标签:param scale nts director order upper sed .so res
本篇主要讲述利用MTCNN的预训练模型得到原图中人脸的分割,代码如下:https://github.com/davidsandberg/facenet
结合博客https://blog.csdn.net/FortiLZ/article/details/81396566?tdsourcetag=s_pctim_aiomsg看起来省力些
要是对MTCNN的训练过程感兴趣的,可以看https://www.cnblogs.com/helloworld0604/p/9808795.html
经过P,R,O三层网络,一层层检测,具体网络构建如下:

class PNet(Network): def setup(self): (self.feed(‘data‘) #pylint: disable=no-value-for-parameter, no-member .conv(3, 3, 10, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv1‘) .prelu(name=‘PReLU1‘) .max_pool(2, 2, 2, 2, name=‘pool1‘) .conv(3, 3, 16, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv2‘) .prelu(name=‘PReLU2‘) .conv(3, 3, 32, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv3‘) .prelu(name=‘PReLU3‘) .conv(1, 1, 2, 1, 1, relu=False, name=‘conv4-1‘) .softmax(3,name=‘prob1‘)) (self.feed(‘PReLU3‘) #pylint: disable=no-value-for-parameter .conv(1, 1, 4, 1, 1, relu=False, name=‘conv4-2‘))
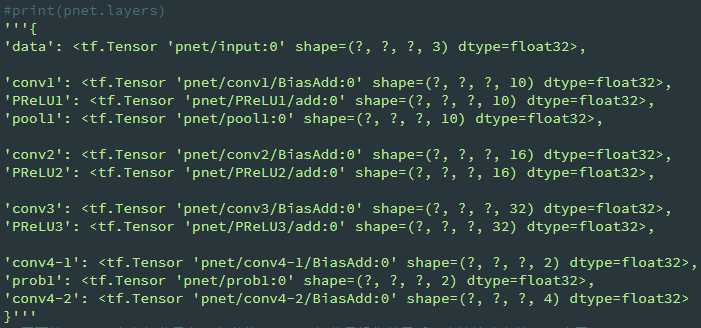

class RNet(Network): def setup(self): (self.feed(‘data‘) #pylint: disable=no-value-for-parameter, no-member .conv(3, 3, 28, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv1‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu1‘) .max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, name=‘pool1‘) .conv(3, 3, 48, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv2‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu2‘) .max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, padding=‘VALID‘, name=‘pool2‘) .conv(2, 2, 64, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv3‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu3‘) .fc(128, relu=False, name=‘conv4‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu4‘) .fc(2, relu=False, name=‘conv5-1‘) .softmax(1,name=‘prob1‘)) (self.feed(‘prelu4‘) #pylint: disable=no-value-for-parameter .fc(4, relu=False, name=‘conv5-2‘))
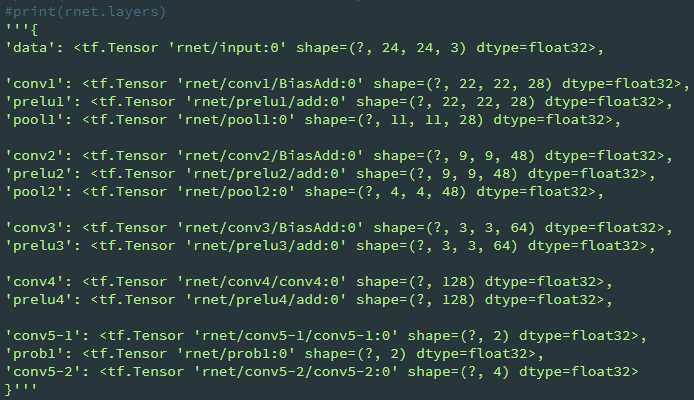

class ONet(Network): def setup(self): (self.feed(‘data‘) #pylint: disable=no-value-for-parameter, no-member .conv(3, 3, 32, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv1‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu1‘) .max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, name=‘pool1‘) .conv(3, 3, 64, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv2‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu2‘) .max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, padding=‘VALID‘, name=‘pool2‘) .conv(3, 3, 64, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv3‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu3‘) .max_pool(2, 