标签:traversal rap code bst poi eem define 接口 bubuko
环境:C++ 11 + win10
IDE:Clion 2018.3
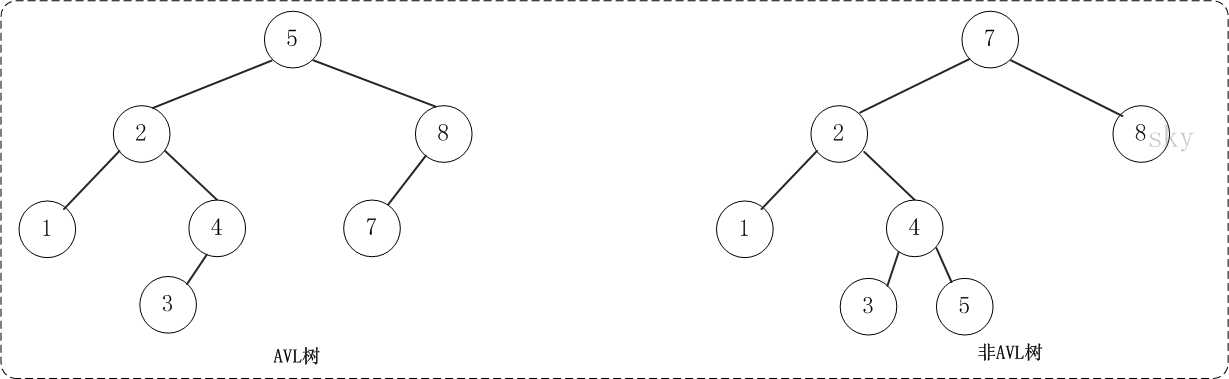
AVL平衡树是在BST二叉查找树的基础上添加了平衡机制。
我们把平衡的BST认为是任一节点的左子树和右子树的高度差为-1,0,1中的一种情况,即不存在相差两层及以上。
所谓平衡机制就是BST在理想情况下搜索复杂度是o(logn)
但是如果在(存在某一节点,该节点的左子树的高度与右子树的高度差>1)这种状况下,复杂度会超过o(logn)
举个极端的例子如加入1,2,3,4,BST就退化为一个线性的链表,复杂度变成了o(n)
为了避免这种情况,我们在BST中引入平衡操作(旋转操作),使得BST始终不存在左右子树超过1高度差的节点。
本次代码基于我的另一篇博客的基础之上,有需要可以翻看 https://www.cnblogs.com/cyrio/p/10118132.html
平衡机制主要通过反转完成,经过归纳,可能出现以下四种不平衡的情况:LL、LR、RL、RR
L=left R=right
我们将不平衡点设为X点,以LR为例,第一个L表示X点的左子树比右子树层数多(>1),第二个R表示多出的那部分在X点的左子树的右子树。(不管他是在X的左子树的右子树的左右哪边,都称为LR)
如图:
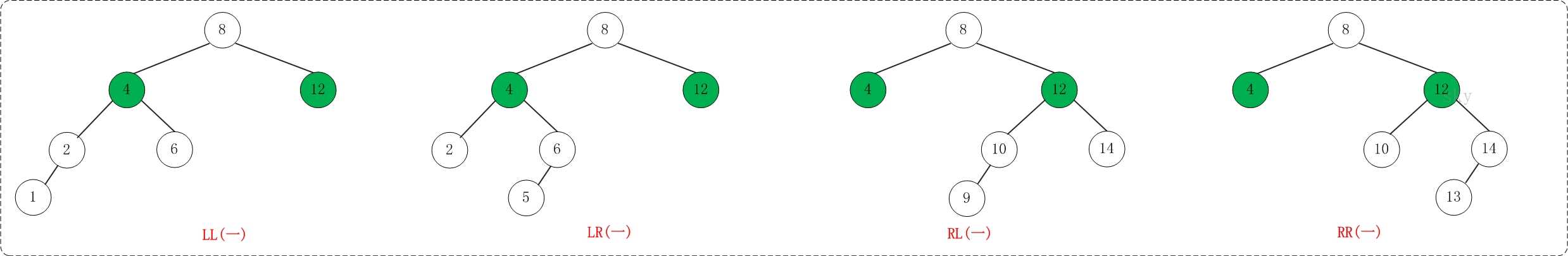
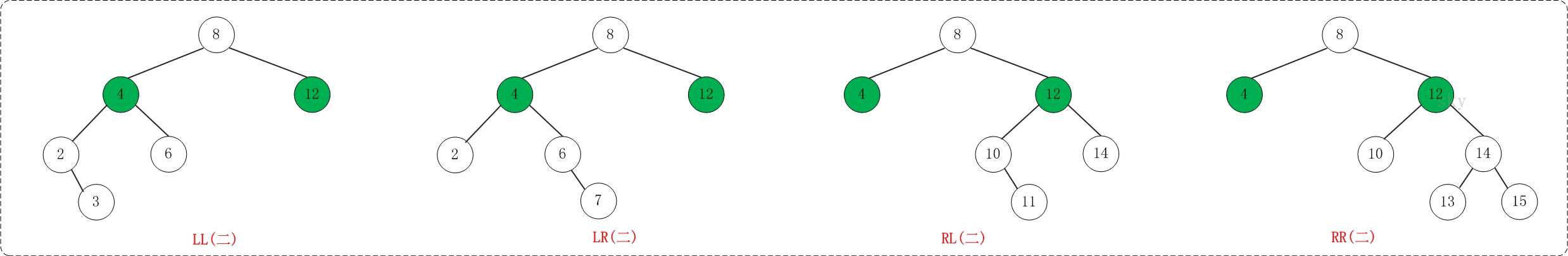
接下来我们以LL、LR、RR、RL四种情况讨论。
1、LL:
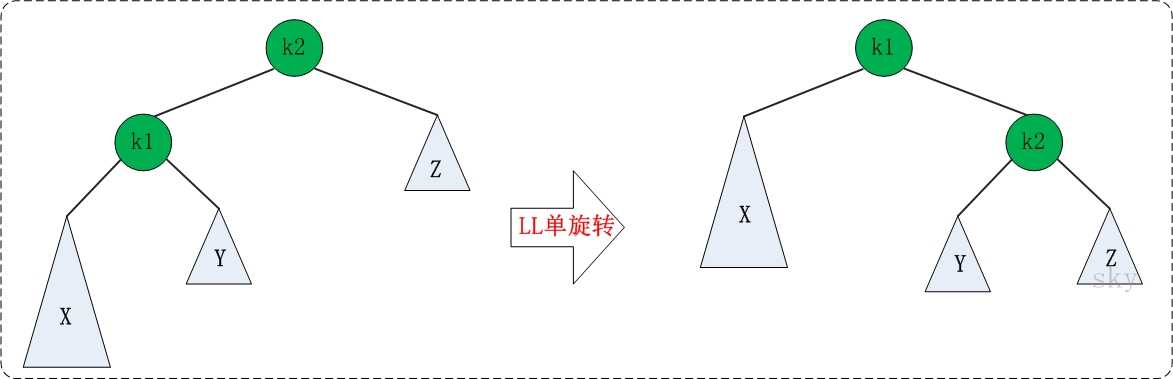
通俗的讲就是把K2从K1那扯下来,然后把Y移到K2的左子树,最后把K2移到K1的右子树。
2、RR:
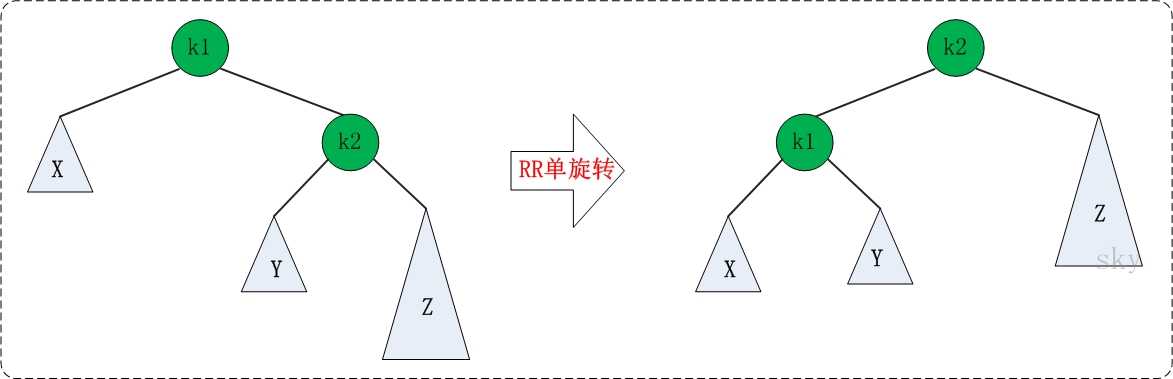
与LL同理,把K1先扯下来,再把Y接到K1的右侧,再把K1作为左子树接到K2。
3、LR:
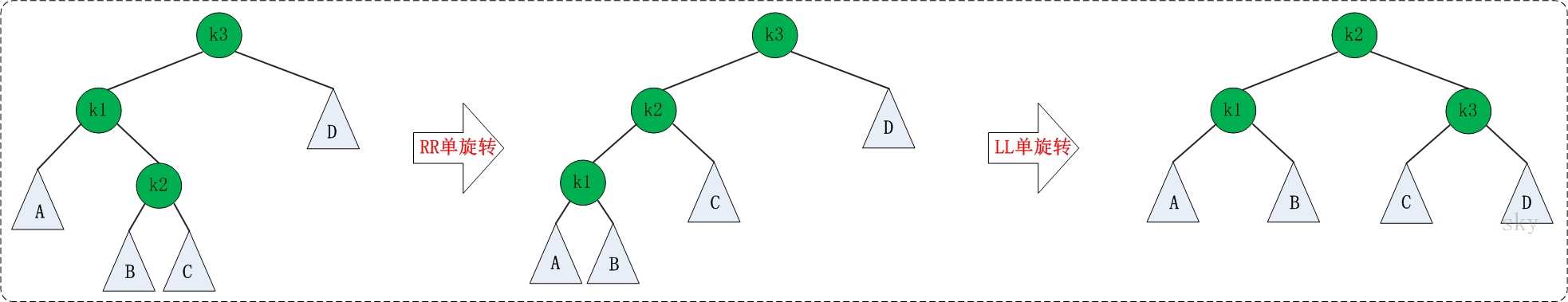
LR需要先做一次RR再做一次LL:
先把K1从K2那扯下来,让K2和K3连,然后把B作为K1的右子树,再把K1连到K2的左子树上。
然后再做LL,把K3从K2上面扯下来,让C作为K3的左子树,再把K3连到K2的右子树。
4、RL:
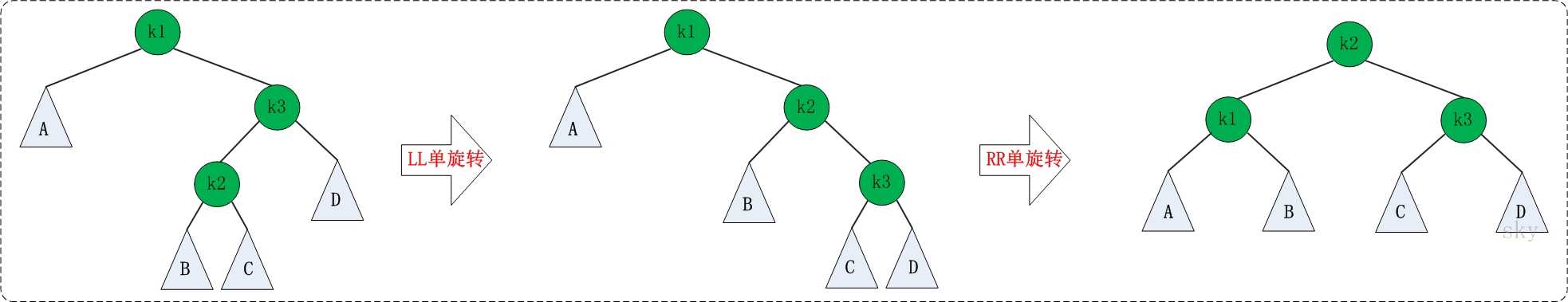
先LL再RR,与LR同理。
以上是主要思想的分析,除了旋转操作,我们还需要添加新的方法:
1、求树的高度:height方法
2、求某节点的左子树和右子树的高度差 :Diff方法
3、一个对整个树进行判断,对里面的X节点进行对应操作:Balance方法
同时AVL中的Insert(插入某一节点)的方法与BST中也略有不同,需要注意的是AVL种的__Insert(PS:带"__"的表示私有内部接口)的参数中第一个为bstNode<T> * & root (需要&引用)
具体代码如下:(此代码为完整代码,可以直接复制进自己的项目查看效果)
myBST.h
