标签:搜索 调试 教程 target int start public yun prim 生成
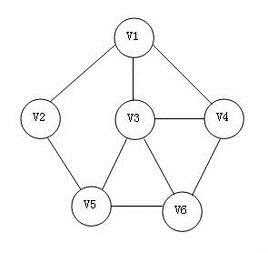
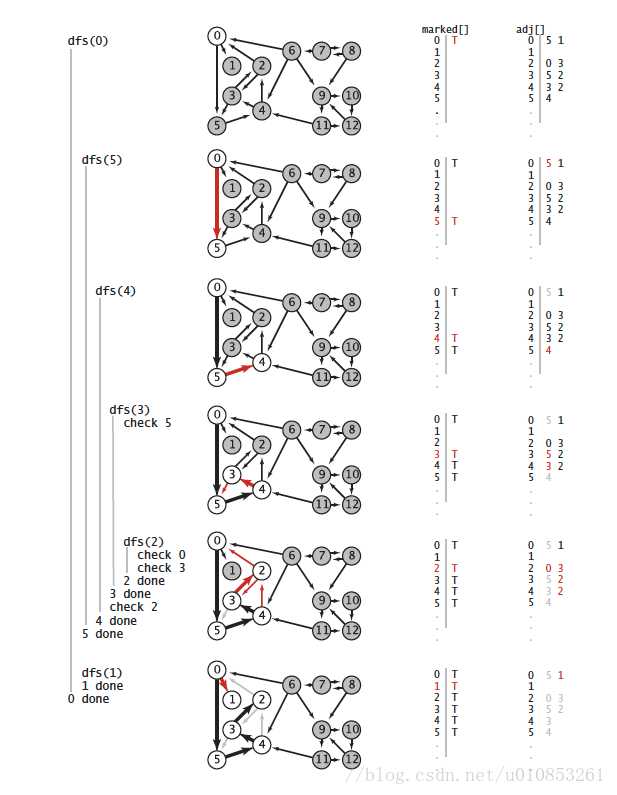
深度优先遍历示意图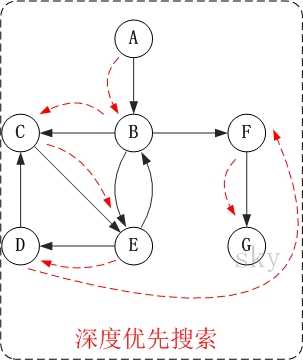
广度优先遍历示意图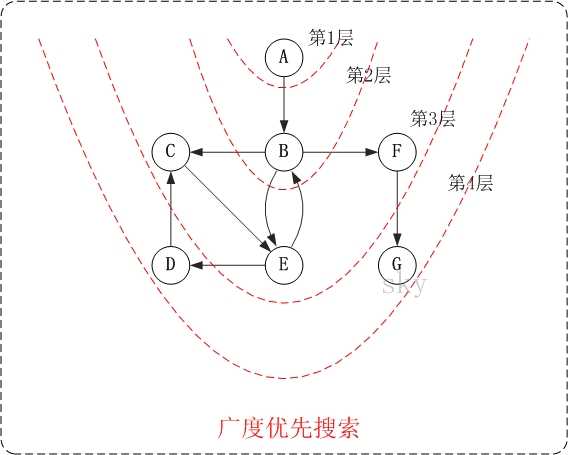
深度遍历与广度遍历代码
public Iterator<T> iteratorDFS(int startIndex)
{
Integer x;
boolean found;
StackADT<Integer> traversalStack = new LinkedStack<Integer>();
UnorderedListADT<T> resultList = new ArrayUnorderedList<T>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[numVertices];
if (!indexIsValid(startIndex))
return resultList.iterator();
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
visited[i] = false;
traversalStack.push(new Integer(startIndex));
resultList.addToRear(vertices[startIndex]);
visited[startIndex] = true;
while (!traversalStack.isEmpty())
{
x = traversalStack.peek();
found = false;
//Find a vertex adjacent to x that has not been visited
// and push it on the stack
for (int i = 0; (i < numVertices) && !found; i++)
{
if (adjMatrix[x.intValue()][i] && !visited[i])
{
traversalStack.push(new Integer(i));
resultList.addToRear(vertices[i]);
visited[i] = true;
found = true;
}
}
if (!found && !traversalStack.isEmpty())
traversalStack.pop();
}
return new GraphIterator(resultList.iterator());
}
public Iterator<T> iteratorDFS(T startVertex)
{
return iteratorDFS(getIndex(startVertex));
}
public Iterator<T> iteratorBFS(int startIndex)
{
Integer x;
QueueADT<Integer> traversalQueue = new LinkedQueue<Integer>();
UnorderedListADT<T> resultList = new ArrayUnorderedList<T>();
if (!indexIsValid(startIndex))
return resultList.iterator();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[numVertices];
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
visited[i] = false;
