标签:print reverse 逆序输出 tab oid 知识点 变量 代码 thml
码云练习地址:https://gitee.com/bubblerui/1601201904
码云考核地址:https://gitee.com/bubblerui/1601201903
输入一个字符串,对该字符串进行逆序,输出逆序后的字符串。
输入格式:输入在一行中给出一个不超过80个字符长度的、以回车结束的非空字符串。
输出格式:在一行中输出逆序后的字符串。
代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main (String[] args){ Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); String str=reader.nextLine(); StringBuffer name =new StringBuffer(str); System.out.print(name.reverse().toString()); } }
知识要点:先定义输函数输入一个字符串,最后输出打印字符串并且逆序输出,使用StringBuffer 对象,StringBuffer 类的常用方法。
设计思路:输入一个字符串,将输入的字符串逆序输出
运行结果: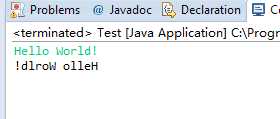
本题要求将给定的n个整数从大到小排序后输出。
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String args[]){ Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); int n = reader.nextInt(); int[] a = new int[n]; int x=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ a[i]=reader.nextInt(); } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<n;j++){ if(a[j]>a[j-1]){ x=a[j]; a[j]=a[j-1]; a[j-1]=x; } } } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ System.out.print(a[i]); if(i!=n-1){ System.out.print(" "); } } } }
知识点:利用for循环语句定义两个数,其中设置一个中间变量进行传值,定义数组,选择排序。
设计思路:定义数组,然后数组中的数比较,交换位置,利用FOR循环,最后输出。
运行结果: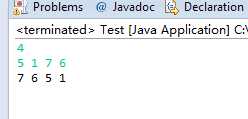
本题要求编写程序,对顺序读入的n个整数,顺次计算后项减前项之差,并按每行三个元素的格式输出结果。
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String args[]){ Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); int n = reader.nextInt(); int[] a = new int[n]; int i=0; int cnt=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++){ a[i]=reader.nextInt(); } for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){ a[i] = a[i + 1] - a[i]; } for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){ if (i == 0){ System.out.printf("%d", a[0]); } else if (cnt == 3){ System.out.printf("\n"); System.out.printf("%d", a[i]); cnt = 0; } else{ System.out.printf(" %d", a[i]); } cnt++; } } }
知识点:定义数组,for循环,其中定义中间变量进行传值。
设计思路:输入n个整数,循环语句,if-else语句剪前项之差
运行结果: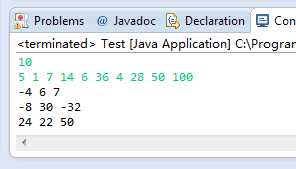
阶段总结:这阶段主要学习了基本的数据类型,运算符和表达式,循环语句,分支语句,并且学习了定义类与对象和子类父类的继承,在学习过程中不能熟练掌握java的编写,知识点运用和使用并不准确,希望以后更加努力。
| 学习内容 | 代码(行) | 博客(字) |
| 第三次过程性考核 | 66 | 900 |
| 数组 | 90 | |
| 运算符,表达式和语句 | 170 | |
| 类与对象,子类与继承 | 80 | |
| 接口与实现 常用类 | 60 |
标签:print reverse 逆序输出 tab oid 知识点 变量 代码 thml
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/bubblerui/p/9894693.html