标签:include 因此 伪代码 printf namespace 一个 cst 输入输出 连接
每次生成一个 \([0,n)\) 的随机整数,如果这个随机数和给出的 \(m\) 个数字中的其中一个数字相等,
那么就停止生成随机数,否则继续生成,求出所有生成的数的和的期望。
第一行两个正整数 \(n,m\),
第二行 \(m\) 个整数 表示障碍,保证两两不同。
输出一行一个实数表示期望,保留 \(6\) 位小数,
2 1
1
1.000000\(n\le 10^7,1\le m\le n,0\le a_i\le n-1\)
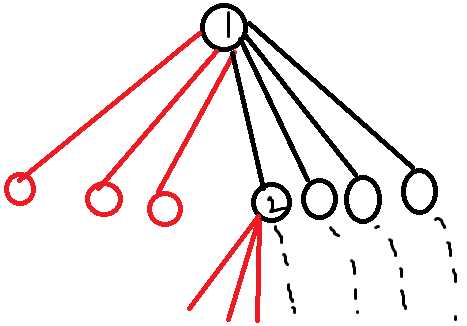
上图中的红色节点表示给出的随机数等于 \(m\) 个数字之一,停止生成;黑色节点表示需要继续生成。
我们发现,图中的 \(1\) 号节点和 \(2\) 号节点状态相同,因此答案一定完全一致。
设 \(ans\) 表示节点 \(1\) 的答案, \(sum_1\) 表示 \(m\) 个数的和, \(sum_2\) 表示\(n\)个数的总和 \(-m\) 个数的和,则 \[ans=\frac{1}{n}*sum_1+\frac{1}{n}*sum_2+\frac{1}{n}*m*ans=\frac{n(n-1)}{2*m}\]
然后发现 \(10^7\) 的数据一点用都没有
还有,本题卡精度
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int read(){
char c=getchar();
bool sgn=0;
int x=0;
while((c<‘0‘||c>‘9‘)&&c!=‘-‘)c=getchar();
if(c==‘-‘)sgn=1,c=getchar();
while(c>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘){
x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-‘0‘;
c=getchar();
}
return sgn?-x:x;
}
char tmp[1000];
int main(){
long long n=read(),m=read();
//以下代码仅用于输出(n*(n-1))/(2*m)
n=n*(n-1)/2;
printf("%lld",n/m);
n%=m;
sprintf(tmp,"%.6lf",double(n)/m);
printf(tmp+1);
return 0;
}众所周知,DH 是一位人生赢家,他不仅能虐暴全场,而且还正在走向人生巅峰;
一天,DH 在刷题的时候碰到了一道大模拟题:
二维坐标上有一些点,保证它们的 x 坐标互不相同,(y 坐标可能相同,可能有 3 点共线),
每个点都有一个权值 ,表示点 i 指向点 ,初始时每个点指向它自己,
模拟过程就是执行以下伪代码:
for i=1 to n do b[i]=i
for i=1 to n do
{
输出 b[i];
if(b[i]不等于 i)L=连接点 i,b[i] 的直线;
else L=过点 i 平行于 x 轴的直线;
对于任意的 x,满足点 x 在直线 L 下方(且不在直线上),b[x]=i;
}DH 表示他要赶着去干人生赢家应该干的事并把这道题扔给了你。
第一行给出正整数 \(n\),
接下来有 \(n\) 行,每行两个正整数 ,表示第 \(i\) 个点的坐标。
\(n\) 行 \(n\) 个数,表示模拟过程中你输出的 \(n\) 个 \(b_i\)。
7
1 10
2 7
3 8
4 2
5 6
6 100
7 10
1
1
1
3
1
6
6\(n,m\le 10^6,max\{x_i\},max\{y_i\}\le 10^9,x_i\)为单调递增以保证互不相同
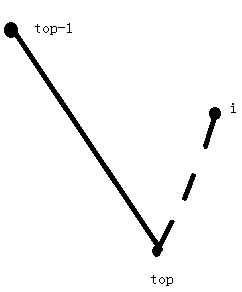
我们维护一个类似凸包的东西,设栈顶元素为 \(top\) ,对于一个新点 \(i\) ,如果 \(y_i>y_top\) ,那么 \(top\) 就没有任何用处,以后的点最多只会连 \(i\) ,不可能会连 \(top\) ,所以弹出 \(top\);
之后,如果出现下面这种情况,也弹出 \(top\) ,因为以后的点最多只会连 \(i\) ,不可能会连 \(top\) 。
#include<cstdio>
#define maxn 1000002
using namespace std;
template<typename tp>
tp read(){
tp x=0;
bool sgn=0;
char c=getchar();
while((c<‘0‘||c>‘9‘)&&c!=‘-‘)c=getchar();
if(c==‘-‘)sgn=1,c=getchar();
while(c>=‘0‘&&c<=‘9‘){
x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-‘0‘;
c=getchar();
}
return sgn?-x:x;
}
template<typename tp>
void write(tp x){
if(x<0)putchar(‘-‘),write(-x);
else{
if(x>=10)write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+‘0‘);
}
}
struct point{
long long x,y;
point(){}
point(long long X,long long Y):x(X),y(Y){}
const point operator -(const point& p)const{
return point(x-p.x,y-p.y);
}
}pnt[maxn];
long long cross(const point& p,const point& q){
return p.x*q.y-p.y*q.x;
}
int st[maxn],top;
int main(){
int n=read<int>();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
pnt[i].x=read<long long>(),pnt[i].y=read<long long>();
while(top>=1&&pnt[i].y>=pnt[st[top]].y)top--;
while(top>=2&&cross(pnt[i]-pnt[st[top]],pnt[st[top]]-pnt[st[top-1]])<=0)top--;
if(top)write(st[top]);
else write(i);
putchar(‘\n‘);
st[++top]=i;
}
return 0;
}标签:include 因此 伪代码 printf namespace 一个 cst 输入输出 连接
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/BlogOfchc1234567890/p/9916878.html