traversalQueue.enqueue(new Integer(startIndex));
visited[startIndex] = true;
while (!traversalQueue.isEmpty())
{
x = traversalQueue.dequeue();
resultList.addToRear(vertices[x.intValue()]);
//Find all vertices adjacent to x that have not been visited
// and queue them up
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
{
if (adjMatrix[x.intValue()][i] && !visited[i])
{
traversalQueue.enqueue(new Integer(i));
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
return new GraphIterator(resultList.iterator());
}
public Iterator<T> iteratorBFS(T startVertex)
{
return iteratorBFS(getIndex(startVertex));
}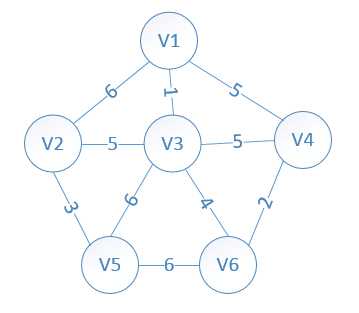
,图2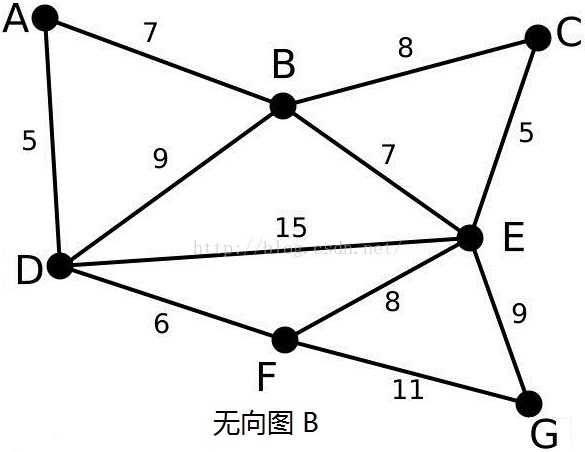
public Graph getMST()
{
int x, y;
int[] edge = new int[2];
StackADT<int[]> vertexStack = new LinkedStack<int[]>();
Graph<T> resultGraph = new Graph<T>();
if (isEmpty() || !isConnected())
return resultGraph;
resultGraph.adjMatrix = new boolean[numVertices][numVertices];
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < numVertices; j++)
resultGraph.adjMatrix[i][j] = false;
resultGraph.vertices = (T[])(new Object[numVertices]);
boolean[] visited = new boolean[numVertices];
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
visited[i] = false;
edge[0] = 0;
resultGraph.vertices[0] = this.vertices[0];
resultGraph.numVertices++;
visited[0] = true;
// Add all edges that are adjacent to vertex 0 to the stack.
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
{
if (!visited[i] && this.adjMatrix[0][i])
{
edge[1] = i;
vertexStack.push(edge.clone());
visited[i] = true;
}
}
while ((resultGraph.size() < this.size()) && !vertexStack.isEmpty())
{
// Pop an edge off the stack and add it to the resultGraph.
