标签:pyc line text hunk cat 数字 格式 orm 组成
1.虚拟环境配置
1 用pychanrm创建--->files-->newproject--->选择虚拟环境
2 settings-->project创建
3 用命令行创建

安装:
pip3 install virtualenv
创建虚拟环境:
(1)virtualenv env_django(创建虚拟环境) #env_django为虚拟环境名
(2)virtualenv --system-site-packages env_django(创建环境,继承原安装的模块)
激活该虚拟环境:
-windows进到目录里,的Script文件夹输入:activate
-linux:soruse env1/Script/activate
退出虚拟环境:
-deactivate
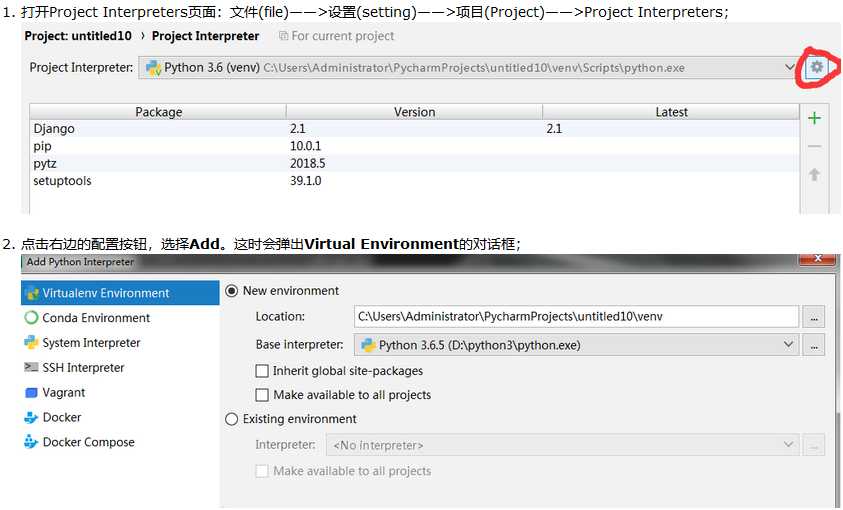
在pycharm中使用虚拟环境
-files--settings--Project--Project Interpreter--add选择虚拟环境路径下的python.exe即可
创建项目时创建虚拟环境
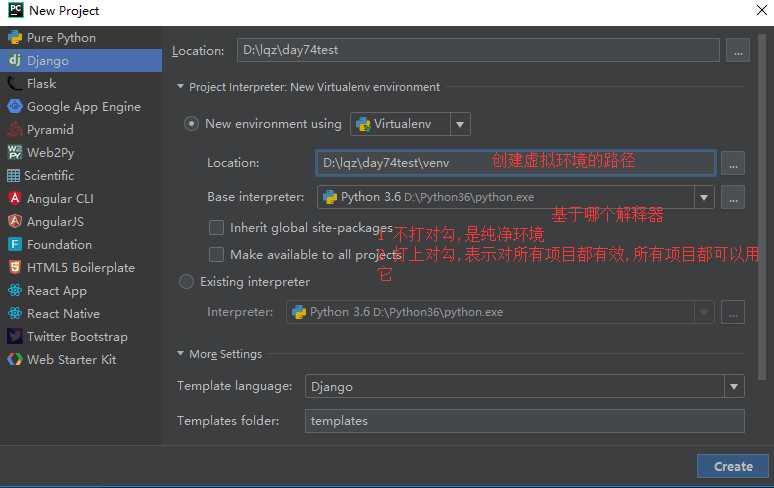
已有项目使用虚拟环境
2.django 2.0和django 1.0 路由层区别(*****url,re_path分组分出来的数据,是字符串)
re_path(‘正则‘,视图函数)
path传的第一个参数,不是正则,准确的路径,不支持正则
5个转换器-->path(‘test/<int:year>‘, views.re_test),
str,匹配除了路径分隔符(/)之外的非空字符串,这是默认的形式
int,匹配正整数,包含0。
slug,匹配字母、数字以及横杠、下划线组成的字符串。
uuid,匹配格式化的uuid,如 075194d3-6885-417e-a8a8-6c931e272f00。
path,匹配任何非空字符串,包含了路径分隔符(/)(不能用?)