2, 2, 2, name=‘pool3‘) .conv(2, 2, 128, 1, 1, padding=‘VALID‘, relu=False, name=‘conv4‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu4‘) .fc(256, relu=False, name=‘conv5‘) .prelu(name=‘prelu5‘) .fc(2, relu=False, name=‘conv6-1‘) .softmax(1, name=‘prob1‘)) (self.feed(‘prelu5‘) #pylint: disable=no-value-for-parameter .fc(4, relu=False, name=‘conv6-2‘)) (self.feed(‘prelu5‘) #pylint: disable=no-value-for-parameter .fc(10, relu=False, name=‘conv6-3‘))
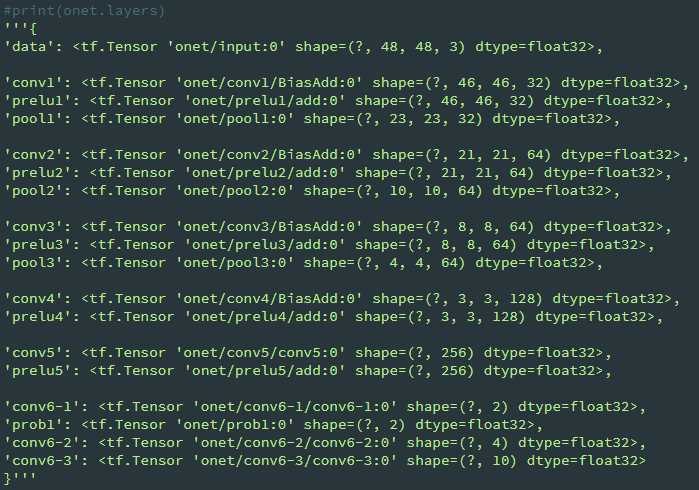
export PYTHONPATH=xx/xx/facenet/src #保证import facenet这句话不出错
import argparse def parse_arguments(argv): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument(‘input_dir‘, type=str, help=‘Directory with unaligned images.‘) # 待检测的图片 parser.add_argument(‘output_dir‘, type=str, help=‘Directory with aligned face thumbnails.‘) #检测出的人脸图的保存目录 parser.add_argument(‘--image_size‘, type=int, help=‘Image size (height, width) in pixels.‘, default=182) #保存的人脸图大小 parser.add_argument(‘--margin‘, type=int, help=‘Margin for the crop around the bounding box (height, width) in pixels.‘, default=44) #检测出人脸后的外围扩充 parser.add_argument(‘--random_order‘, help=‘Shuffles the order of images to enable alignment using multiple processes.‘, action=‘store_true‘) parser.add_argument(‘--gpu_memory_fraction‘, type=float, help=‘Upper bound on the amount of GPU memory that will be used by the process.‘, default=1.0) parser.add_argument(‘--detect_multiple_faces‘, type=bool, help=‘Detect and align multiple faces per image.‘, default=False) return parser.parse_args(argv)
def detect_face(img, minsize, pnet, rnet, onet, threshold, factor): """Detects faces in an image, and returns bounding boxes and points for them. img: input image minsize: minimum faces‘ size 20 pnet, rnet, onet: caffemodel threshold: threshold=[th1, th2, th3], th1-3 are three steps‘s threshold [ 0.6, 0.7, 0.7 ] factor: the factor used to create a scaling pyramid of face(图像金字塔) sizes to detect in the image. 0.709 """ #print(‘img shape before detect:‘,img.shape) factor_count=0 total_boxes=np.empty((0,9)) points=np.empty(0) h=img.shape[0] w=img.shape[1] minl=np.amin([h, w]) m=12.0/minsize minl=minl*m # create scale pyramid scales=[] while minl>=12: #满足这个条件,即min(h,w)>=minsize scales += [m*np.power(factor, factor_count)] minl = minl*factor factor_count += 1 #print(‘scales:‘,scales) #若min(h,w)==250,则有8个scale,乘过(12/minsize)*250*factor^8<12可理解为250*factor^N<minsize,求N即可 # first stage for scale in scales: #print(‘******scale:‘,scale) hs=int(np.ceil(h*scale)) ws=int(np.ceil(w*scale)) im_data = imresample(img, (hs, ws)) im_data = (im_data-127.5)*0.0078125 #print(‘im_data:‘,im_data.shape) img_x = np.expand_dims(im_data, 0) img_y = np.transpose(img_x, (0,2,1,3)) #print(‘img_y (to the pnet):‘,img_y.shape) out = pnet(img_y)-----------------------------------------------------------------------第一层用PNet模型预测 out0 = np.transpose(out[0], (0,2,1,3)) out1 = np.transpose(out[1], (0,2,1,3)) #print(‘out0 (after pnet):‘,out0.shape) #print("out0",out0[0,:2,:2,:]) #from ipdb import set_trace;set_trace() boxes, _ = generateBoundingBox(out1[0,:,:,1].copy(), out0[0,:,:,:].copy(), scale, threshold[0]) ‘‘‘ 最终输出的 boundingbox 是形如 (x, 9),其中前4位是 block 在原图中的坐标, 第5位是判定为人脸的概率,后4位是 boundingbox regression 的值。 具体 boundingbox regression 到底是什么,现在还不清楚。 ‘‘‘ # inter-scale nms ‘‘‘ NMS (Non-Maximum Suppression):在上述生成的 bb 中,找出判定为人脸概率最大的那个 bb,计算出这个 bb 的面积, 然后计算其余 bb 与这个 bb 重叠面积的大小,用重叠面积除以:(Min) 两个 bb 中面积较小者;(Union) 两个 bb 的总和面积。 如果这个值大于 threshold,那么就认为这两个 bb 框的是同一个地方,舍弃判定概率小的; 如果小于 threshold,则认为两个 bb 框的是不同地方,保留判定概率小的。重复上述过程直至所有 bb 都遍历完成。 将图片按照所有的 scale 处理过一遍后,会得到在原图上基于不同 scale 的所有的 bb,然后对这些 bb 再进行一次 NMS,并且这次 NMS 的 threshold 要提高。 ‘‘‘ pick = nms(boxes.copy(), 0.5, ‘Union‘) if boxes.size>0 and pick.size>0: boxes = boxes[pick,:] #print(boxes[:,2]-boxes[:,0]) #print(boxes[:,3]-boxes[:,1]) total_boxes = np.append(total_boxes, boxes, axis=0) #print(‘all scales has done!!!‘) numbox = total_boxes.shape[0] if numbox>0: pick = nms(total_boxes.copy(), 0.7, ‘Union‘) total_boxes = total_boxes[pick,:] # 因为pnet的移动大小是12*12,对于一种scale,regw和regh是差不多的 # 校准bb,得到了真真正正的在原图上 bb 的坐标 regw = total_boxes[:,2]-total_boxes[:,0] regh = total_boxes[:,3]-total_boxes[:,1] qq1 = total_boxes[:,0]+total_boxes[:,5]*regw qq2 = total_boxes[:,1]+total_boxes[:,6]*regh qq3 = total_boxes[:,2]+total_boxes[:,7]*regw qq4 = total_boxes[:,3]+total_boxes[:,8]*regh total_boxes = np.transpose(np.vstack([qq1, qq2, qq3, qq4, total_boxes[:,4]])) total_boxes = rerec(total_boxes.copy()) #调整成正方形 total_boxes[:,0:4] = np.fix(total_boxes[:,0:4]).astype(np.int32) dy, edy, dx, edx, y, ey, x, ex, tmpw, tmph = pad(total_boxes.copy(), w, h) #把超过原图边界的坐标剪裁一下 # print(dy[0], edy[0], dx[0], edx[0], y[0], ey[0], x[0], ex[0], tmpw[0], tmph[0]) # (1, 76, 1, 76, 85, 160, 189, 264, 76, 76) #print("*********** second stage **************") numbox = total_boxes.shape[0] #45 if numbox>0: # second stage tempimg = np.zeros((24,24,3,numbox)) for k in range(0,numbox): tmp = np.zeros((int(tmph[k]),int(tmpw[k]),3)) #tmp生成的图片是高*宽的,rnet的输入要求是宽*高,别忘记转置 tmp[dy[k]-1:edy[k],dx[k]-1:edx[k],:] = img[y[k]-1:ey[k],x[k]-1:ex[k],:] if