标签:color capacity 分配 rod span 分析方法 vat pop 编程
提起栈相比一定会听到过这样几个关键词:后进先出,先进后出,入栈,出栈。
栈这种数据结构,数组完全可以代替其功能。
但是存在即是真理,其目的就是避免暴漏不必要的操作。
如角色一样,不同的情景或者角色拥有不同的操作权限。
那我们来了解一下栈,栈是一种线性数据结构,并且只能从一端压入或者弹出 = 添加或者修改。
基于数组实现的栈是顺序栈,基于链表实现的链式栈。
接下来我们看一下.Net 是怎么实现栈的?
注释说的很明白:这是一个基于数组实现的顺序栈,其入栈时间复杂度O(n),出栈复杂度为O(1)

// A simple stack of objects. Internally it is implemented as an array, // so Push can be O(n). Pop is O(1). [DebuggerTypeProxy(typeof(System.Collections.Stack.StackDebugView))] [DebuggerDisplay("Count = {Count}")] [System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)] [Serializable] public class Stack : ICollection, ICloneable { private Object[] _array; // Storage for stack elements [ContractPublicPropertyName("Count")] private int _size; // Number of items in the stack. private int _version; // Used to keep enumerator in sync w/ collection. [NonSerialized] private Object _syncRoot; private const int _defaultCapacity = 10; public Stack() { _array = new Object[_defaultCapacity]; _size = 0; _version = 0; }
入栈:我们也看到这个是基于数组并且支持的那个太扩容的栈,默认大小围为10,当存满之后就会两倍扩容。

// Pushes an item to the top of the stack. // public virtual void Push(Object obj) { //Contract.Ensures(Count == Contract.OldValue(Count) + 1); if (_size == _array.Length) { Object[] newArray = new Object[2*_array.Length]; Array.Copy(_array, 0, newArray, 0, _size); _array = newArray; } _array[_size++] = obj; _version++; }
正如注释中提到的,入栈时间复杂度可以达到O(n),出栈可以是O(1)
so Push can be O(n). Pop is O(1).
出栈Pop,复杂度为O(1)很好理解,
上面提到的动态栈是操作受限的数组,并且不会产生新的内存申请或者数据的搬移
我们只要是获取到最后一个,然后弹出(也就是删除)即可。
入栈Push,我们接下来分析一下出栈为什么复杂度为O(n):
前面有一篇《算法复杂度》 https://www.cnblogs.com/sunchong/p/9928293.html ,提到过:最好、最坏、平均
对于下面的入栈代码:
最好情况时间复杂度:不会有扩容和数据迁移,所以直接追加即可,复杂度为O(1)
最坏情况时间复杂度:需要扩容后并且搬移原来n个数据,然后再插入新的数据,复杂度为 O(n)
那么平均时间复杂度是多少呢?这里需要结合摊还分析法,进行复杂度分析。为什么这里要使用摊还分析法呢?
先耐心地看看其定义:
分析一个操作序列中所执行的所有操作的平均时间分析方法。
与一般的平均分析方法不同的是,它不涉及概率的分析,可以保证最坏情况下每个操作的平均性能。
总结一下摊还分析:执行的所有操作的平均时间,不扯概率。
一头雾水也不要紧,就当看明白了。就拿摊还分析来直接分析:
public virtual void Push(Object obj) { //Contract.Ensures(Count == Contract.OldValue(Count) + 1); if (_size == _array.Length)
{ Object[] newArray = new Object[2*_array.Length]; Array.Copy(_array, 0, newArray, 0, _size); _array = newArray; } _array[_size++] = obj; _version++; }
入栈的最坏情况复杂度是O(n),但是这个最坏情况时间复杂度是在n+1次插入的时候发生的,
剩下的n次是不需要扩容搬移数据,只是简单的入栈 O(1),所以均摊下来的复杂度是O(1)。
那么为什么微软的工程师在备注里写下push复杂度是O(n)?--这里指的是空间复杂度O(n)
那么站这种数据结构的应用有很多场景,其中一种就是我们的线程栈或者说函数栈。
当开启一个线程时,Windows系统为每个线程分配一个1M大小的线程栈。分配这个用来干什么呢?
存储方法中的参数和变量。趁这个机会,我们了解一下CLR的内存模型。
首先对于C#代码时如何编程机器代码的呢?
c#代码 -> 编译器 -> IL -> JIT -> CPU指令
当一个线程执行到以下方法时会有什么操作呢?
