标签:1.2 project lines context elf 密码 OLE nes 默认
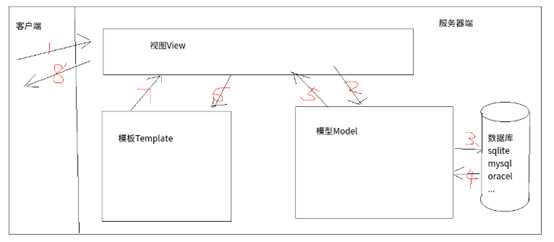
课程介绍

pip list
pip freeze
pip install django==1.8.2
pip install django==1.11.4
import django django.get_version()
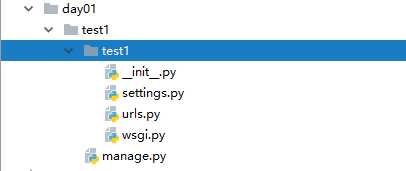
django-admin startproject test1
在settings.py文件中,通过DATABASES项进行数据库设置
django支持的数据库包括:sqlite、mysql等主流数据库
Django默认使用SQLite数据库
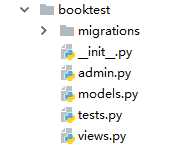
python manage.py startapp booktest
from django.db import models class BookInfo(models.Model): btitle = models.CharField(max_length=20) bpub_date = models.DateTimeField() def __str__(self): return "%d" % self.pk class HeroInfo(models.Model): hname = models.CharField(max_length=20) hgender = models.BooleanField() hcontent = models.CharField(max_length=100) hBook = models.ForeignKey(‘BookInfo‘) def __str__(self): return "%d" % self.pk
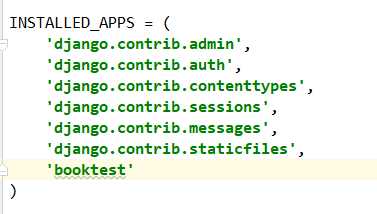
生成迁移文件:根据模型类生成sql语句
python manage.py makemigrations
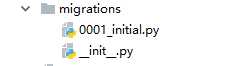
迁移文件被生成到应用的migrations目录
执行迁移:执行sql语句生成数据表
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py shell
# 引入需要的包: from booktest.models import BookInfo,HeroInfo from django.utils import timezone from datetime import * # 查询所有图书信息: BookInfo.objects.all() # 新建图书信息: b = BookInfo() b.btitle="射雕英雄传" b.bpub_date=datetime(year=1990,month=1,day=10) b.save() # 查找图书信息: b=BookInfo.objects.get(pk=1) # 输出图书信息: b b.id b.btitle # 修改图书信息: b.btitle=u"天龙八部" b.save() # 删除图书信息: b.delete() # 关联对象的操作 # 对于HeroInfo可以按照上面的操作方式进行 # 添加,注意添加关联对象 h=HeroInfo() h.hname=u‘郭靖‘ h.hgender=True h.hcontent=u‘降龙十八掌‘ h.hBook=b h.save() # 获得关联集合:返回当前book对象的所有hero b.heroinfo_set.all() # 有一个HeroInfo存在,必须要有一个BookInfo对象,提供了创建关联的数据: h=b.heroinfo_set.create(hname=u‘黄蓉‘,hgender=False,hcontent=u‘打狗棍法‘)
python manage.py runserver ip:port
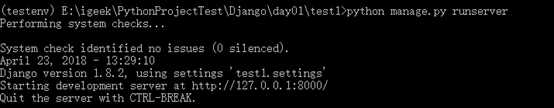
python manage.py runserver 8080
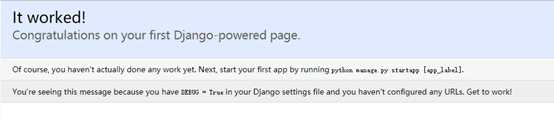
python manage.py createsuperuser,按提示输入用户名、邮箱、密码
LANGUAGE_CODE = ‘zh-Hans‘ TIME_ZONE = ‘Asia/Shanghai‘
from django.contrib import admin from models import BookInfo admin.site.register(BookInfo)
class QuestionAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): ... admin.site.register(Question, QuestionAdmin)
# list_display:显示字段,可以点击列头进行排序 list_display = [‘pk‘, ‘btitle‘, ‘bpub_date‘] # list_filter:过滤字段,过滤框会出现在右侧 list_filter = [‘btitle‘] # search_fields:搜索字段,搜索框会出现在上侧 search_fields = [‘btitle‘] # list_per_page:分页,分页框会出现在下侧 list_per_page = 10 # 添加、修改页属性 # fields:属性的先后顺序 fields = [‘bpub_date‘, ‘btitle‘] # fieldsets:属性分组 fieldsets = [ (‘basic‘,{‘fields‘: [‘btitle‘]}), (‘more‘, {‘fields‘: [‘bpub_date‘]}), ]
# 接下来实现关联注册 from django.contrib import admin from models import BookInfo,HeroInfo class HeroInfoInline(admin.StackedInline): model = HeroInfo extra = 2 class BookInfoAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): inlines = [HeroInfoInline] admin.site.register(BookInfo, BookInfoAdmin) # 可以将内嵌的方式改为表格 class HeroInfoInline(admin.TabularInline) # 布尔值的显示 # 发布性别的显示不是一个直观的结果,可以使用方法进行封装 def gender(self): if self.hgender: return ‘男‘ else: return ‘女‘ gender.short_description = ‘性别‘ # 在admin注册中使用gender代替hgender class HeroInfoAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): list_display = [‘id‘, ‘hname‘, ‘gender‘, ‘hcontent‘]
#coding:utf-8 from django.http import HttpResponse def index(request): return HttpResponse("index") def detail(request,id): return HttpResponse("detail %s" % id)
# 在test1/urls.py插入booktest,使主urlconf连接到booktest.urls模块 url(r‘^‘, include(‘booktest.urls‘)), # 在booktest中的urls.py中添加urlconf from django.conf.urls import url from . import views urlpatterns = [ url(r‘^$‘, views.index), url(r‘^([0-9]+)/$‘, views.detail), ]
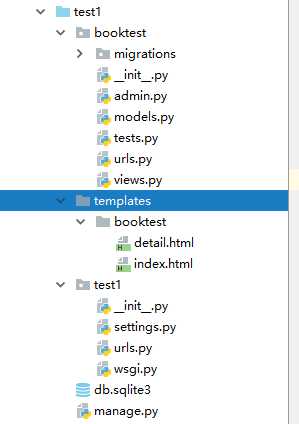
‘DIRS‘: [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ‘templates‘)],
{{输出值,可以是变量,也可以是对象.属性}}
{%执行代码段%}