tmp.shape[0]>0 and tmp.shape[1]>0 or tmp.shape[0]==0 and tmp.shape[1]==0: tempimg[:,:,:,k] = imresample(tmp, (24, 24)) else: return np.empty() tempimg = (tempimg-127.5)*0.0078125 #print(‘temping:‘,tempimg.shape) #(24, 24, 3, 45) tempimg1 = np.transpose(tempimg, (3,1,0,2)) #print(‘before rnet:‘,tempimg1.shape) #(45, 24, 24, 3) out = rnet(tempimg1)----------------------------------------------------------------第二层用RNet out0 = np.transpose(out[0]) #(4,45) out1 = np.transpose(out[1]) #(2,45) score = out1[1,:] ipass = np.where(score>threshold[1]) #print("ipass:",ipass[0].shape)#(8,) total_boxes = np.hstack([total_boxes[ipass[0],0:4].copy(), np.expand_dims(score[ipass].copy(),1)]) #(8,5) mv = out0[:,ipass[0]] #再根据rnet预测出的回归校准bb if total_boxes.shape[0]>0: pick = nms(total_boxes, 0.7, ‘Union‘) total_boxes = total_boxes[pick,:] #print(‘total_boxes:‘,total_boxes.shape) #(5,5) total_boxes = bbreg(total_boxes.copy(), np.transpose(mv[:,pick])) total_boxes = rerec(total_boxes.copy()) #print("*********** third stage **************") numbox = total_boxes.shape[0] # 5 if numbox>0: # third stage total_boxes = np.fix(total_boxes).astype(np.int32) dy, edy, dx, edx, y, ey, x, ex, tmpw, tmph = pad(total_boxes.copy(), w, h) tempimg = np.zeros((48,48,3,numbox)) for k in range(0,numbox): tmp = np.zeros((int(tmph[k]),int(tmpw[k]),3)) tmp[dy[k]-1:edy[k],dx[k]-1:edx[k],:] = img[y[k]-1:ey[k],x[k]-1:ex[k],:] if tmp.shape[0]>0 and tmp.shape[1]>0 or tmp.shape[0]==0 and tmp.shape[1]==0: tempimg[:,:,:,k] = imresample(tmp, (48, 48)) else: return np.empty() tempimg = (tempimg-127.5)*0.0078125 #(48, 48, 3, 5) tempimg1 = np.transpose(tempimg, (3,1,0,2)) out = onet(tempimg1)-------------------------------------------------------------------第三层用ONet out0 = np.transpose(out[0]) #(4,5) out1 = np.transpose(out[1]) #(10,5) out2 = np.transpose(out[2]) #(2,5) score = out2[1,:] points = out1 ipass = np.where(score>threshold[2]) points = points[:,ipass[0]] #print("ipass:",ipass[0].shape)#(5,) total_boxes = np.hstack([total_boxes[ipass[0],0:4].copy(), np.expand_dims(score[ipass].copy(),1)]) mv = out0[:,ipass[0]] w = total_boxes[:,2]-total_boxes[:,0]+1 h = total_boxes[:,3]-total_boxes[:,1]+1 points[0:5,:] = np.tile(w,(5, 1))*points[0:5,:] + np.tile(total_boxes[:,0],(5, 1))-1 points[5:10,:] = np.tile(h,(5, 1))*points[5:10,:] + np.tile(total_boxes[:,1],(5, 1))-1 if total_boxes.shape[0]>0: #最后一个阶段是先校准再nms,且采用‘min’的方式 total_boxes = bbreg(total_boxes.copy(), np.transpose(mv)) pick = nms(total_boxes.copy(), 0.7, ‘Min‘) total_boxes = total_boxes[pick,:] points = points[:,pick] #print(‘total_boxes:‘,total_boxes.shape) #(1,5) return total_boxes, points
