标签:详细介绍 直接 numpy head .sh 趋势 otl 效果 sha
查看版本
import tushare
print(tushare.__version__)1.2.12
import tushare as ts
ts.get_hist_data(‘600848‘) #一次性获取全部日k线数据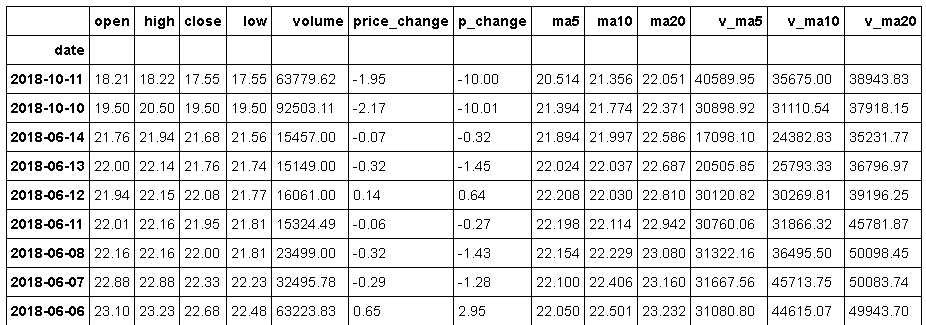
import tushare as ts
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = ts.get_hist_data(‘000001‘,start=‘2017-01-01‘,end=‘2018-10-10‘)
df.head(10)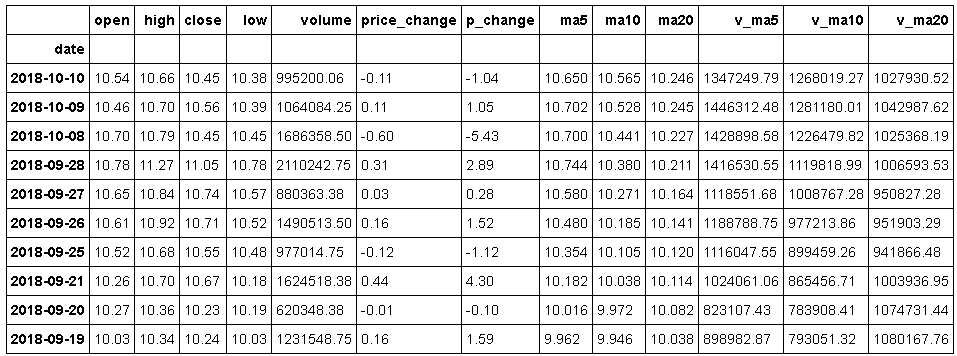
sz=df.sort_index(axis=0, ascending=True) #对index进行升序排列
sz_return=sz[[‘p_change‘]] #选取涨跌幅数据
train=sz_return[0:255] #划分训练集
test=sz_return[255:] #测试集
#对训练集与测试集分别做趋势图
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
train[‘p_change‘].plot()
plt.legend(loc=‘best‘)
plt.show()
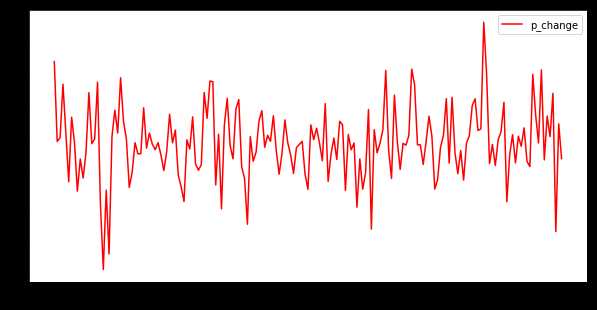
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
test[‘p_change‘].plot(c=‘r‘)
plt.legend(loc=‘best‘)
plt.show()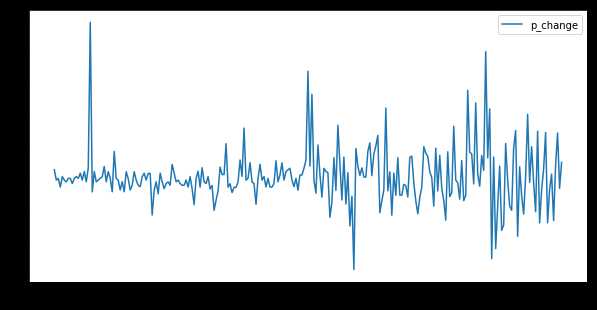
直接用训练集平均值作为测试集的预测值
#Simple Average
from math import sqrt
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
y_hat_avg = test.copy() #copy test列表
y_hat_avg[‘avg_forecast‘] = train[‘p_change‘].mean() #求平均值
