标签:sum first spl ted select sklearn src elf ural
Step 1, donwload the Miniconda and installing it on your computer.
Beacause some of classmates dont have a conda environment in their computer, hence we need to explain how to install it.
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/miniconda/
Step 2, create a conda virtual envriomment
In this ariticle, we assume that there is a CPU version of PyTorch is going to be installed. To specifically distinguish CPU version and GPU version, we`re going to create a virtual environment with CPU version of PyTorch.
In the Conda Prompt run the following commands:
conda create -n PyTorch-CPU pipStep 3, install PyTorch
On the website of PyTorch(https://pytorch.org/), there is a guidance on the page. To chose the most appropriate options(e.g. as the follow figure).
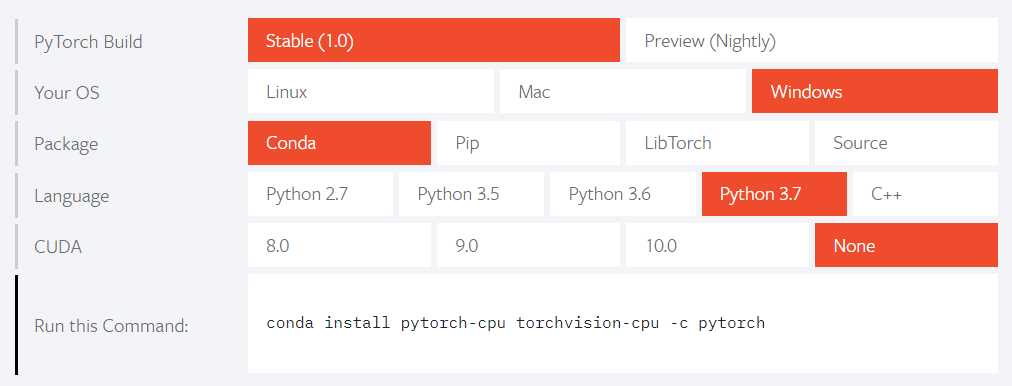
In the Conda Prompt run the following commands:
activate PyTorh-CPU
conda install pytorch-cpu torchvision-cpu -c pytorchCongratulations, installation of PyTorch is complete!
Before we start ours building. We have to access the dataset and clean it.
Here we have accessed 西瓜数据集3.0. And we convert the character-described features to numeric.
# encoding:utf8
# 西瓜3.0 数据集
waterMelons = [
# 1
[‘青绿‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘凹陷‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 2
[‘乌黑‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘沉闷‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘凹陷‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 3
[‘乌黑‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘凹陷‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 4
[‘青绿‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘沉闷‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘凹陷‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 5
[‘浅白‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘凹陷‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 6
[‘青绿‘, ‘稍蜷‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘稍凹‘, ‘软粘‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 7
[‘乌黑‘, ‘稍蜷‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘稍糊‘, ‘稍凹‘, ‘软粘‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 8
[‘乌黑‘, ‘稍蜷‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘稍凹‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘好瓜‘],
# 9
[‘乌黑‘, ‘稍蜷‘, ‘沉闷‘, ‘稍糊‘, ‘稍凹‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 10
[‘青绿‘, ‘硬挺‘, ‘清脆‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘平坦‘, ‘软粘‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 11
[‘浅白‘, ‘硬挺‘, ‘清脆‘, ‘模糊‘, ‘平坦‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 12
[‘浅白‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘模糊‘, ‘平坦‘, ‘软粘‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 13
[‘青绿‘, ‘稍蜷‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘稍糊‘, ‘凹陷‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 14
[‘浅白‘, ‘稍蜷‘, ‘沉闷‘, ‘稍糊‘, ‘凹陷‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 15
[‘乌黑‘, ‘稍蜷‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘清晰‘, ‘稍凹‘, ‘软粘‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 16
[‘浅白‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘浊响‘, ‘模糊‘, ‘平坦‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘坏瓜‘],
# 17
[‘青绿‘, ‘蜷缩‘, ‘沉闷‘, ‘稍糊‘, ‘稍凹‘, ‘硬滑‘, ‘坏瓜‘]
]
features = list() # [[青绿, 乌黑, 浅白], [蜷缩, 硬挺...], ...]
def numeric(data):
l = list()
for i,s in enumerate(data):
val = features[i].index(s)
l.append(val)
return l
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
for melon in waterMelons:
for i, feature in enumerate(melon):
try:
if feature not in features[i]:
features[i].append(feature)
except IndexError:
features.append([feature])
f = open(‘data/WaterMelon.txt‘, encoding=‘utf8‘, mode=‘w‘)
for melon in waterMelons:
val = numeric(melon)
f.write("%s\n" % val)
Here we implement a neural network with input layer and log softmax layer.
There are 12 parameters need to be trained:
\[
input \times hiddens \times output = parameters\6 \times 2 = 12
\]
# encoding:utf8
import torch
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.layer = torch.nn.Linear(6, 2)
self.softmax = torch.nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer(x)
out = self.softmax(out)
return out
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
x, y = list(), list()
with open(‘data/WaterMelon.txt‘, encoding=‘utf8‘) as f:
for line in f:
l = eval(line.strip())
x.append(l[:-1])
y.append(l[-1])
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=33)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = torch.Tensor(x_train), torch.Tensor(x_test), torch.Tensor(y_train).long(), torch.Tensor(y_test).long()
model = Model()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
criticism = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# train
for epoch in range(500):
out = model(x_train)
loss = criticism(out, y_train)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# test
y_pred = model(x_test)
_, predicted = torch.max(y_pred, 1)
acc = torch.sum(y_test == predicted ).numpy() / len(x_test)
print(acc)
We got the accuracy 0.8, sometimes we got 1.
LOL!
PyTorch in Action: A Step by Step Tutorial
标签:sum first spl ted select sklearn src elf ural
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/fengyubo/p/10120667.html