标签:nbsp thml amp ons nal inf rom ati lock
np.linalg.norm() computes the norm of a NumPy array according to an order, ord, which specifies the metric by which the norm takes. For example, if we are given an array
with numbers ????xi then we can compute the Frobenius Norm or more commonly called the 2-norm by doing:
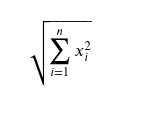
In NumPy you can also use np.linalg.norm() to compute the norm of a matrix, or a matrix‘s columns or rows, treating each as their own array.
example:
1 import numpy as np 2 from numpy.linalg import norm 3 np.set_printoptions(threshold=‘nan‘) 4 5 a1 = np.array([1,2,3]) 6 a2 = np.array([0,0,-3]) 7 testa = np.array([[ 1.76405235, 0.40015721, 0.97873798], 8 [ 2.2408932 , 2.2677152 , -0.57712067], 9 [ 0.95008842, 0.79873121, -0.68033952], 10 [ 0.4105985 , 0.55464207, 0.77393398]]) 11 12 testb = np.array([[ 1.76405235, 0.40015721, 0.97873798], 13 [ 2.2408932 , 2.2677152 , -0.57712067], 14 [ 0.95008842, 0.79873121, -0.68033952], 15 [ 0.4105985 , 0.55464207, 0.77393398]]) 16 dist=lambda x, y: norm(x - y, ord=1) 17 18 print np.linalg.norm([2,-1,3,-4], np.inf) # returns 2, 19 20 print np.linalg.norm(a1 - a2, ord=1) # returns 2,
Refer:
标签:nbsp thml amp ons nal inf rom ati lock
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dylancao/p/10019999.html