def generateBoundingBox(imap, reg, scale, t): # use heatmap to generate bounding boxes #print("generateBoundingBox-scale:",scale) stride=2 cellsize=12 imap = np.transpose(imap) dx1 = np.transpose(reg[:,:,0]) dy1 = np.transpose(reg[:,:,1]) dx2 = np.transpose(reg[:,:,2]) dy2 = np.transpose(reg[:,:,3]) y, x = np.where(imap >= t) #返回的是另外两维的序号 #print("y:",y.shape) # (H,) if y.shape[0]==1: #只有一个概率>threshold的block dx1 = np.flipud(dx1) #上下翻转 dy1 = np.flipud(dy1) dx2 = np.flipud(dx2) dy2 = np.flipud(dy2) score = imap[(y,x)] #取可能是人脸的block的概率值 reg = np.transpose(np.vstack([ dx1[(y,x)], dy1[(y,x)], dx2[(y,x)], dy2[(y,x)] ])) #print("reg:",reg.shape) #(H,4) if reg.size==0: reg = np.empty((0,3)) bb = np.transpose(np.vstack([y,x])) #print("bb:",bb.shape) #(H,2) # 计算原图中的位置 q1 = np.fix((stride*bb+1)/scale) #np.fix():Round to nearest integer towards zero. q2 = np.fix((stride*bb+cellsize-1+1)/scale) boundingbox = np.hstack([q1, q2, np.expand_dims(score,1), reg]) #(H,2)+(H,2)+(H,1)+(H,4) #print("boundingbox:",boundingbox.shape) #(H,9) #print(boundingbox[1,:]) #array([ 8.50000000e+01, 1.05000000e+02, 1.03000000e+02, 1.23000000e+02, 6.87459767e-01, -1.91520154e-02, -7.52890855e-03, -7.97504187e-03, 2.32149601e-01]) return boundingbox, reg

def nms(boxes, threshold, method): if boxes.size==0: return np.empty((0,3)) x1 = boxes[:,0] y1 = boxes[:,1] x2 = boxes[:,2] y2 = boxes[:,3] s = boxes[:,4] area = (x2-x1+1) * (y2-y1+1) I = np.argsort(s) #返回排序后的索引 pick = np.zeros_like(s, dtype=np.int16) counter = 0 while I.size>0: i = I[-1] pick[counter] = i counter += 1 idx = I[0:-1] xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idx]) yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idx]) xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idx]) yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idx]) w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2-xx1+1) h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2-yy1+1) inter = w * h # 相交面积 if method is ‘Min‘: o = inter / np.minimum(area[i], area[idx]) else: o = inter / (area[i] + area[idx] - inter) I = I[np.where(o<=threshold)] pick = pick[0:counter] #保留下来的box的序号 return pick
得到人脸框坐标和关键点坐标之后,即可以将其裁剪和描绘出来了,可自行学习align_dataset_mtcnn.py中的实现
自己看的过程中,最为困惑的点就是网络是如何训练的,训练样本是什么样子的,解答都在https://www.cnblogs.com/helloworld0604/p/9808795.html中
21个项目玩转深度学习:基于TensorFlow的实践详解06—人脸检测和识别——MTCNN人脸检测
标签:param scale nts director order upper sed .so res
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/helloworld0604/p/9831725.html