标签:集群 clu hdd == room 存储空间 root 算法 set
ceph crush的问题看一遍忘一遍,现将《ceph源码分析》一书中相关章节摘抄如下:
4.2.1 层级化的Cluster Map
例4-1 Cluster Map定义
层级化的Cluster Map定义了OSD集群具有层级关系的静态拓扑结构。OSD的层级使得CRUSH算法在选择OSD时实现了机架感知(rack awareness)的能力,也就是通过规则定义,使得副本可以分布在不同的机架、不同的机房中,提供数据的安全性。
层级化的Cluster Map的一些基本概念如下:
·Device:最基本的存储设备,也就是OSD,一个OSD对应一个磁盘存储设备。
·bucket:设备的容器,可以递归的包含多个设备或者子类型的bucket。bucket的类型:bucket可以有很多的类型,例如host就代表了一个节点,可以包含多个device。Rack就是机架,包含多个host等。在Ceph里默认的有root、datacenter、room、row、rack、host六个等级。用户也可以自己定义新的类型。每个device都设置了自己的权重,和自己的存储空间相关。bucket的权重就是子bucket(或者设备)的权重之和。
#bucket类型 # types type 0 osd type 1 host type 2 chassis type 3 rack type 4 row type 5 pdu type 6 pod type 7 room type 8 datacenter type 9 region type 10 root
下列举例说明bucket的用法:
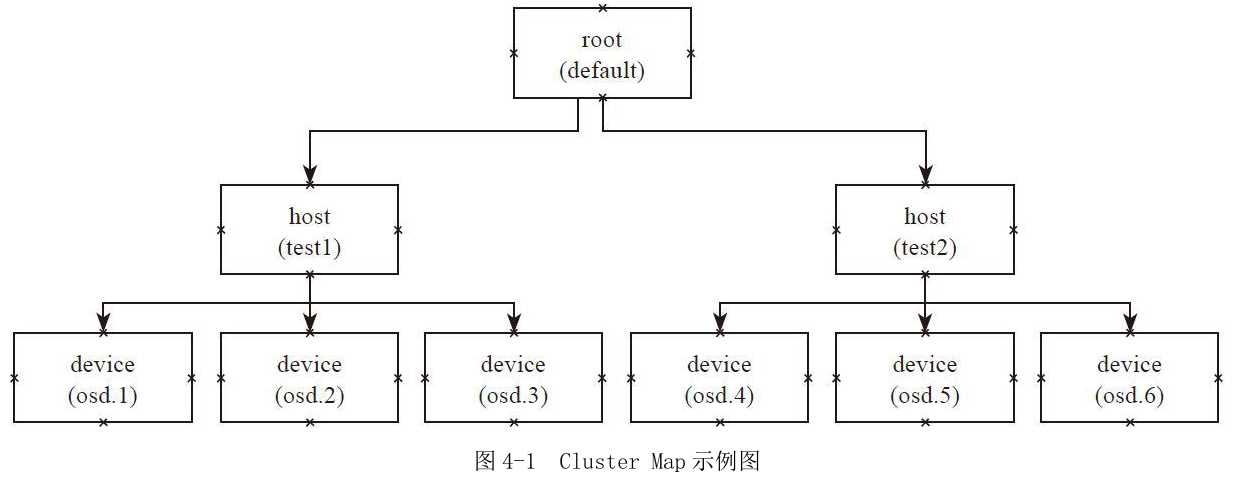
host test1 { //类型host,名字为test1
id -2 // bucket的id,一般为负值
# weight 3.000 //权重,默认为子item的权重之和
alg straw // bucket随机选择的算法
hash 0 // bucket随机选择的算法使用的hash函数,这里0代表使用hash函数jenkins1
item osd.1 weight 1.000 // item1:osd.1和权重值
item osd.2 weight 1.000
item osd.3 weight 1.000
}
host test2{
id -3
# weight 3.000
alg straw
hash 0
item osd.3 weight 1.000
item osd.4 weight 1.000
item osd.5 weight 1.000
}
root default{ // root类型的bucket,名字为default
id -1 // id号
# weight 6.000
alg straw //随机选择的算法
hash 0 // rjenkins1
item test1 weight 3.000
item test2 weight 3.000
}
4.2.2 Placement Rules
