标签:fine 去除 www vue cli learn sele inf tin
var定义的变量:只有全局作用域和函数作用域。有变量提升,先打印后定义变量不会报错,打印结果为undefined
let定义的变量:没有变量提升 ——>有局部作用域和函数作用域、块级作用域
不能重复定义
块级作用域
const定义的变量:
没有变量提升
定义了以后不能修改
定义的时候必须赋值
不能重复定义
带来了块级作用域
用反引号来进行字符串的拼接
用${} 来存储变量
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
let oDiv = document.getElementById(‘app‘);
oDiv.innerHTML = ‘<h1>Hello Vue‘ +
‘</h1>‘;
let name1 = ‘wjs‘;
let name2 = ‘gxx‘;
// 这里是反引号
oDiv.innerHTML = `
<h1>Hello ${name1}</h1>
<h2>Hello ${name2}</h2>
`
</script>
数组、对象
简单的用途:数据的交换
<script>
let ary = [1, 2, 3];
let [a, b, c] = ary;
console.log(a, b, c);
let obj = {
username: ‘wjs‘,
age: 24,
};
let {username: user, age: age} = obj; // 默认是这样所以↓
console.log(user,age);
let k = 1;
let v = 2;
[k, v] = [v, k]; // 等号左右类型必须一样,要么都是字典,要么都是列表
console.log(k, v);
</script>
1、默认值参数
<script>
// 默认值参数
function foo(x, y = 10) {
let number = y;
return number;
}
ret = foo(1, 2);
ret1 = foo(1);
ret2 = foo(1, 0);
console.log(ret);
console.log(ret1);
console.log(ret2);
</script>
2、箭头函数(v => v 参数 箭头 返回值)
<script>
// 箭头函数
// 一个函数
let foo1 = v => v;
ret3 = foo1(10);
console.log(ret3);
</script>
3、0个或者多个参数
<script>
// 0个或者多个参数
let bar = (x, y) => {
return x + y;
};
ret4 = bar(1, 2);
console.log(ret4);
</script>
4、箭头函数和普通函数的区别
<script>
// 普通函数(谁调用就指向谁)
// 箭头函数(在哪里定义的作用域,this就指向定义时的作用域)
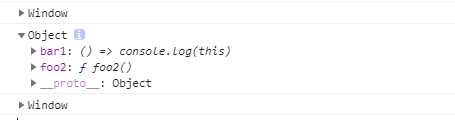
function foo2() {
console.log(this); // 这里指向windows
}
let bar1 = () => console.log(this);
let obj = {
foo2:foo2,
bar1:bar1,
};
foo2(); // 指向windows
obj.foo2(); // 指向object
obj.bar1(); // 指向windows
</script>
class 关键字 定义一个类:
必须要有constructor方式(构造方法),如果没有,则() {}
必须使用new 来实例化,
类的继承:
必须在子类的constructor方法里面写super()方法
<script>
class Wjs {
constructor(username, age, hobby = ‘learn‘) {
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
this.account = account;
}
showInfo() {
console.log(this.username, this.age, this.account);
}
}
// extends继承
class Gxx extends Wjs {
constructor(username, age) {
// 继承父类的username、age,hobby继承的父类的默认值
super(username, age);
// this.username = username;
// this.age = age;
}
}
let gxx = new Gxx(‘gxx‘, 22);
gxx.showInfo();
</script>
解决了箭头函数this的指向问题
<script>
let obj = {
name: ‘wjs‘,
foo() {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
obj.foo();
</script>
<div id="app">{{ greeting }}</div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘, //
data: {
greeting: ‘Hello Vue‘,
}
})
</script>
v-text
<div id="app" v-text="greeting"></div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
new Vue({
el:‘#app‘,
data:{
greeting:‘Hello Vue‘,
}
})
</script>
v-html
<div id="app" v-html="greeting"></div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
new Vue({
el:‘#app‘,
data:{
greeting:‘<h1>Hello Vue</h1>‘,
}
})
</script>
v-for 循环
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="hobby in funingbo">{{ hobby }}</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="student in students">姓名:{{student.name}},年龄:{{student.age}},爱好:{{student.hobby}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
funingbo: [‘人‘, ‘生‘, ‘太‘, ‘悲‘, ‘凉‘],
students: [
{
name: ‘wjs‘,
age: 24,
hobby: ‘痴心妄想‘,
},
{
name: ‘gxx‘,
age: 22,
hobby: ‘有上进心‘,
},
{
name: ‘zq‘,
age: 23,
hobby: ‘好学‘,
},
]
}
})
</script>
v-if、v-else-if
<div id="app">
<div v-for="role in roles">
<div v-if="role == ‘gxx‘">
<h1>v-if {{role}} 你好</h1>
</div>
<div v-else-if="role == ‘zq‘">
<h1>v-else-if {{role}} 你好</h1>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
roles: [‘gxx‘, ‘zq‘]
}
})
</script>
v-show 是否展示的语法:true 展示,false 不展示
<div id="app">
<div v-for="role in roles">
<div v-if="role == ‘gxx‘" v-show="isShow">
<h1>v-if {{role}} 你好</h1> // 这个标签不展示
</div>
<div v-else-if="role == ‘zq‘">
<h1>v-else-if {{role}} 你好</h1>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
roles: [‘gxx‘, ‘zq‘],
isShow: false,
}
})
</script>
v-bind 绑定属性 简写为 :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="static/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
.active {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: deepskyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<a v-bind:href="jd">京东</a>
