标签:分隔符 www. 添加 read 参考资料 元素 tle tar 符号
LinkedBinarySearchTree<T> result = new LinkedBinarySearchTree<>();
result.root = root.getRight();
return result;contains方法为判断是否存在目标元素,通过结合find方法,find方法是返回一个boolean值,在此基础上,将找到的结点的元素值返回即可。部分关键代码如下:
public boolean contains(T targetElement)
{
if(find(targetElement)!=null)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public T find(T targetElement) throws ElementNotFoundException
{
BinaryTreeNode<T> current = findNode(targetElement, root);
if (current == null)
throw new ElementNotFoundException("LinkedBinaryTree");
return (current.getElement());
}
private BinaryTreeNode<T> findNode(T targetElement,
BinaryTreeNode<T> next)
{
if (next == null)
return null;
if (next.getElement().equals(targetElement))
return next;
BinaryTreeNode<T> temp = findNode(targetElement, next.getLeft());
if (temp == null)
temp = findNode(targetElement, next.getRight());
return temp;
}public Iterator<T> iteratorPostOrder()
{
ArrayUnorderedList<T> tempList = new ArrayUnorderedList<T>();
postOrder(root,tempList);
return new TreeIterator(tempList.iterator());
}
protected void postOrder(BinaryTreeNode<T> node,
ArrayUnorderedList<T> tempList)
{
if (node !=null){
postOrder(node.getLeft(),tempList);
postOrder(node.getRight(),tempList);
tempList.addToRear(node.getElement());
}
}
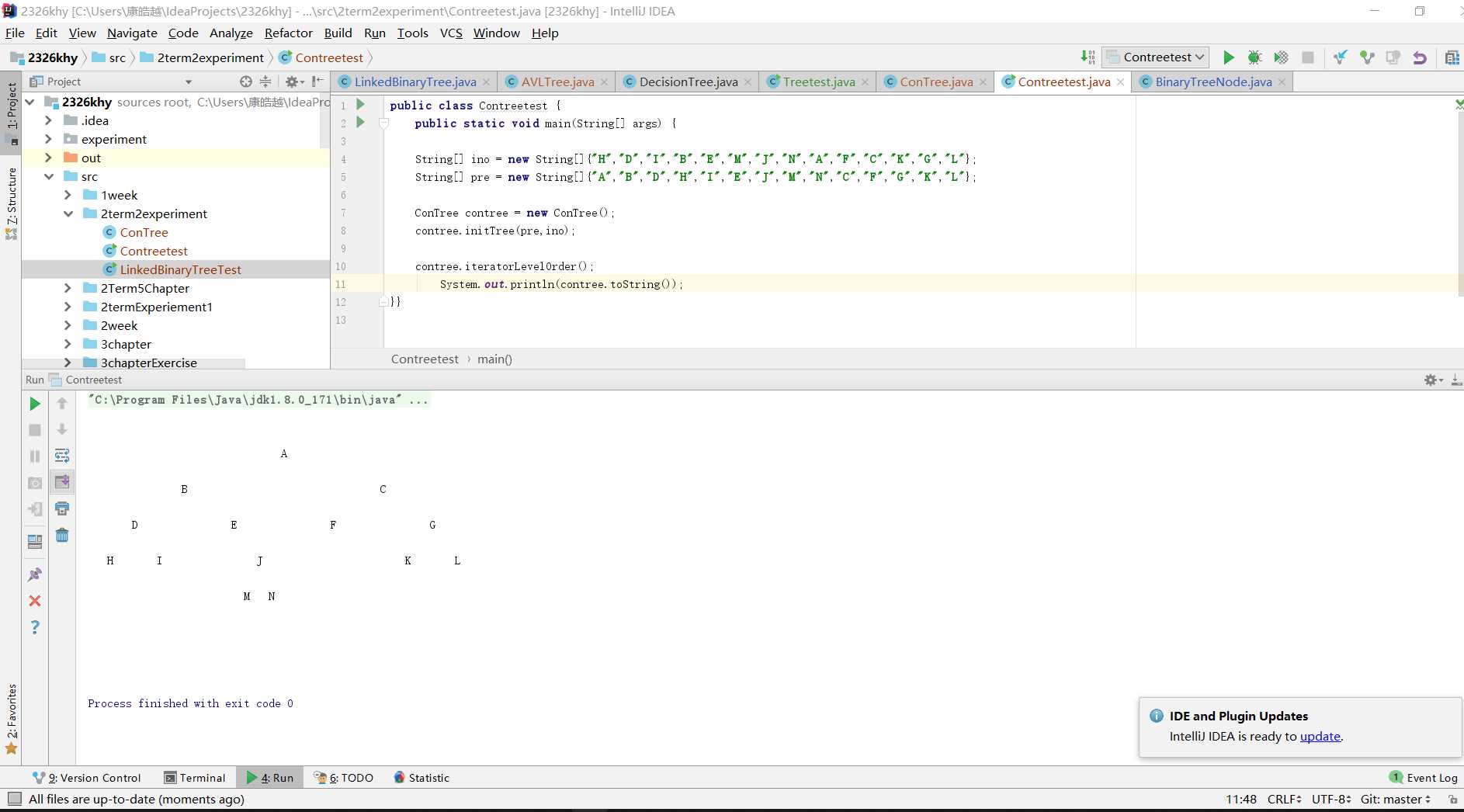
public BinaryTreeNode initTree(String[] preorder, int s1, int e1, String[] inorder, int s2, int e2) {//s1是前序开始值,e1是结束值
if (s1 > e1 || s2 > e2) {
return null;
}
String rootE = preorder[s1];//前序定根