Cluster Map反映了存储系统层级的物理拓扑结构。Placement Rules决定了一个PG的对象副本如何选择的规则,通过这些可以自己设定规则,用户可以设定副本在集群中的分布。其定义格式如下:
tack(a) choose choose firstn {num} type {bucket-type} chooseleaf firstn {num} type {bucket-type}、 If {num} == 0, choose pool-num-replicas buckets (all available). If {num} > 0 && < pool-num-replicas, choose that many buckets. If {num} < 0, it means pool-num-replicas - {num}. Emit
Placement Rules的执行流程如下:
1)take操作选择一个bucket,一般是root类型的bucket。
2)choose操作有不同的选择方式,其输入都是上一步的输出:
a)choose firstn深度优先选择出num个类型为bucket-type个的子bucket。
b)chooseleaf先选择出num个类型为bucket-type个子bucket,然后递归到页节点,选择一个OSD设备:
·如果num为0,num就为pool设置的副本数。
·如果num大于0,小于pool的副本数,那么就选择出num个。
·如果num小于0,就选择出pool的副本数减去num的绝对值。
3)emit输出结果。
操作chooseleaf firstn{num}type{bucket-type}可以等同于两个操作:
a)choose firstn{num}type{bucket-type}
b)choose firstn 1 type osd
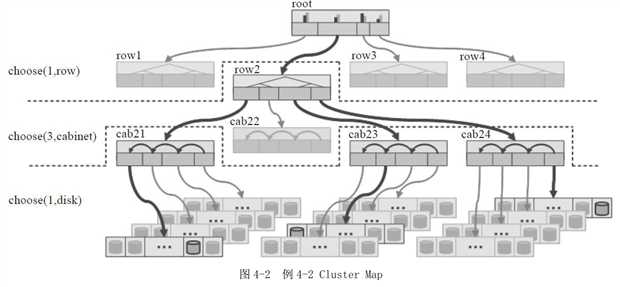
例4-2
Placement Rules:三个副本分布在三个Cabinet中。
如图4-2所示的Cluster Map:顶层是一个root bucket,每个root下有四个row类型bucket。每个row下面有4个cabinet,每个cabinet下有若干个OSD设备(图中有4个host,每个host有若干个OSD设备,但是在本crush map中并没有设置host这一级别的bucket,而是直接把4个host上的所有OSD设备定义为一个cabinet):
rule replicated_ruleset { ruleset 0 // ruleset的编号id type replicated //类型:repliated或者erasure code min_size 1 //副本数最小值 max_size 10 //副本数最大值 step take root //选择一个root bucket,做下一步的输入 step choose firstn 1 type row //选择一个row,同一排 step choose firstn 3 type cabinet //选择三个cabinet, 三副本分别在不同的cabinet step choose firstn 1 type osd //在上一步输出的三个cabinet中,分别选择一个osd step emit }
