标签:override dHash while color 查看 alt 内容 返回 ==
原理
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。
实现1
最常见的实现是使用一个链表保存缓存数据,详细算法实现如下:
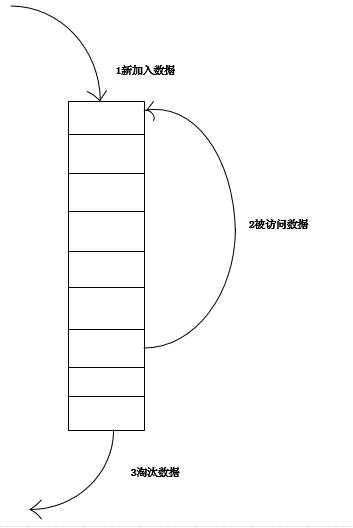
1. 新数据插入到链表头部;
2. 每当缓存命中(即缓存数据被访问),则将数据移到链表头部;
3. 当链表满的时候,将链表尾部的数据丢弃。
分析
【命中率】
当存在热点数据时,LRU的效率很好,但偶发性的、周期性的批量操作会导致LRU命中率急剧下降,缓存污染情况比较严重。
【复杂度】
实现简单。
【代价】
命中时需要遍历链表,找到命中的数据块索引,然后需要将数据移到头部。
使用LinkedHashMap实现
LinkedHashMap底层就是用的HashMap加双链表实现的,而且本身已经实现了按照访问顺序的存储。此外,LinkedHashMap中本身就实现了一个方法removeEldestEntry用于判断是否需要移除最不常读取的数,方法默认是直接返回false,不会移除元素,所以需要重写该方法。即当缓存满后就移除最不常用的数。
1 public class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> { 2 3 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 4 5 //缓存大小 6 private int cacheSize; 7 8 public LRUCache(int cacheSize) { 9 //第三个参数true是关键 10 super(10, 0.75f, true); 11 this.cacheSize = cacheSize; 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * 缓存是否已满 16 */ 17 @Override 18 protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) { 19 boolean r = size() > cacheSize; 20 if (r) { 21 System.out.println("清除缓存key:" + eldest.getKey()); 22 } 23 return r; 24 } 25 26 //测试 27 public static void main(String[] args) { 28 LRUCache<String, String> cache = new LRUCache<String, String>(5); 29 cache.put("1", "1"); 30 cache.put("2", "2"); 31 cache.put("3", "3"); 32 cache.put("4", "4"); 33 cache.put("5", "5"); 34 35 System.out.println("初始化:"); 36 System.out.println(cache.keySet()); 37 System.out.println("访问3:"); 38 cache.get("3"); 39 System.out.println(cache.keySet()); 40 System.out.println("访问2:"); 41 cache.get("2"); 42 System.out.println(cache.keySet()); 43 System.out.println("增加数据6,7:"); 44 cache.put("6", "6"); 45 cache.put("7", "7"); 46 System.out.println(cache.keySet()); 47 }
实现2
LRUCache的链表+HashMap实现
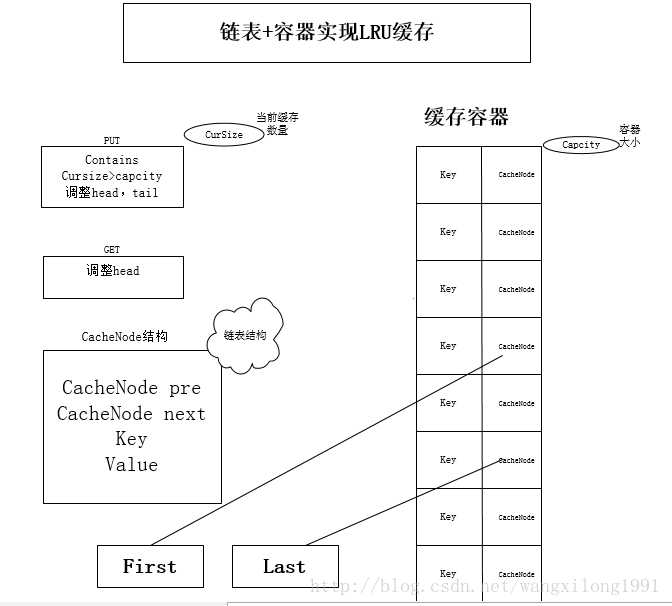
传统意义的LRU算法是为每一个Cache对象设置一个计数器,每次Cache命中则给计数器+1,而Cache用完,需要淘汰旧内容,放置新内容时,就查看所有的计数器,并将最少使用的内容替换掉。
它的弊端很明显,如果Cache的数量少,问题不会很大, 但是如果Cache的空间过大,达到10W或者100W以上,一旦需要淘汰,则需要遍历所有计算器,其性能与资源消耗是巨大的。效率也就非常的慢了。
它的原理: 将Cache的所有位置都用双连表连接起来,当一个位置被命中之后,就将通过调整链表的指向,将该位置调整到链表头的位置,新加入的Cache直接加到链表头中。
这样,在多次进行Cache操作后,最近被命中的,就会被向链表头方向移动,而没有命中的,而想链表后面移动,链表尾则表示最近最少使用的Cache。
当需要替换内容时候,链表的最后位置就是最少被命中的位置,我们只需要淘汰链表最后的部分即可。
上面说了这么多的理论, 下面用代码来实现一个LRU策略的缓存。
非线程安全,若实现安全,则在响应的方法加锁。
1 public class LRUCacheDemo<K, V> { 2 3 private int currentCacheSize; 4 private int CacheCapcity; 5 private HashMap<K, CacheNode> caches; 6 private CacheNode first; 7 private CacheNode last; 8 9 public LRUCacheDemo(int size) { 10 currentCacheSize = 0; 11 this.CacheCapcity = size; 12 caches = new HashMap<>(size); 13 } 14 15 public void put(K k, V v) { 16 CacheNode node = caches.get(k); 17 if (node == null) { 18 if (caches.size() >= CacheCapcity) { 19 caches.remove(last.key); 20 removeLast(); 21 } 22 node = new CacheNode(); 23 node.key = k; 24 } 25 node.value = v; 26 moveToFirst(node); 27 caches.put(k, node); 28 } 29 30 public Object get(K k) { 31 CacheNode node = caches.get(k); 32 