BinaryTreeNode head = new BinaryTreeNode(rootE);
int rootG = findRoot(inorder, rootE, s2, e2);//在中序中找到根的位置
BinaryTreeNode left = initTree(preorder, s1 + 1, s1 + rootG - s2, inorder, s2, rootG - 1);//开始使用递归,通过根的索引值确定数组中各个子树的位置,将其分割
BinaryTreeNode right = initTree(preorder, s1 + rootG - s2 + 1, e1, inorder, rootG + 1, e2);
head.setLeft(left);
head.setRight(right);
return head;
}
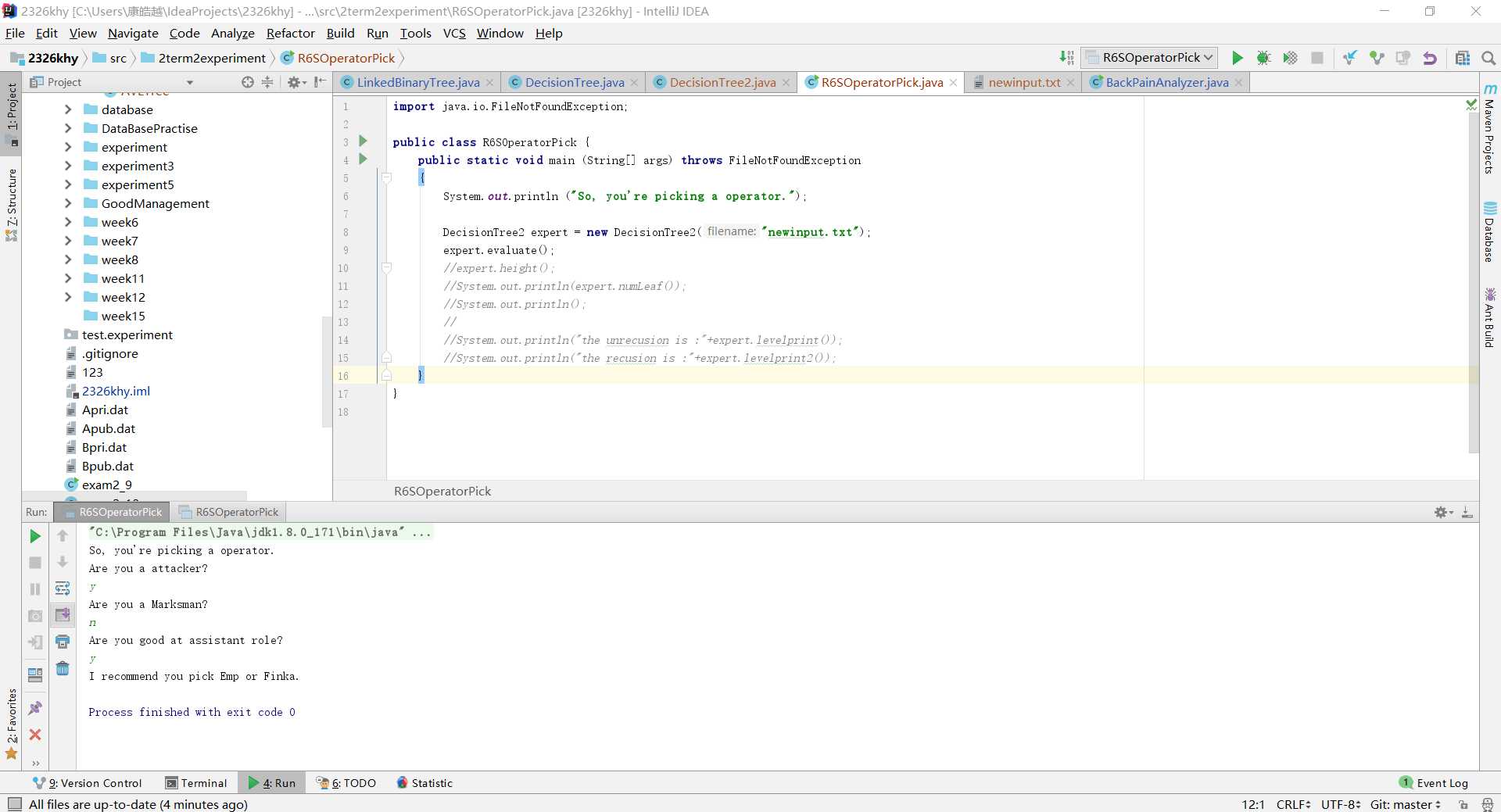
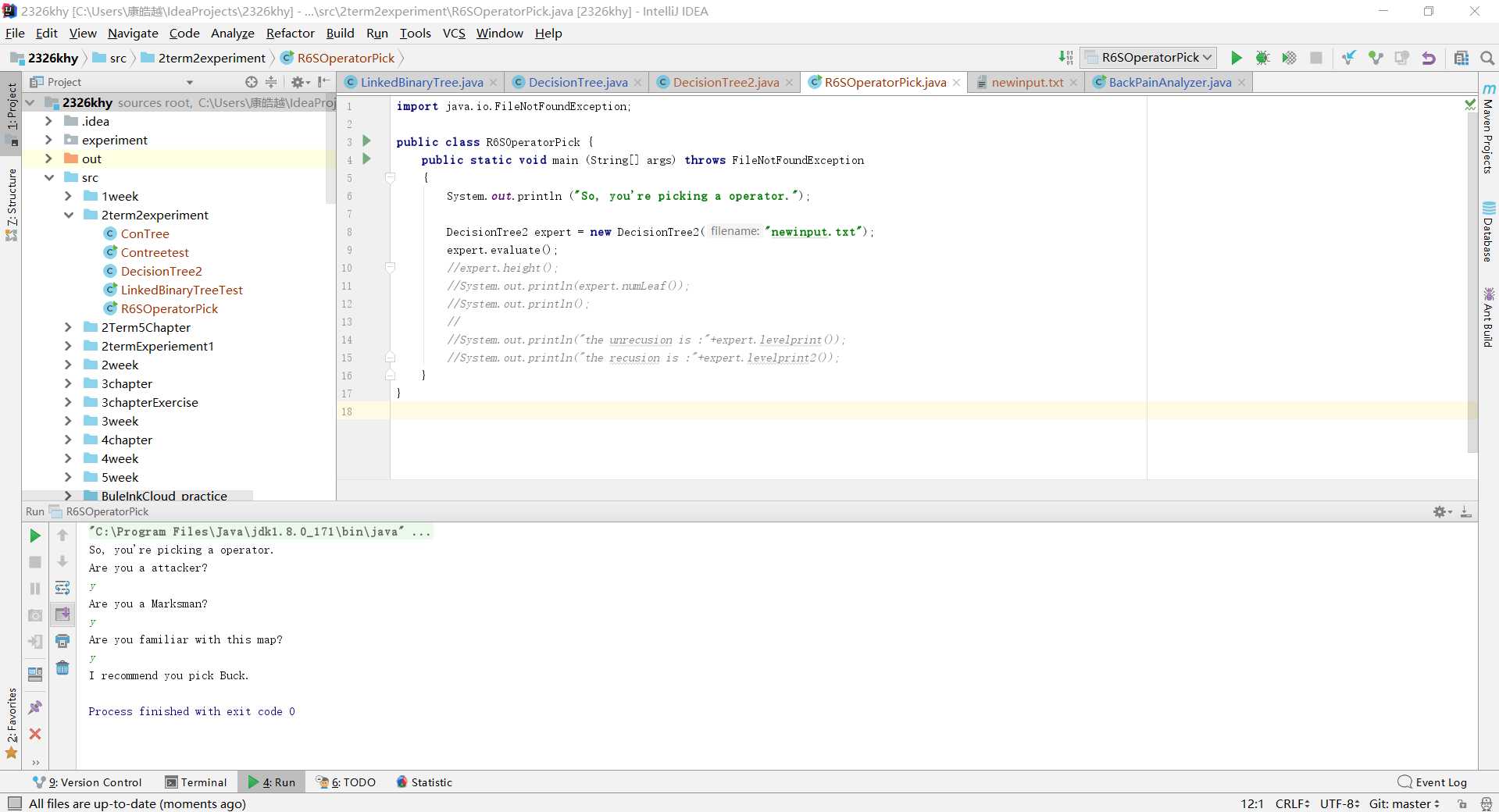
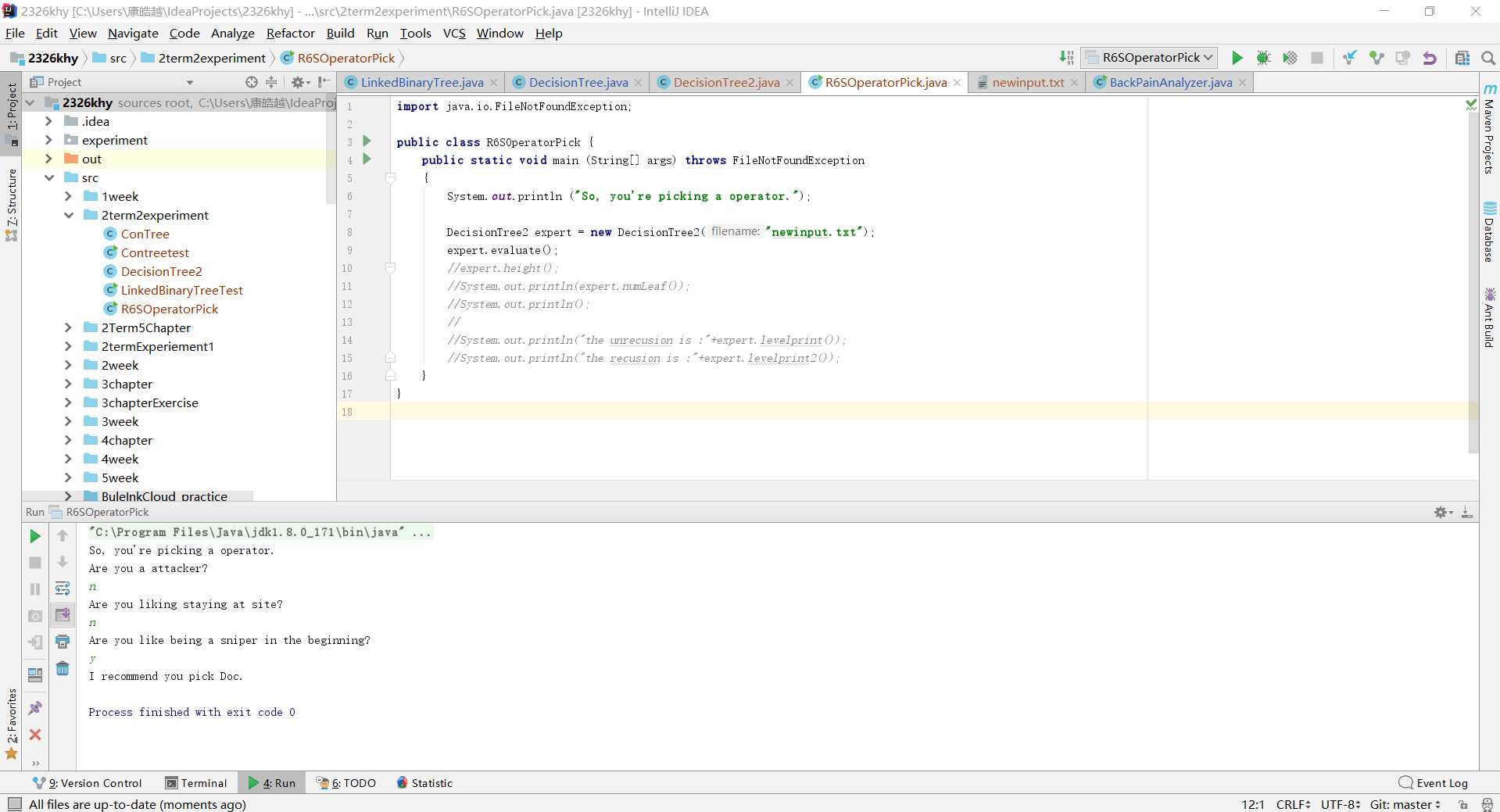
public void evaluate()
{
LinkedBinaryTree<String> current = tree;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while (current.size() > 1)
{
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
if (scan.nextLine().equalsIgnoreCase("N"))
current = current.getRight();
