标签:lin 逻辑 ice 介绍 int 逻辑回归 instance 停止 学习
1. 防止过拟合的方法有哪些?
过拟合(overfitting)是指在模型参数拟合过程中的问题,由于训练数据包含抽样误差,训练时,复杂的模型将抽样误差也考虑在内,将抽样误差也进行了很好的拟合。
产生过拟合问题的原因大体有两个:训练样本太少或者模型太复杂。
防止过拟合问题的方法:
(1)增加训练数据。
考虑增加训练样本的数量
使用数据集估计数据分布参数,使用估计分布参数生成训练样本
使用数据增强
(2)减小模型的复杂度。
a.减少网络的层数或者神经元数量。这个很好理解,介绍网络的层数或者神经元的数量会使模型的拟合能力降低。
b.参数范数惩罚。参数范数惩罚通常采用L1和L2参数正则化(关于L1和L2的区别联系请戳这里)。
c.提前终止(Early stopping);
d.添加噪声。添加噪声可以在输入、权值,网络相应中添加。
e.结合多种模型。这种方法中使用不同的模型拟合不同的数据集,例如使用 Bagging,Boosting,Dropout、贝叶斯方法

而在深度学习中,通常解决的方法如下
Early stopping方法的具体做法是,在每一个Epoch结束时(一个Epoch集为对所有的训练数据的一轮遍历)计算validation data的accuracy,当accuracy不再提高时,就停止训练。
获取更多数据(从数据源头获取更多数据 根据当前数据集估计数据分布参数,使用该分布产生更多数据 数据增强(Data Augmentation))
正则化(直接将权值的大小加入到 Cost 里,在训练的时候限制权值变大)
dropout:在训练时,每次随机(如50%概率)忽略隐层的某些节点;
2. 使用逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)对鸢尾花数据(多分类问题)进行预测,可以直接使用sklearn中的LR方法,并尝试使用不同的参数,包括正则化的方法,正则项系数,求解优化器,以及将二分类模型转化为多分类模型的方法。
获取鸢尾花数据的方法:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
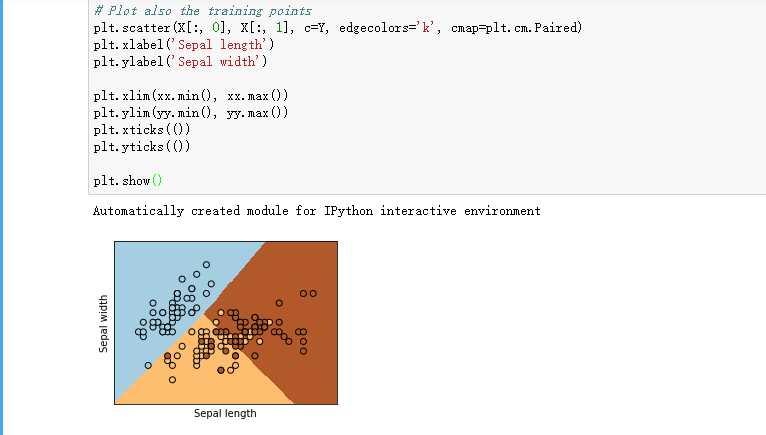
print(__doc__) # Code source: Ga?l Varoquaux # Modified for documentation by Jaques Grobler # License: BSD 3 clause import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import linear_model, datasets # import some data to play with iris = datasets.load_iris() X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features. Y = iris.target h = .02 # step size in the mesh logreg = linear_model.LogisticRegression(C=1e5) # we create an instance of Neighbours Classifier and fit the data. logreg.fit(X, Y) # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each # point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max]. x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5 y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)) Z = logreg.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # Put the result into a color plot Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) plt.figure(1, figsize=(4, 3)) plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Paired) # Plot also the training points plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, edgecolors=‘k‘, cmap=plt.cm.Paired) plt.xlabel(‘Sepal length‘) plt.ylabel(‘Sepal width‘) plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max()) plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max()) plt.xticks(()) plt.yticks(()) plt.show()
标签:lin 逻辑 ice 介绍 int 逻辑回归 instance 停止 学习
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xingnie/p/9902265.html