这段代码也很简单,就是在Main方法中调用了GetCode()方法,其他的都是一些临时变量。
static void Main(string[] args) { string parentCode = "PI001"; string newCode = string.Empty; newCode = GetCode(parentCode); } static string GetCode(string sourceCode) { string currentMaxCode = "001001"; string newCode = $"{sourceCode}{currentMaxCode}"; return newCode; }
首先线程会分配1M内存用于存储临时变量和参数;
进入Main方法时,会将参数和返回地址依次压栈
static void Main(string[] args)
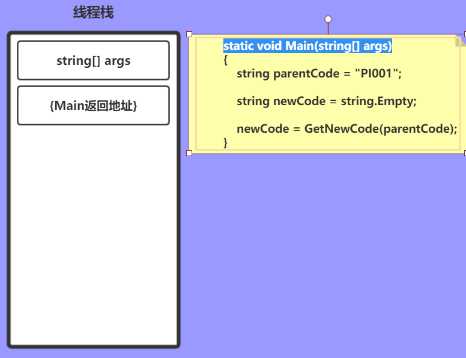
string parentCode = "PI001"; string newCode = string.Empty;
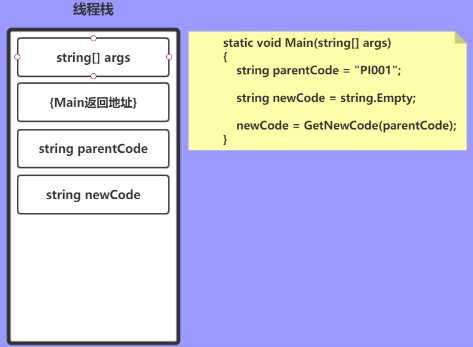
接下来开始进入到 GetCode() 方法,此时与之前一样压入参数和返回地址
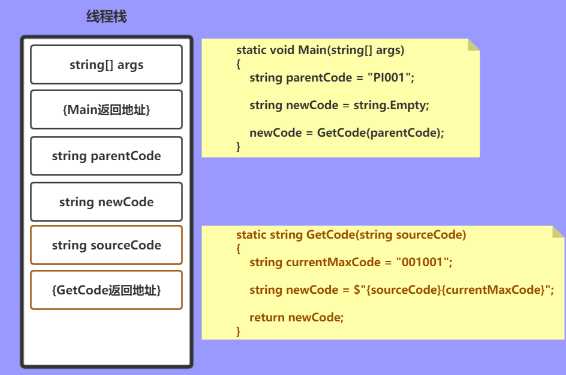
string currentMaxCode = "001001"; string newCode = $"{sourceCode}{currentMaxCode}";
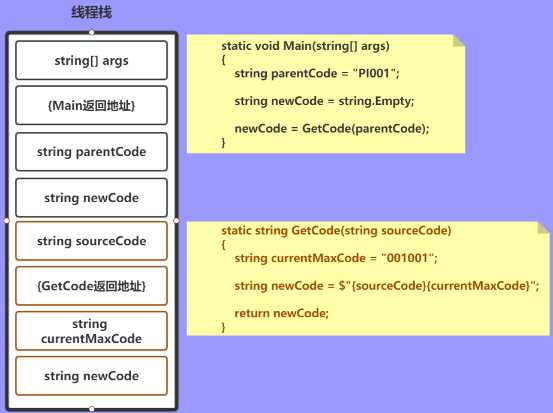
既然说到了栈,那我们不得不再说一下托管堆,再来一段代码图解:
这是父类和子类的具体代码,可以略过此处。

1 public class BaseProduct 2 { 3 public string GetCode() 4 { 5 string maxCode = "001"; 6 return maxCode; 7 } 8 9 public virtual string Trim(string source) 10 { 11 return source.Trim(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 public class Product : BaseProduct 16 { 17 private static string _type="PI"; 18 19 public override string Trim(string source) 20 { 21 return source.Replace(" ", string.Empty); 22 } 23 24 public static string GetNewCode(string parentCode) 25 { 26 string currentMaxCode = "001001001"; 27 string newCode = $"{parentCode}{currentMaxCode}"; 28 return newCode; 29 30 } 31 }
