标签:等于 重复 题解 dup ida arrays 数组 width array
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
示例 1:
输入: candidates =[10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target =8, 所求解集为: [ [1, 7], [1, 2, 5], [2, 6], [1, 1, 6] ]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5, 所求解集为: [ [1,2,2], [5] ]
这道题感觉全排列II来说还要简单一些,整体还是递归回溯框架。
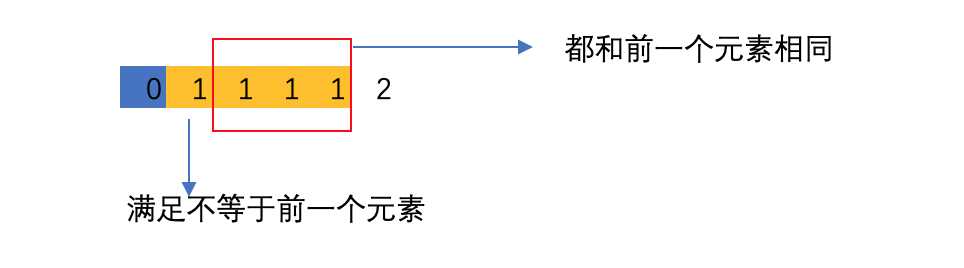
首先我们需要将数组进行排序,这样可以把相同元素放在一起,递归过程中保证同一个位置同一个值只使用一次。也就是如果已经在第1个位置上枚举了“1”这个数字,那么即使之后仍然有“1”的取值,也都跳过不进行枚举。
在实际的实现中,我们不妨这样枚举,即将nums数组排序后,只有nums[i]不等于nums[i-1]时,才将nums[i]视作一种可能的取值,即:
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 确保在一个位置不会枚举两个相同的数
if (i == nums.size() - 1 || nums[i] != nums[i -1]) {
}
}
或者说,我们是跳过当前元素,其实这样的意思谁说,同一个取值的元素,我只取最左边的一个。
if(i > start && nums[i] == nums[i-1])
continue; // skip duplicates
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, target, 0);
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums, int remain, int start){
if(remain < 0) return;
else if(remain == 0)
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
else{
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++){
if(i > start && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // skip duplicates
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums, remain - nums[i], i + 1);
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
标签:等于 重复 题解 dup ida arrays 数组 width array
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/MrSaver/p/9938877.html