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>图书列表</h1> <ul> {%for book in booklist%} <li> <a href="{{book.id}}"> {{book.btitle}} </a> </li> {%endfor%} </ul> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>详细页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>{{book.btitle}}</h1>
<ul>
{%for hero in book.heroinfo_set.all%}
<li>{{hero.hname}}---{{hero.hcontent}}</li>
{%endfor%}
</ul>
</body>
</html>

from django.http import HttpResponse from django.template import RequestContext, loader from models import BookInfo def index(request): booklist = BookInfo.objects.all() template = loader.get_template(‘booktest/index.html‘) context = RequestContext(request, {‘booklist‘: booklist}) return HttpResponse(template.render(context)) def detail(reqeust, id): book = BookInfo.objects.get(pk=id) template = loader.get_template(‘booktest/detail.html‘) context = RequestContext(reqeust, {‘book‘: book}) return HttpResponse(template.render(context))
# 在index.html模板中,超链接是硬编码的,此时的请求地址为“127.0.0.1/1/” <a href="{{book.id}}">
# 看如下情况:将urlconf中详细页改为如下,链接就找不到了 url(r‘^book/([0-9]+)/$‘, views.detail),
#此时的请求地址应该为“127.0.0.1/book/1/” #问题总结:如果在模板中地址硬编码,将来urlconf修改后,地址将失效 #解决:使用命名的url设置超链接 #修改test1/urls.py文件,在include中设置namespace url(r‘^admin/‘, include(admin.site.urls)), url(r‘^‘, include(‘booktest.urls‘, namespace=‘booktest‘)),
# 修改booktest/urls.py文件,设置name url(r‘^book/([0-9]+)/$‘, views.detail, name="detail"),
# 修改index.html模板中的链接 <a href="{%url ‘booktest:detail‘ book.id%}">
from django.shortcuts import render from models import BookInfo def index(reqeust): booklist = BookInfo.objects.all() return render(reqeust, ‘booktest/index.html‘, {‘booklist‘: booklist}) def detail(reqeust, id): book = BookInfo.objects.get(pk=id) return render(reqeust, ‘booktest/detail.html‘, {‘book‘: book})
标签:1.2 project lines context elf 密码 OLE nes 默认
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mint-diary/p/9753386.html