edge = vertexStack.pop();
x = edge[0];
y = edge[1];
resultGraph.vertices[y] = this.vertices[y];
resultGraph.numVertices++;
resultGraph.adjMatrix[x][y] = true;
resultGraph.adjMatrix[y][x] = true;
visited[y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
{
if (!visited[i] && this.adjMatrix[i][y])
{
edge[0] = y;
edge[1] = i;
vertexStack.push(edge.clone());
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
return resultGraph;
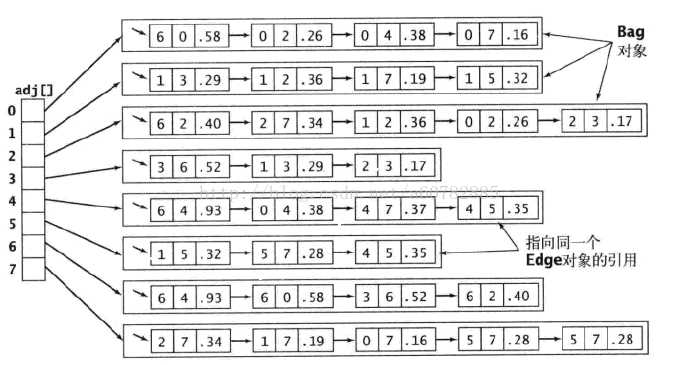
}邻接列表的示意图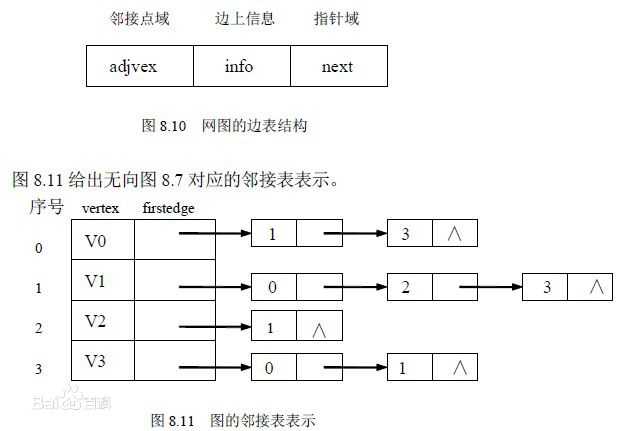
矩阵的非0元素必然是边的2倍
public interface GraphADT<T>
{
/**
* Adds a vertex to this graph, associating object with vertex.
*
* @param vertex the vertex to be added to this graph
*/
public void addVertex(T vertex);
/**
* Removes a single vertex with the given value from this graph.
*
* @param vertex the vertex to be removed from this graph
*/
public void removeVertex(T vertex);
/**
* Inserts an edge between two vertices of this graph.
*
* @param vertex1 the first vertex
* @param vertex2 the second vertex
*/
public void addEdge(T vertex1, T vertex2);
/**
* Removes an edge between two vertices of this graph.
*
* @param vertex1 the first vertex
* @param vertex2 the second vertex
*/
public void removeEdge(T vertex1, T vertex2);
/**
* Returns a breadth first iterator starting with the given vertex.
*
* @param startVertex the starting vertex
* @return a breadth first iterator beginning at the given vertex
*/
public Iterator iteratorBFS(T startVertex);
/**
* Returns a depth first iterator starting with the given vertex.
*
* @param startVertex the starting vertex
* @return a depth first iterator starting at the given vertex
*/
public Iterator iteratorDFS(T startVertex);
/**
* Returns an iterator that contains the shortest path between
* the two vertices.
*
* @param startVertex the starting vertex
* @param targetVertex the ending vertex
* @return an iterator that contains the shortest path
* between the two vertices
*/
public Iterator iteratorShortestPath(T startVertex, T targetVertex);
/**
* Returns true if this graph is empty, false otherwise.
*
* @return true if this graph is empty
*/
public boolean isEmpty();
/**
* Returns true if this graph is connected, false otherwise.
*
* @return true if this graph is connected
*/
public boolean isConnected();
/**
* Returns the number of vertices in this graph.
*
* @return the integer number of vertices in this graph
*/
public int size();
/**
* Returns a string representation of the adjacency matrix.
*
* @return a string representation of the adjacency matrix
*/
public String toString();
}
public interface NetworkADT<T> extends GraphADT<T>
{
/**
* Inserts an edge between two vertices of this graph.
*
* @param vertex1 the first vertex
* @param vertex2 the second vertex
* @param weight the weight
*/
public void addEdge(T vertex1, T vertex2, double weight);
/**
* Returns the weight of the shortest path in this network.