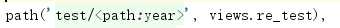
3.自定义转换器在urls中定义
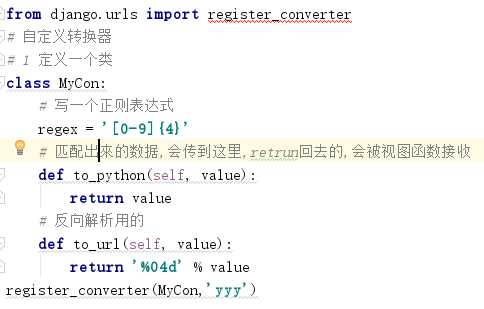
在urls.py文件内的urlpatterns内写入
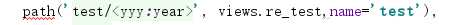
4.视图层之HttpRequest对象
def test(request): print(type(request)) from django.core.handlers.wsgi import WSGIRequest # 前台Post传过来的数据,包装到POST字典中 request.POST # 前台浏览器窗口里携带的数据,包装到GET字典中 request.GET # 前台请求的方式 request.method # post提交的数据,body体的内容 request.body # 取出请求的路径,取不到数据部分 print(request.path) # 取出请求的路径,能取到数据部分 print(request.get_full_path()) print(request.META) # post提交数据格式,放到body体中 # name=lqz&age=18&sex=1 return HttpResponse(‘ok‘)
5.视图层之HttpResponse对象
三件套:render,HttpResponse,redirect
render函数:
def test(request): if request.method==‘GET‘: temp=Template(‘<h1>{{ user }}</h1>‘) con=Context({‘user‘:‘lqz‘}) ret=temp.render(con) print(ret) # return render(request,‘index.html‘) return HttpResponse(ret)
6.视图层之JsonResponse对象
-导入:from django.http import JsonResponse #视图函数中: def test(request): import json dic={‘name‘:‘lqz‘,‘age‘:18} ll = [‘name‘, ‘age‘] # 把字典转换成json格式,返回到前台 return HttpResponse(json.dumps(dic)) # 把列表转换成json格式,返回到前台 return HttpResponse(json.dumps(ll)) # 把字典转换成json格式,返回到前台 return JsonResponse(dic) # 报错,默认不支持列表形式 return JsonResponse(ll) # 支持列表形式 return JsonResponse(ll,safe=False)
7.CBV和FBV
基于类的视图(CBV)
from django.views import View class Test(View): def get(self, request): return HttpResponse(‘get-test‘) def post(self, request): return HttpResponse(‘post-test‘)
基于函数的视图(FBV)
8.简单文件上传
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{#<form action="" method="post" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">#} <input type="file" name="myfile"> <input type="text" name="password"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form>
def fileupload(request): if request.method==‘GET‘: return render(request,‘fileupload.html‘) if request.method==‘POST‘: # FILES print(request.FILES) print(type(request.FILES.get(‘myfile‘))) # 从字典里根据名字,把文件取出来 myfile=request.FILES.get(‘myfile‘) from django.core.files.uploadedfile import InMemoryUploadedFile # 文件名字 name=myfile.name # 打开文件,把上传过来的文件存到本地 with open(name,‘wb‘) as f: # for line in myfile.chunks(): #chunks为django内部封装的方法该方法也可以拿到文件全部内容 for line in myfile: f.write(line) return HttpResponse(‘ok‘)
编码方式multipart/form-data或者:application/x-www-form-urlencoded传的数据,都可以从POST中取出来
标签:pyc line text hunk cat 数字 格式 orm 组成
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/layerluo/p/9932690.html