我们隐藏这些方法的具体实现,只预览他们的之间的关系:
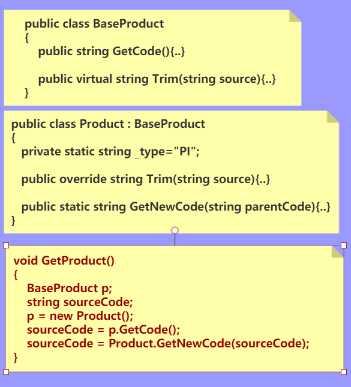
接下来,线程即将进入到下面的这个方法:
void GetProduct() { BaseProduct p; string sourceCode; p = new Product(); sourceCode = p.GetCode(); sourceCode = Product.GetNewCode(sourceCode); }
JIT在编译到此方法前会注意到这个方法所有的引用类型,
并向CLR发出通知,加载程序级,在托管对中创建相关的类型对象数据结构。
这也就是我们所能理解的静态字段为什么不是在实例化的时候创建,着其实根本上就是两个概念。
静态资源是属于类结构的,而实例资源时属于实例本身。下面的图忽略String类型。
类型对象包括:对象指针、同步块索引、静态资源、方法表
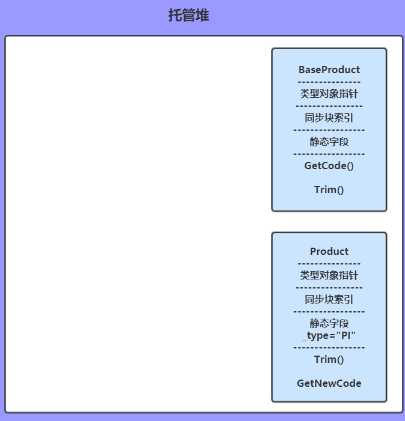
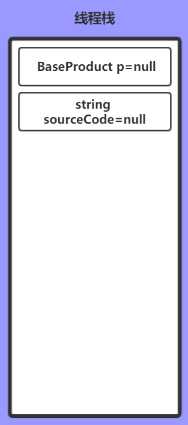
BaseProduct p; string sourceCode;
方法变量入栈,并且引用类型初始化为null
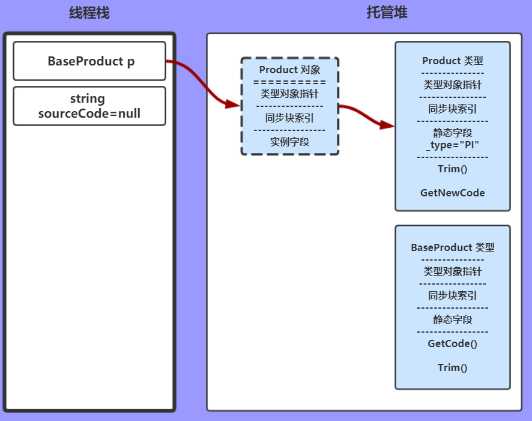
p = new Product();
实例化Product ,托管堆创建Product对象,并将这个对象的指针指向Product类型。
将线程栈中的变量p指针,指向新创建的Product对象。
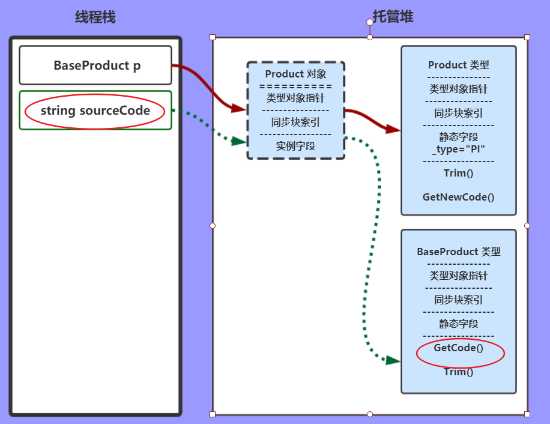
sourceCode = p.GetCode();
JIT找到这个变量p的Product对象,再找到对应的Product类型,表中找到此方法GetCode();
当然这个方法实际是父类的方法,所以JIT会一直向上找,直到找到为止。
图中是个虚拟路线,计算结果赋值给 string sourceCode
sourceCode = Product.GetNewCode(sourceCode);
和上一步类似,只不过这次是调用的静态方法。发出类型Product,静态方法是GetNewCode()
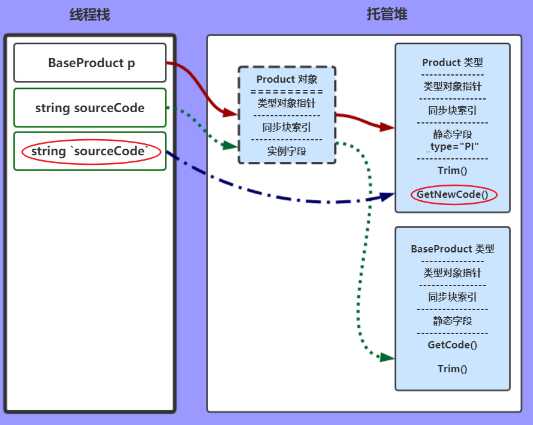
以上内容就是 JIT、CLR、线程栈、托管堆的一些运行时关系。
大家可以转载此链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunchong/p/10011657.html
大家可以关注这个公众号~~~~~


标签:color capacity 分配 rod span 分析方法 vat pop 编程
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunchong/p/10011657.html