标签:编译 back 异步调用 col manage bubuko call fromWei div
接上一章的内容,这篇介绍 deploy相关和结果演示。
deploy一个合约的过程中,需要计算发布的消耗和nonce值。
当进行每笔交易时,发送人设定Gas Limit 和Gas Price,将 Gas Limit*Gas Price ,就得到了ETH交易佣金的成本。
nonce:以太坊要求一个账户的每笔交易有一个连续的计数。每个节点将根据计数顺序严格执行来自一个用户的交易。
app.js中有下面两个函数:
var web3 = new Web3(new Web3.providers.HttpProvider("http://localhost:8545")); function etherSpentInPendingTransactions(address, callback) { web3.currentProvider.sendAsync({ method: "txpool_content", params: [], jsonrpc: "2.0", id: new Date().getTime() }, function (error, result) { console.log(result) if(typeof(result.result.pending)!="undefined" && result.result.pending) { if(result.result.pending[address]) { var txns = result.result.pending[address]; var cost = new BigNumber(0); for(var txn in txns) { cost = cost.add((new BigNumber(parseInt(txns[txn].value))).add((new BigNumber(parseInt(txns[txn].gas))).mul(new BigNumber(parseInt(txns[txn].gasPrice))))); } callback(null, web3.fromWei(cost, "ether")); } else { callback(null, "0"); } } else { callback(null, "0"); } }) }
上面函数的流程:
1 使用sendAsync异步调用JSON PRC,调用的方法是 :txpool_content,这个方法用于查询交易池中待处理的交易,返回的结果属性有pending和queqed。想了解这个函数可以查看:https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/wiki/Management-APIs#txpool_content
2 通过返回结果的属性 pending和账户的地址获取所以交易:
var txns = result.result.pending[address];对交易的结果进行循环,累加每个交易的value和gas消耗,就是所有将要打包到下个块的交易的总消耗。
在介绍一下getNonce函数:
function getNonce(address, callback) { web3.eth.getTransactionCount(address, function(error, result){ var txnsCount = result; web3.currentProvider.sendAsync({ method: "txpool_content", params: [], jsonrpc: "2.0", id: new Date().getTime() }, function (error, result) { if(result.result.pending) { if(result.result.pending[address]) { txnsCount = txnsCount + Object.keys(result.result.pending[address]).length; callback(null, txnsCount); } else { callback(null, txnsCount); } } else { callback(null, txnsCount); } }) }) }
eth中每个交易的nonce是累加的,它是把挖出的交易总数和待定的交易总数加起来得到的。
所以对于deploy函数来说,只需要利用上面两个函数构造交易的消耗cost和nonce值然后调用sendRawTranstaction,当然还需要对交易签署,需要提供秘钥,所以界面设计也会需要账户秘钥。代码如下:
app.get("/deploy", function(req, res){
var code = req.query.code;
var arguments = JSON.parse(req.query.arguments);
var address = req.query.address;
var output = solc.compile(code, 1);
var contracts = output.contracts;
for(var contractName in contracts)
{
var abi = JSON.parse(contracts[contractName].interface);
var byteCode = contracts[contractName].bytecode;
var contract = web3.eth.contract(abi);
var data = contract.new.getData.call(null, ...arguments, {
data: byteCode
});
console.log(data);
console.log(web3.eth.defaultAccount)
var gasRequired = web3.eth.estimateGas({
from:address,
data: "0x" + data
});
web3.eth.getBalance(address, function(error, balance){
var etherAvailable = web3.fromWei(balance, "ether");
etherSpentInPendingTransactions(address, function(error, balance){
etherAvailable = etherAvailable.sub(balance)
if(etherAvailable.gte(web3.fromWei(new BigNumber(web3.eth.gasPrice).mul(gasRequired), "ether")))
{
getNonce(address, function(error, nonce){
var rawTx = {
gasPrice: web3.toHex(web3.eth.gasPrice),
gasLimit: web3.toHex(gasRequired),
from: address,
nonce: web3.toHex(nonce),
data: "0x" + data
};
var privateKey = ethereumjsUtil.toBuffer(req.query.key, ‘hex‘);
var tx = new ethereumjsTx(rawTx);
tx.sign(privateKey);
web3.eth.sendRawTransaction("0x" + tx.serialize().toString(‘hex‘), function(err, hash) {
res.send({result: {
hash: hash,
}});
});
})
}
else
{
res.send({error: "Insufficient Balance"});
}
})
})
break;
}
})
到这里基本流程已经很清晰了。具体的代码可以到git上下载:https://github.com/figo050518/deployContract
配置app.js的web3地址。
进入项目根目录 执行 npm install
node app.js 启动前端服务。
我定义的端口是7070。下面是笔者执行的截图:
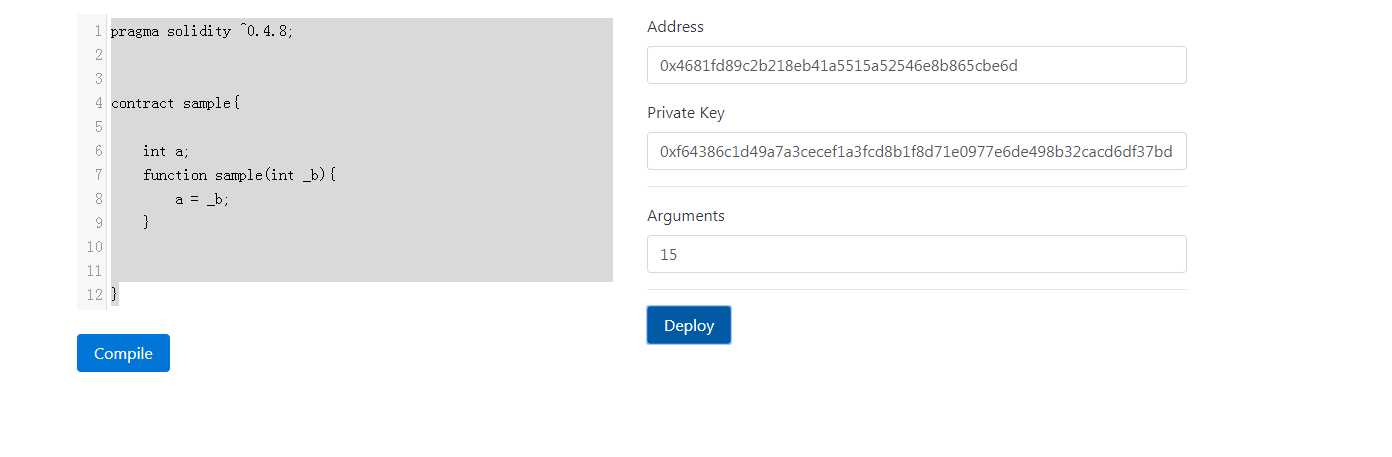
到这里就完成了一个编译 部署合约的平台,前端页面没有过多介绍,读者可以看下源码。
【以太坊开发】如何开发一个编译以太坊智能合约并且发布的平台(二)
标签:编译 back 异步调用 col manage bubuko call fromWei div
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gzhlt/p/10043113.html