*
* @param vertex1 the first vertex
* @param vertex2 the second vertex
* @return the weight of the shortest path in this network
*/
public double shortestPathWeight(T vertex1, T vertex2);
}
public void addEdge(T vertex1, T vertex2)
{
addEdge(getIndex(vertex1), getIndex(vertex2));
}
public void addEdge(int index1, int index2)
{
if (indexIsValid(index1) && indexIsValid(index2))
{
adjMatrix[index1][index2] = true;
adjMatrix[index2][index1] = true;
modCount++;
}
}
问题1:在做PP15.1的时候,进行测试连通方法的时候,我故意想要将所有顶点连接在一起,最后测试的时候,测试结果却是没有连通,图。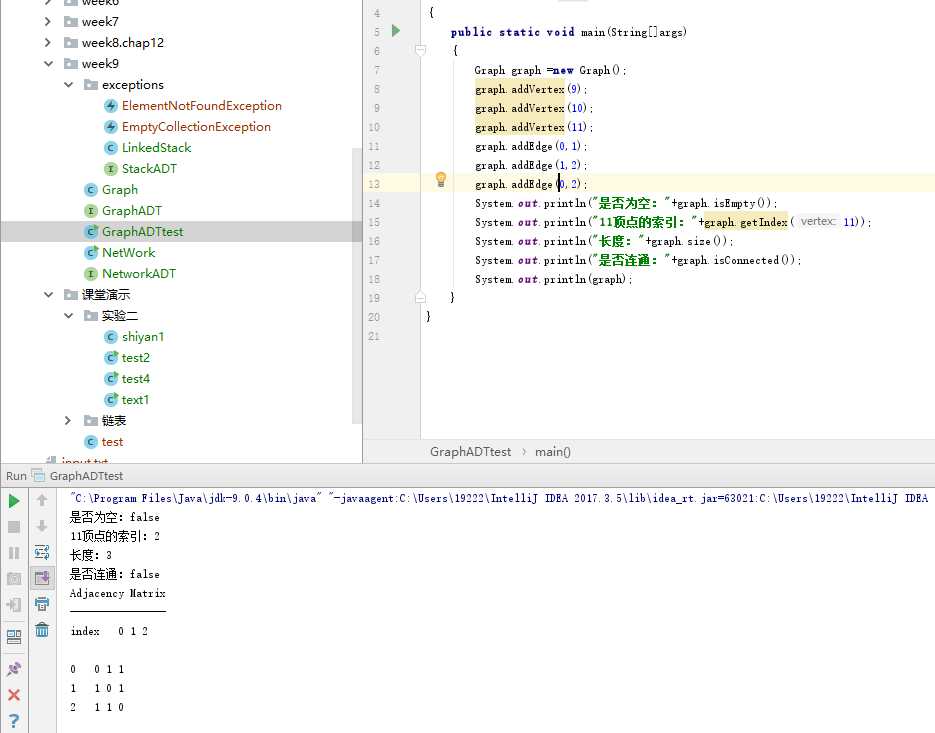
解决方案:在检查代码的过程中图,我发现了我的返回错误的要求不仅要建立A到B的边,也要建立B到A的边,否则就错误。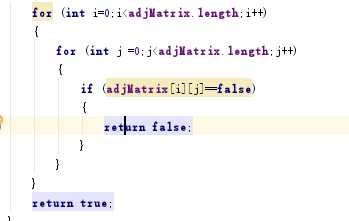
-图代码
基于评分标准,我给李楠的博客打分:7分。得分情况如下:
正确使用Markdown语法(加1分)
模板中的要素齐全(加1分)
教材学习中的问题和解决过程, (加3分)
代码调试中的问题和解决过程, 无问题
感想,体会真切的(加1分)
点评认真,能指出博客和代码中的问题的(加1分)
实现网络图的时候对于各种遍历运用极度不熟悉。
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 10/10 | |
| 第二周 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 10/20 | |
| 第三周 | 1500/1500 | 1/3 | 10/30 | |
| 第四周 | 2761/4261 | 2/5 | 25/55 | |
| 第五周 | 814/5075 | 1/6 | 15/70 | |
| 第六周 | 1091/6166 | 1/7 | 15/85 | |
| 第七周 | 1118/7284 | 1/8 | 15/100 | |
| 第八周 | 1235/8519 | 2/10 | 15/115 | |
| 第九周 | 1757/10276 | 1/11 | 25/140 |
20172333 2018-2019-1 《程序设计与数据结构》第九周学习总结
标签:搜索 调试 教程 target int start public yun prim 生成
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanyujun527/p/9979247.html