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.plot(train[‘p_change‘], label=‘Train‘)
plt.plot(test[‘p_change‘], label=‘Test‘)
plt.plot(y_hat_avg[‘avg_forecast‘], label=‘Average Forecast‘)
plt.legend(loc=‘best‘)
plt.show()
rms = sqrt(mean_squared_error(test.p_change, y_hat_avg.avg_forecast))
print(rms)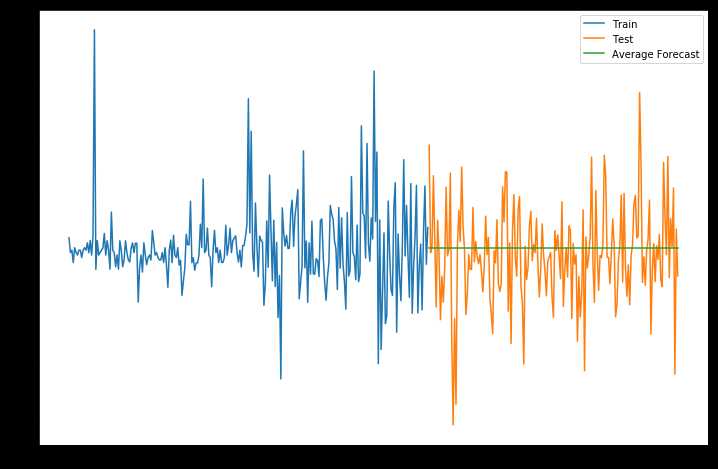
2.1722839490457657
直接用移动平均法最后一个值作为测试集的预测值
#Moving Average
from math import sqrt
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
y_hat_avg = test.copy()
y_hat_avg[‘moving_avg_forecast‘] = train[‘p_change‘].rolling(30).mean().iloc[-1]
#30期的移动平均,最后一个数作为test的预测值
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.plot(train[‘p_change‘], label=‘Train‘)
plt.plot(test[‘p_change‘], label=‘Test‘)
plt.plot(y_hat_avg[‘moving_avg_forecast‘], label=‘Moving Average Forecast‘)
plt.legend(loc=‘best‘)
plt.show()
rms = sqrt(mean_squared_error(test.p_change, y_hat_avg.moving_avg_forecast))
print(rms)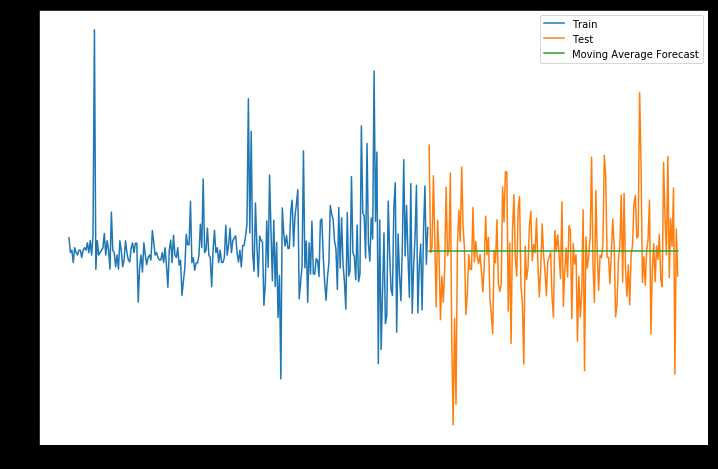
2.1545970719308243
可以看到,最后移动平均法的均方误差最低,预测效果最好。
标签:详细介绍 直接 numpy head .sh 趋势 otl 效果 sha
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hankleo/p/9939725.html