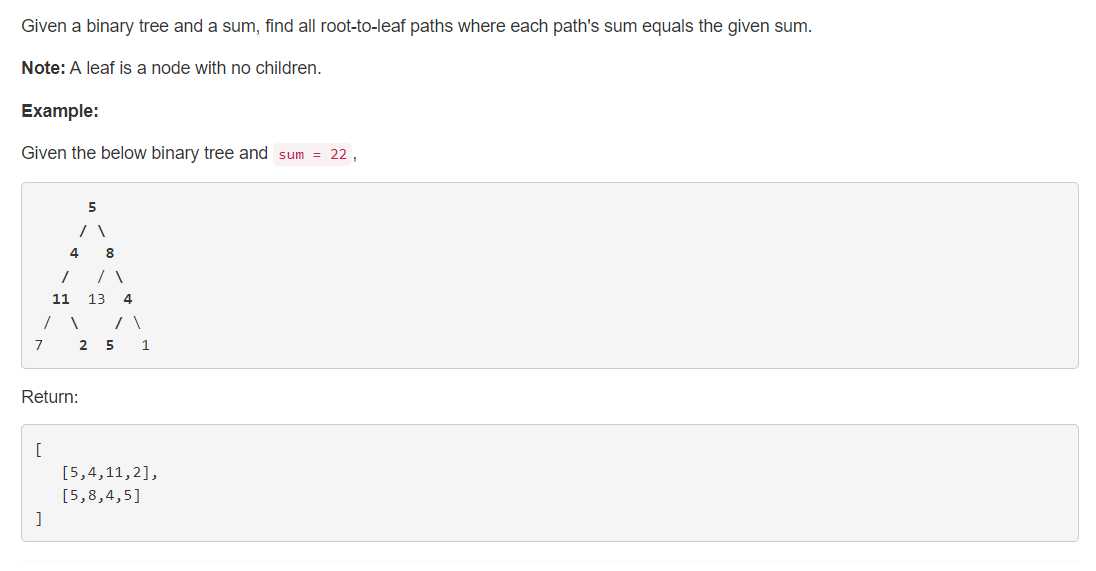
2、分析
给出一棵二叉树,求从根到叶节点的所有节点值和为 sum 的路径的所有节点集合。
二、解答
1、思路:
方法一、
采用递归。
深度优先遍历求出所有从根到叶节点的路径,将和为 sum 的进行记录。
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) { List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); List<Integer> targetList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); pathSum(root, sum, resultList, targetList); return resultList; } private void pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum, List<List<Integer>> resultList, List<Integer> targetList) { if(root == null) // 跳出条件 return; targetList.add(root.val); if(root.left == null && root.right == null && sum == root.val) { resultList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(targetList)); targetList.remove(targetList.size()-1); return; } else { pathSum(root.left, sum - root.val, resultList, targetList); pathSum(root.right, sum - root.val, resultList, targetList); } targetList.remove(targetList.size()-1); }
方法二、
采用后续遍历的迭代方法,进行记录和为 sum 的所有路径。
注意: pre 用于记录此右节点是否访问过,否则将陷入死循环。
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum3(TreeNode root, int sum) { List<List<Integer>> resultList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); if(root == null) return resultList; List<Integer> targetList = new ArrayList<>(); // postOrder Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); int target = 0; TreeNode cur = root; TreeNode pre = null; while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while(cur != null) { target += cur.val; targetList.add(cur.val); stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } cur = stack.peek(); if(cur.right != null && cur.right != pre) { cur = cur.right; continue; } if(cur.left == null && cur.right == null && target == sum) resultList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(targetList)); targetList.remove(targetList.size()-1); target -= cur.val; stack.pop(); pre = cur; cur = null; } return resultList; }
标签:pop push stack inf path sum pre val add continue
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/skillking/p/9742403.html