if (node == null) { 33 return null; 34 } 35 moveToFirst(node); 36 return node.value; 37 } 38 39 public Object remove(K k) { 40 CacheNode node = caches.get(k); 41 if (node != null) { 42 if (node.pre != null) { 43 node.pre.next = node.next; 44 } 45 if (node.next != null) { 46 node.next.pre = node.pre; 47 } 48 if (node == first) { 49 first = node.next; 50 } 51 if (node == last) { 52 last = node.pre; 53 } 54 } 55 return caches.remove(k); 56 } 57 58 public void clear() { 59 first = null; 60 last = null; 61 caches.clear(); 62 } 63 64 private void moveToFirst(CacheNode node) { 65 if (first == node) { 66 return; 67 } 68 if (node.next != null) { 69 node.next.pre = node.pre; 70 } 71 if (node.pre != null) { 72 node.pre.next = node.next; 73 } 74 if (node == last) { 75 last = last.pre; 76 } 77 if (first == null || last == null) { 78 first = last = node; 79 return; 80 } 81 node.next = first; 82 first.pre = node; 83 first = node; 84 first.pre = null; 85 } 86 87 private void removeLast() { 88 if (last != null) { 89 last = last.pre; 90 if (last == null) { 91 first = null; 92 } else { 93 last.next = null; 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 98 @Override 99 public String toString() { 100 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 101 CacheNode node = first; 102 while (node != null) { 103 sb.append(String.format("%s:%s ", node.key, node.value)); 104 node = node.next; 105 } 106 return sb.toString(); 107 } 108 109 class CacheNode { 110 CacheNode pre; 111 CacheNode next; 112 Object key; 113 Object value; 114 115 public CacheNode() { 116 } 117 } 118 119 public static void main(String[] args) { 120 LRUCache<Integer, String> lru = new LRUCache<Integer, String>(3); 121 lru.put(1, "a"); // 1:a 122 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 123 lru.put(2, "b"); // 2:b 1:a 124 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 125 lru.put(3, "c"); // 3:c 2:b 1:a 126 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 127 lru.put(4, "d"); // 4:d 3:c 2:b 128 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 129 lru.put(1, "aa"); // 1:aa 4:d 3:c 130 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 131 lru.put(2, "bb"); // 2:bb 1:aa 4:d 132 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 133 lru.put(5, "e"); // 5:e 2:bb 1:aa 134 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 135 lru.get(1); // 1:aa 5:e 2:bb 136 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 137 lru.remove(11); // 1:aa 5:e 2:bb 138 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 139 lru.remove(1); //5:e 2:bb 140 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 141 lru.put(1, "aaa"); //1:aaa 5:e 2:bb 142 System.out.println(lru.toString()); 143 } 144 }
本文参考整理于 https://blog.csdn.net/wangxilong1991/article/details/70172302 ,感谢原作者的精彩分享!!!
标签:override dHash while color 查看 alt 内容 返回 ==
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/iliuyuet/p/9942106.html