else
current = current.getLeft();
}
System.out.println (current.getRootElement());
}
if(isOp(temp)&&isHighOp(temp)){//有高级符号
BinaryTreeNode current = new BinaryTreeNode(temp);
current.setLeft(numlist.remove(numlist.size()-1));
num2 = scan.nextToken();
current.setRight(new BinaryTreeNode(num2));
numlist.add(current);
}
public T removeMin() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
T result = null;
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyCollectionException("LinkedBinarySearchTree");
else
{
if (root.left == null)
{
result = root.element;
root = root.right;
}
else
{
BinaryTreeNode<T> parent = root;
BinaryTreeNode<T> current = root.left;
while (current.left != null)
{
parent = current;
current = current.left;
}
result = current.element;
parent.left = current.right;
}
modCount--;
}
TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。
TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
TreeMap 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
另外,TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fastl的。
// 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap
// 将map中的元素逐个添加到TreeMap中,并返回map的中间元素作为根节点。
private final Entry<K,V> buildFromSorted(int level, int lo, int hi,
int redLevel,
Iterator it,
java.io.ObjectInputStream str,
V defaultVal)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
if (hi < lo) return null;
// 获取中间元素
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
Entry<K,V> left = null;
// 若lo小于mid,则递归调用获取(middel的)左孩子。
if (lo < mid)