// 这里 : 为v-bind的简写,[]表示可以传多个值并用逗号隔开,如果是一个值得话可以不写[]。
<div :class="[isActive]"></div>
</div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
let vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
jd: ‘https://www.jd.com‘,
isActive: ‘active‘,
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
v-on 绑定点击事件 简写为 @
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="static/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
.active {
color: deepskyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<a v-bind:class="{ active:isActive }">山人</a>
<!--<button v-on:click="changeColor">点击山人变蓝</button>-->
<!--v-on 的简写 @-->
<button @click="changeColor">点击山人变蓝</button>
</div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
let vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
isActive: false,
},
methods: {
changeColor: function () {
this.isActive = !this.isActive;
},
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
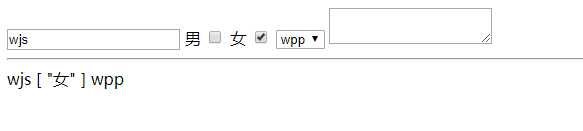
v-model ----修改后的数据能够及时(官方称之为响应式)的渲染到模板层
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="name">
<label for="">男</label>
<input type="checkbox" value="男" v-model="genders">
<label for="">女</label>
<input type="checkbox" value="女" v-model="genders">
<select v-model="girlfriends">
<option>gxx</option>
<option>zq</option>
<option>wpp</option>
</select>
<textarea></textarea>
<hr>
{{ name }}
{{ genders }}
{{ girlfriends }}
</div>
<script>
// 数据模板引擎
// v-开头的指令是帮助我们渲染数据用的
let vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
name: ‘wjs‘,
genders: [],
girlfriends: [],
},
})
</script>
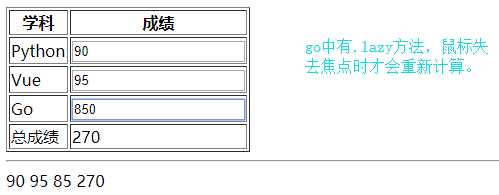
计算属性
<div id="app">
<table border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>学科</th>
<th>成绩</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Python</td>
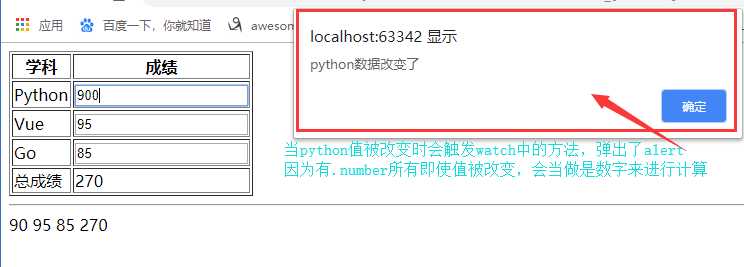
<!--.number修改input框中的值时,就是以数字来重新计算的,如果没有.number就会把所有的值当做字符串拼接起来。-->
<td><input type="text" v-model.number="python"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Vue</td>
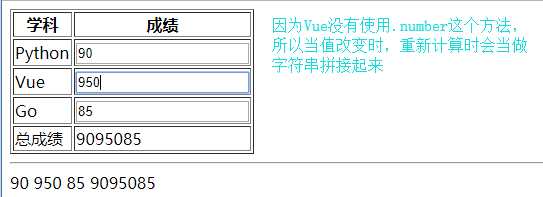
<!--.trim去除两边的空格-->
<td><input type="text" v-model.trim="vue"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Go</td>
<!--.lazy为当鼠标失去焦点时才会重新计算-->
<td><input type="text" v-model.lazy="go"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>总成绩</td>
<td>{{ sumScore }}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<hr>
{{ python }}
{{ vue }}
{{ go }}
{{ sumScore }}
</div>
<script>
// 计算属性放在缓存中,只有数据修改时才重新计算
let vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
python: 90,
vue: 95,
go: 85,
},
computed: {
// 这里return返回的值会传给sumScore变量
sumScore: function () {
console.log(1);
return this.python + this.vue + this.go;
},
},
watch: {
// 这里python变量必须是data中存在的,而且watch它不会有值返回给python
python: function () {
alert(‘python数据改变了‘)
}
}
})
</script>
获取DOM元素
<div id="app">
<div ref="myRef">山人</div>
<button v-on:click="changeColor">点击山人变蓝</button>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
isActive: ‘active‘,
},
methods: {
changeColor: function () {
this.$refs.myRef.className = this.isActive;
}
}
})
</script>


v-pos 自定义指令
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="static/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: deepskyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:class="{ box:isShow }" v-pos.right.bottom="leftBottom">山人</div>
</div>
<script>
// pos是固定的写法
Vue.directive(‘pos‘, function (el, bindding) {
console.log(‘el:‘, el);
console.log(‘bingding:‘, bindding);
// 这里value获取的是下面写的isShow赋给的值也就是所写的true,
if (bindding.value) {
el.style[‘position‘] = ‘fixed‘;
for (let key in bindding.modifiers) {
el.style[key] = 0;
// el.style[‘right‘] = 0;
// el.style[‘bottom‘] = 0;
}
}
});
let vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
leftBottom: true,
isShow: true, // isShow通过bindding.value
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
标签:fine 去除 www vue cli learn sele inf tin
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wjs521/p/9926204.html