#ifndef TEST1_MYBST_H #define TEST1_MYBST_H #include <iomanip> #include "bstNode.h" #include <vector> #include <deque> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; template <typename T> class myBST{ private: bstNode<T> * root = nullptr; bstNode<T> * __search(bstNode<T> * root , const T &key){ if (nullptr == root) return nullptr; if (key == root->data) return root; else if (key < root->data) return __search(root->left, key); else return __search(root->right, key); } //查找关键字是否存在 bstNode<T> * __treeMin(bstNode<T> * root , bstNode<T> * &parent){ bstNode<T> * curr = root; while(curr->left!= nullptr){ parent = curr; curr = curr->left; } return curr; } //返回最小节点(一路向左) bstNode<T> * __Insert(bstNode<T> * &root, const T &key){ if (nullptr == root) { root = new bstNode<T>(key); return root; }//递归返回条件 else if (key < root->data) { root->left = __Insert(root->left,key);//递归左子树 //balance operation root = __Balance(root);//平衡操作包含了四种旋转 } else if (key>root->data) { root->right = __Insert(root->right,key);//递归右子树 //balance operation root = __Balance(root);//平衡操作包含了四种旋转 } return root; } //插入指定值 bool __Delete(const T &key){ bool found = false;//存储有没有找到key的变量 if(isEmpty()){ cerr<<"BST为空"<<endl; return false; } bstNode<T> * curr = root; bstNode<T> * parrent = nullptr; while(curr!= nullptr) { if (key == curr->data) { found = true; break; } else { parrent = curr; if (key < curr->data) curr = curr->left; else curr = curr->right; } } if(!found){ cerr<<"未找到key!"<<endl; return false; } if (parrent == nullptr){//删除根节点 root = nullptr; delete(curr); return true; } /* 删除的节点有三种可能: 1、叶子结点 2、一个孩子的节点 3、两个孩子的节点 */ if (__isLeaf(curr)){ //删除的点是叶子结点 if(parrent->left==curr) parrent->left= nullptr; else parrent->right= nullptr; delete(curr); return true; } else if(__isNodeWithTwoChild(curr)){ //是两个孩子的节点 //以当前右子树中的最小值取代他 