left = buildFromSorted(level+1, lo, mid - 1, redLevel,
it, str, defaultVal);
// 获取middle节点对应的key和value
K key;
V value;
if (it != null) {
if (defaultVal==null) {
Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>)it.next();
key = entry.getKey();
value = entry.getValue();
} else {
key = (K)it.next();
value = defaultVal;
}
} else { // use stream
key = (K) str.readObject();
value = (defaultVal != null ? defaultVal : (V) str.readObject());
}
// 创建middle节点
Entry<K,V> middle = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null);
// 若当前节点的深度=红色节点的深度,则将节点着色为红色。
if (level == redLevel)
middle.color = RED;
// 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
if (left != null) {
middle.left = left;
left.parent = middle;
}
if (mid < hi) {
// 递归调用获取(middel的)右孩子。
Entry<K,V> right = buildFromSorted(level+1, mid+1, hi, redLevel,
it, str, defaultVal);
// 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
middle.right = right;
right.parent = middle;
}
return middle;
}TreeMap的put操作 TreeMap在进行put操作时,主要有以下步骤: (1)判断树是否是空的,如果是空的,直接将当前插入的k-v当做是根节点,完成了插入操作; (2)如果树不是空的,获取比较器(不管是自定义的比较器还是默认的比较器),对树从根节点开始遍历, (3)如果k小于结点的key,那么开始遍历左子节点,如果大于结点的key,开始遍历右子节点,如果相等,说明k已经在TreeMap中存在了,就用新的value值覆盖旧的value值,完成了插入操作; (4)如果k在TreeMap中不存在,将k插入到其相应的位置,此时由于树的结构进行了变化,需要检验其是否满足红黑性的元素,调用fixAfterInsertion方法。
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
private V getForNullKey() {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
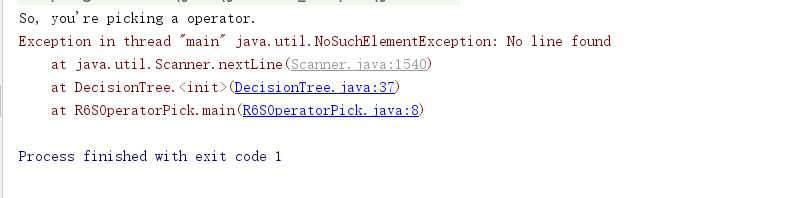
在用Scanner方法时,它是用从后往前的顺序进行扫描的,注意这张图,右边比左边多了一行,而且是空白的一行。我们先看一下nextLine的方法
