标签:分发 create actor info top [] html consumer main
上篇我们学习了rabbitmq的作用以及直连交换机的代码实现,这篇我们继续看如何用代码实现扇形交换机和主题交换机
/** * 生产者 */ public class LogProducer { //交换机名称 public final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs"; public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); Connection connection = null; Channel channel = null; try { connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME,"fanout"); for (int i = 0; i < 5;i++){ String message = "Hello Rabbit " + i; channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME,"",null,message.getBytes()); System.out.println("EmitLog send message " + message); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { channel.close(); connection.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
Consumer1
/** * 消费者 */ public class Consumer1 { public final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs"; public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); Connection connection = null; Channel channel = null; try { connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); channel = connection.createChannel(); String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); //声明一个交换机,发布模式为fanout-扇形 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME,"fanout"); //将队列和交换机绑定起来,因为扇形交换机和路由键无关,所以这里路由键设为空字符串即可 channel.queueBind(queueName,EXCHANGE_NAME,""); QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel); //当连接断开时,队列会自动被删除 channel.basicConsume(queueName,true,consumer); System.out.println("ReceiveLogTopic1 Waitting for message"); while (true){ QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery(); String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8"); System.out.println("ReceiveLogTopic1 receives message " + message); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Cosumer2
/** * 消费者2 */ public class Consumer2 { public final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs"; public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); Connection connection = null; Channel channel = null; try { connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); channel = connection.createChannel(); String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); //声明一个交换机,发布模式为fanout-扇形 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME,"fanout"); //将队列和交换机绑定起来,因为扇形交换机和路由键无关,所以这里路由键设为空字符串即可 channel.queueBind(queueName,EXCHANGE_NAME,""); QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel); //当连接断开时,队列会自动被删除 channel.basicConsume(queueName,true,consumer); System.out.println("ReceiveLog2 Waitting for message"); while (true){ QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery(); String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8"); System.out.println("ReceiveLog2 receives message " + message); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
先启动Consumer1,Consumer2,再启动LogProducer。结果如下:
LogProducer:
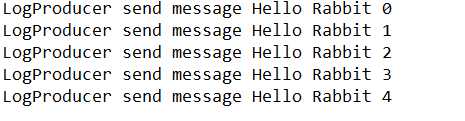
Consumer1:

Consumer2:

从输出结果中我们可以看出,扇形交换机所接受到的消息会被分发到所有绑定到该交换机上的队列中,和路由键无关。
/** * 生产者 */ public class Producer { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs"; // 路由关键字 private static final String[] routingKeys = new String[]{ "quick.orange.rabbit", "lazy.orange.elephant", "quick.orange.fox", "lazy.brown.fox", "quick.brown.fox", "quick.orange.male.rabbit", "lazy.orange.male.rabbit"}; public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); Connection connection = null; Channel channel = null; try { connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic"); //循环发送具有不同routing key的message for (String routingKey : routingKeys) { String message = routingKey + "--->biu~"; channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, routingKey, null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("Producer -> routingkey: " + routingKey + ", send message " + message); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { channel.close(); connection.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
Consumer1
/** * 消费者1 */ public class Consumer1 { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs"; // 路由关键字 private static final String[] routingKeys = new String[]{"*.orange.*"}; public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); Connection connection = null; Channel channel = null; try { connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明队列 String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic"); //将队列与交换器用routingkey绑定起来 for (String routingKey : routingKeys) { channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, routingKey); System.out.println("Consumer1 -> queue: " + queueName + ", exchange_name: " + EXCHANGE_NAME + ", routingKey: " + routingKey); } //接收消息 QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel); channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer); System.out.println("Consumer1 waitting for message"); while (true){ QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery(); String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8"); Envelope envelope = delivery.getEnvelope(); String routingKey = envelope.getRoutingKey(); System.out.println("Consumer1 receive message " + message + ", routingKey: " + routingKey); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Consumer2
/** * 消费者2 */ public class Consumer2 { private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs"; // 路由关键字 private static final String[] routingKeys = new String[]{"*.*.rabbit", "lazy.#"}; public static void main(String[] args) { ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(); Connection connection = null; Channel channel = null; try { connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明队列 String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic"); //将队列与交换器用routingkey绑定起来 for (String routingKey : routingKeys) { channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, routingKey); System.out.println("Consumer2 -> queue: " + queueName + ", exchange_name: " + EXCHANGE_NAME + ", routingKey: " + routingKey); } //接收消息 QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel); channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer); System.out.println("Consumer2 waitting for message"); while (true){ QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery(); String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8"); Envelope envelope = delivery.getEnvelope(); String routingKey = envelope.getRoutingKey(); System.out.println("Consumer2 receive message " + message + ", routingKey: " + routingKey); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
同样先运行消费者,再运行生产者,结果如下:
Producer:

Consumer1:
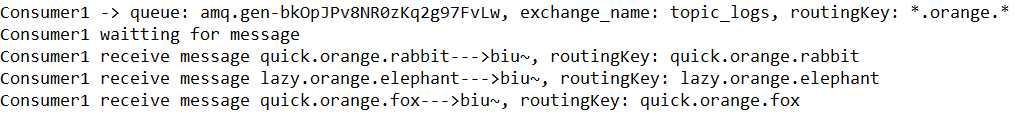
Consumer2:
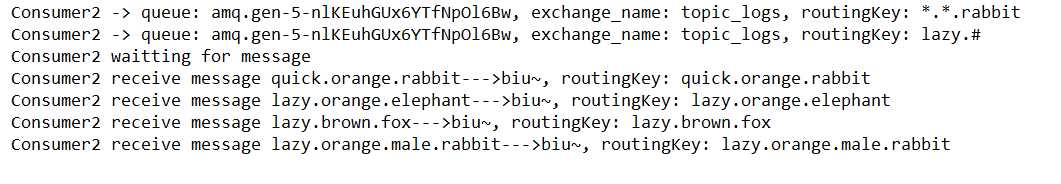
由运行结果我们可以看到:消息被交换机按照模式路由键的规则路由到相应的队列中。
rabbitmq学习(三):rabbitmq之扇形交换机、主题交换机
标签:分发 create actor info top [] html consumer main
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wutianqi/p/10055160.html