根据上面的定义和图4-2的Cluster Map所示,选择算法的执行过程如下:
1)选中root bucket作为下一个步骤的输入。
2)从root类型的bucket中选择一个row类的子bucket,其选择的算法在root的定义中设置,一般设置为straw算法。
3)从上一步的输出row中,选择三个cabinet,其选择的算法在row中定义。
4)从上一步输出的三个cabinet中,分别选择一个OSD,并输出。
根据本rule sets,选择出三个OSD设备分布在一个row上的三个cabinet中。
例4-3
Placement Rules:主副本分布在SSD上,其他副本分布在HDD上。
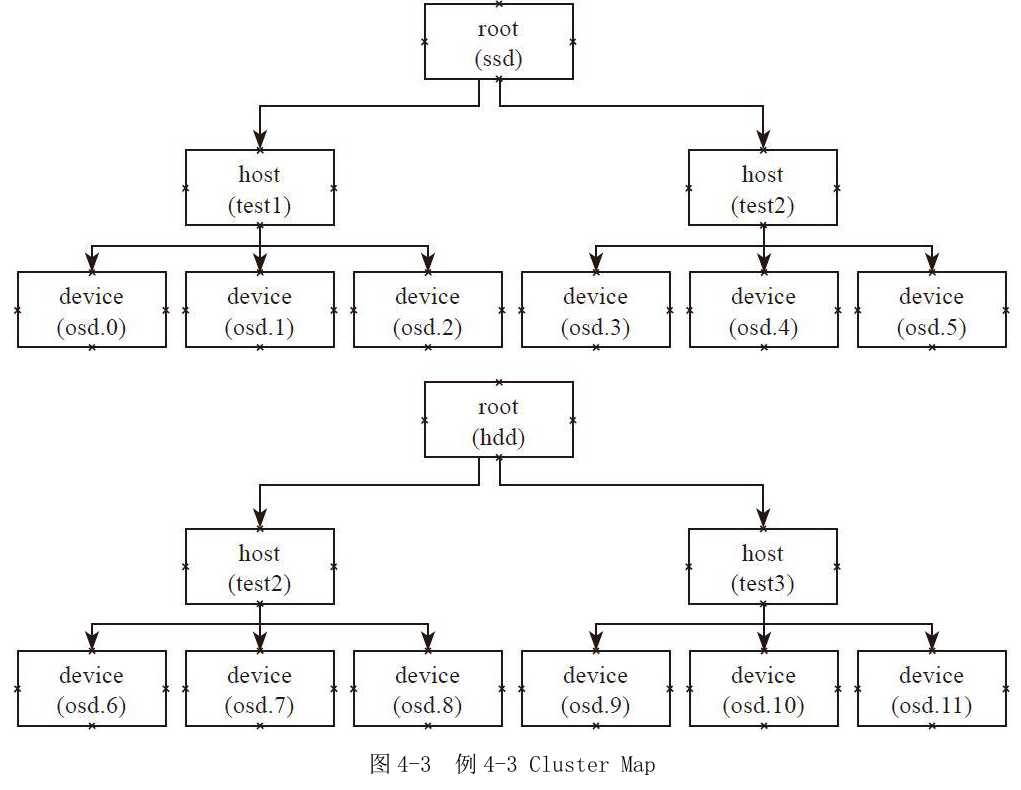
如图4-3所示的Cluster Map:定义了两个root类型的bucket,一个是名为SSD的root类型的bucket,其OSD存储介质都是SSD盘。它包函两个host,每个host上的设备都是SSD磁盘;另一个是名为HDD的root类型的bucket,其OSD的存储介质都是HDD磁盘,它有两个host,每个host上的设备都是HDD磁盘。
rule ssd-primary { ruleset 5 type replicated min_size 5 max_size 10 step take ssd //选择ssd这个root bucket为输入 step chooseleaf firstn 1 type host //选择一个host,并递归选择叶子节点osd step emit //输出结果 step take hdd //选择hdd这个root bucket为输入 step chooseleaf firstn -1 type host //选择总副本数减一个host,并分别递归选择一个叶子节点osd step emit //输出结果 }
根据图4-3所示的Cluster Map,代码中的rulesets的执行过程如下:
1)首先take操作选择ssd为root类型的bucket。
2)在ssd的root中先选择一个host,然后以该host为输入,递归至叶子节点,选择一个osd设备。
3)输出选择的设备,也就是ssd设备。
4)选择hdd作为root的输入。
5)选择2个host(副本数减一,默认3副本),并分别递归选择一个OSD设备,最终选择出两个hdd设备。
6)输出最终的结果。
最终输出3个设备,一个是SSD类型的磁盘,另外两个是HDD磁盘。通过上述规则,就可以把PG的主副本分布在SSD类型的OSD上,其他副本分布在HDD类型的磁盘上。
标签:集群 clu hdd == room 存储空间 root 算法 set
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bugutian/p/9792653.html