- nextLine
public String nextLine()此扫描器执行当前行,并返回跳过的输入信息。 此方法返回当前行的其余部分,不包括结尾处的行分隔符。当前位置移至下一行的行首。
因为此方法会继续在输入信息中查找行分隔符,所以如果没有行分隔符,它可能会缓冲所有输入信息,并查找要跳过的行。
返回:
跳过的行
抛出:
NoSuchElementException - 如果未找到这样的行
IllegalStateException - 如果此扫描器已关闭
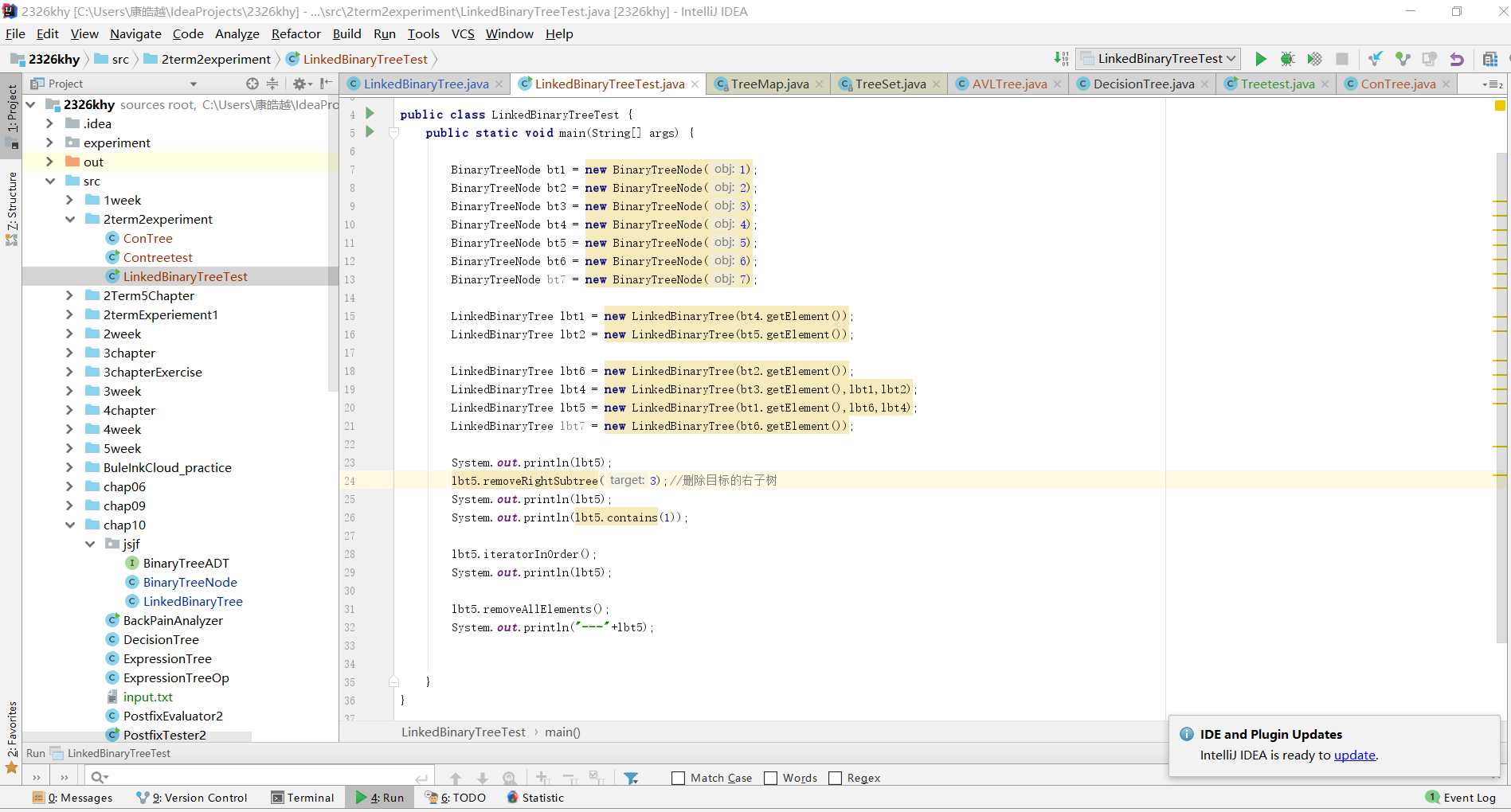
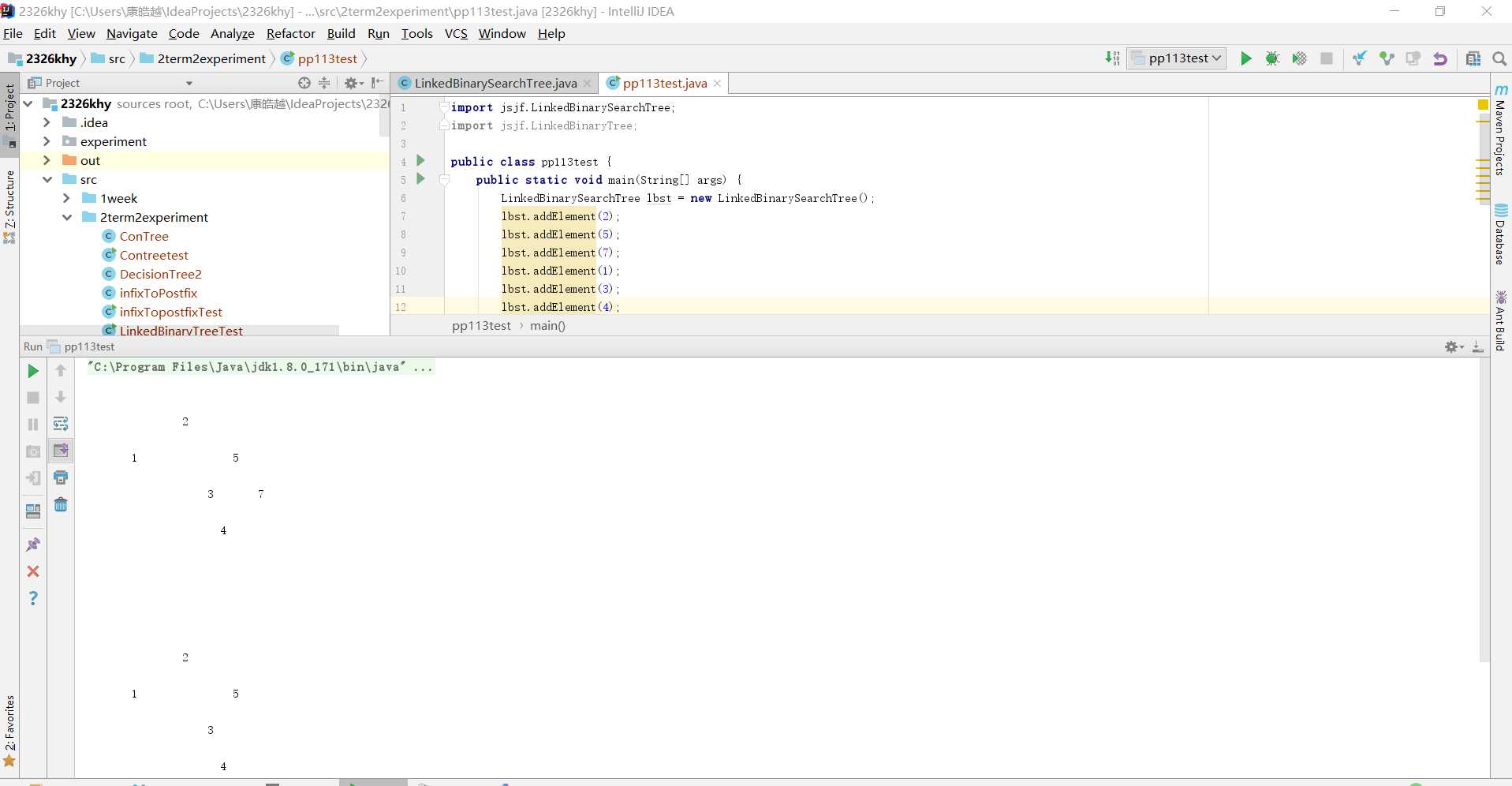
public void postfix(){
LinkedBinaryTree lbt = new LinkedBinaryTree();
lbt.root = btnode2;
Iterator it = lbt.iteratorPostOrder();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.print(it.next().toString()+" ");
}问题代码,现在每次都将其实例化,但是却并没有得到存储,随着这个方法的每一次调用,都产生了一个新的树,导致出现了空。
学号 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》实验二报告
标签:分隔符 www. 添加 read 参考资料 元素 tle tar 符号
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/326477465-a/p/9940712.html