标签:分享图片 state 技术分享 实现 history redo game list 修饰符
使用面向对象编程的方式实现撤销功能时,需要事先保存实例的相关状态信息。然后,在撤销时,还需要根据所保存的信息将实例恢复至原来的状态。这个时候你需要使用Memento设计模式。(以及实例实现对状态的保存)
破坏封装性:
将依赖于实例内部结构的代码分散地编写在程序中的各个地方,导致程序变得难以维护。
包====>>>名字=====>>>说明
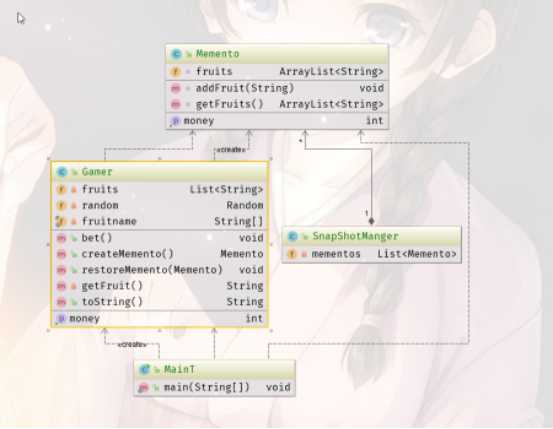
game |Memento|表示Gamer状态的类
game |Gamer表示游戏主人公的类。它会生成Memento的实例进行游戏的类。它会事先保存Memento的实例,之后会根据需要恢复Gamer的状态
null | MainT 这里为了方便起见使用MainT作为责任人保存用户状态
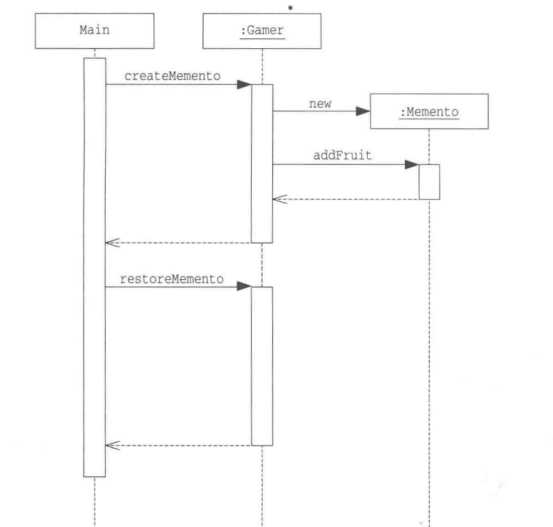
时序图:
public class Gamer {
/**
* 下面的money 与 fruits 就是按照一般的定义方式去定义
* 但是我们提取Memento的时候需要注意这个的获取规则
*/
// 获得金钱
private int money;
// 获得的水果
private List<String> fruits=new ArrayList<>();
private Random random=new Random();
private final static String[] fruitname=new String[]{
"苹果","葡萄","香蕉","橘子"
};
public Gamer(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
/**
* 开始游戏
* 骰子结果1,2 ,6进行不同的操作
*/
public void bet(){
int dice=random.nextInt(6)+1;
if(dice==1){
this.money+=100;
System.out.println("金钱增加了!");
}else if(dice==2){
this.money/=2;
System.out.println("金钱减半了!");
}else if(dice==6){
String f=getFruit();
System.out.println("获得了水果["+f+"]!");
this.fruits.add(f);
}else{
System.out.println("什么也不发生");
}
}
/**
* 快照方法
*/
public Memento createMemento(){
Memento memento = new Memento(this.money);
Iterator<String> iterator = fruits.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
String s = iterator.next();
if(s.startsWith("好吃的")){
memento.addFruit(s);
}
}
return memento;
}
/**
* 撤销方法
*/
public void restoreMemento(Memento memento){
this.money=memento.money;
this.fruits=memento.fruits;
}
private String getFruit() {
String prefix="";
if(random.nextBoolean()){
prefix="好吃的";
}
return prefix+fruitname[random.nextInt(fruitname.length)];
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Gamer{" +
"money=" + money +
", fruits=" + fruits +
'}';
}
}
public class Memento {
/**
* 使用过程中因为Memento与Gamer是强关联关系,但是又因为是在同一个game包下,
* 使用可见性修饰符显得比较重要:
* 这里的两个字段在同一个包下都是可以访问
*/
int money;
ArrayList<String> fruits;
/**
* 窄接口
*/
public int getMoney(){
return money;
}
/**
* 这里是宽接口
* @param money
*/
Memento(int money) {
this.money = money;
this.fruits = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* 这里是宽接口
*/
void addFruit(String fruit){
fruits.add(fruit);
}
/**
* 这里是宽接口
*/
ArrayList<String> getFruits(){
return (ArrayList<String>) fruits.clone();
}
}
public class MainT {
/**
* 这里的状态只是单个快照点,当你需要多个快照点的时候,
* 单独创建一个snapshot类来管理,可以使用集合等,
* 这里写个例子
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gamer gamer = new Gamer(100);
//保存的一个快照 初始状态
Memento memento = gamer.createMemento();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("===="+i);
System.out.println("当前状态"+gamer);
//开始游戏
gamer.bet();
System.out.println("还有多少钱"+gamer.getMoney()+"元");
if(gamer.getMoney()>memento.getMoney()){
System.out.println("//保存新状态");
memento=gamer.createMemento();
}else if(gamer.getMoney()<memento.getMoney()/2){
System.out.println("金钱减少一半了,恢复到原来的状态");
gamer.restoreMemento(memento);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class SnapShotManger implements Serializable {
private List<Memento> mementos=new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 实现java.io.Serializable接口
* 用objectoutputstream的writeobject方法
* 用objectInputStream的 readobject方法
*/
/**
* 保存
*/
/**
* 恢复
*/
}
标签:分享图片 state 技术分享 实现 history redo game list 修饰符
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dgwblog/p/9873969.html