bstNode<T> * parrent = curr; bstNode<T> * tmp = __treeMin(curr->right,parrent); curr->data = tmp->data; if(parrent->right==tmp) parrent->right== nullptr; else parrent->left== nullptr; delete(tmp); return true; } else{ //只有一个孩子的节点 if(curr->left!= nullptr){ if(curr->left == curr){ parrent->left=curr->left; delete(curr); return true; } else{ parrent->right=curr->right; delete(curr); return true; } } if(curr->right!= nullptr){ if(curr->left == curr){ parrent->left=curr->left; delete(curr); return true; } else{ parrent->right=curr->right; delete(curr); return true; } } } return false; } //删除指定值 bool __isLeaf(bstNode<T> * const & root){ if(root->left== nullptr && root->right== nullptr) return true; else return false; }//判断是否是叶子节点 bool __isNodeWithTwoChild(bstNode<T> * const & root){ if(root->left!= nullptr && root->right!= nullptr) return true; else return false; }//判断是否有两个孩子 void __InorderTraversal(bstNode<T> *root,std::vector<int>&result){ if(nullptr == root) return; __InorderTraversal(root->left,result); cout<<root->data<<" "; result.push_back(root->data); __InorderTraversal(root->right,result); }//中序遍历 void __PreorderTraversal(bstNode<T> *root,std::vector<int>&result){ if(nullptr == root) return; cout<<root->data<<" "; result.push_back(root->data); __InorderTraversal(root->left,result); __InorderTraversal(root->right,result); }//前序遍历 void __PostorderTraversal(bstNode<T> *root,std::vector<int>&result){ if(nullptr == root) return; __InorderTraversal(root->left,result); __InorderTraversal(root->right,result); cout<<root->data<<" "; result.push_back(root->data); }//后序遍历 void __DeleteAllNodes(bstNode<T> *root){ if (root == nullptr) return; __DeleteAllNodes(root->left); __DeleteAllNodes(root->right); __Delete(root->data); }//删除所有节点 void __BFTraversal(vector<T>&result) { deque<bstNode<T> *> TQueue; bstNode<T> *pointer = root; if (pointer != nullptr) { TQueue.push_back(pointer); } while (!TQueue.empty()) { pointer = TQueue.front(); TQueue.pop_front(); cout << pointer->data << " "; result.push_back(pointer->data); if (pointer->left != nullptr) TQueue.push_back(pointer->left); if (pointer->right != nullptr) TQueue.push_back(pointer->right); } } //广度搜索来进行周游 void __Graph(int indent,bstNode<T>* root){ if(root != 0){ __Graph(indent + 8, root->right); cout<<setw(indent)<<" "<<root->data<<endl; __Graph(indent + 8, root->left); } } //横着画图的内部接口 bstNode<T> * __GetRoot(){ return root; } //返回根节点的内部接口 //以下为AVL平衡树新加的方法 int __height(const bstNode<T>* root){ if(root == nullptr){ return 0; } return max(__height(root->left),__height(root->right))+1; } //求树的高度 int __diff(const bstNode<T>* root){ return __height(root->left)-__height(root->right); } //求节点的高度差(平衡因子) bstNode<T> * __ll__Rotation(bstNode<T> * root){ bstNode<T> * tmp; tmp = root->left; root->left = tmp->right; tmp->right = root; return tmp; } //单旋转-左左 bstNode<T> * __rr__Rotation(bstNode<T> * root){ bstNode<T> * tmp; tmp = root->right; root->right = tmp->left; tmp->left = root; return tmp; } //单旋转-右右 bstNode<T> * __lr__Rotation(bstNode<T> * root){ bstNode<T> * tmp; tmp = root->left; root->left = __rr__Rotation(tmp); return __ll__Rotation(root); } //双旋转-左右型,先右后左转(注意此处相反) bstNode<T> * __rl__Rotation(bstNode<T> * root){ bstNode<T> * tmp; tmp = root->right; root->right = __ll__Rotation(tmp); return __rr__Rotation(root); } //双旋转-右左型,先左后右转 bstNode<T> * __Balance(bstNode<T> * root){ int balanceFactor = __diff(root);//__diff用来计算平衡因子(左右子树高度差) if (balanceFactor > 1)//左子树高于右子树 { if (__diff(root->left) > 0)//左左外侧 root=__ll__Rotation(root); else//左右内侧 root=__lr__Rotation(root); } else if (balanceFactor < -1)//右子树高于左子树 { if (__diff(root->right) > 0)//右左内侧 root=__rl__Rotation(root); else//右右外侧 root=__rr__Rotation(root); } return root; } //平衡的内部操作 public: myBST(){ root = nullptr; } //默认构造 myBST(vector<T> arr){ root = nullptr; for(int i =0;i<(T)arr.size();i++){ Insert(arr[i]); } } myBST(T * arr,int len){ root = nullptr; for(int i =0;i<len;i++){ __Insert(*(arr+i)); } } ~myBST(){ bstNode<T> * curr = root; __DeleteAllNodes(curr); }//析构 bool isEmpty() const{ return root == nullptr; }//判断树空 bool search(const T &key){ bstNode<T> * temp = __search(root, key); return (temp == nullptr) ? false : true; }//查找关键字是否存在的对外接口 bool Insert(const T &key){ return __Insert(root,key); }//插入节点的外部接口 bool Delete(const T &key){ return __Delete(key); }//删除节点的外部接口 void InorderTraversal(vector<T>&result){ __InorderTraversal(root, result); }//中序遍历的外部接口 void PreorderTraversal(vector<T>&result){ __PreorderTraversal(root, result); }//前序遍历的外部接口 void PostorderTraversal(vector<T>&result){ __PostorderTraversal(root, result); }//后序遍历的外部接口 void BFTraversal(vector<T>&result){ return __BFTraversal(result); } //广度搜索外部接口 void Graph(int indent,bstNode<T>* root){ return __Graph(indent,root); } //横着画图的外部接口 bstNode<T> * GetRoot(){ return __GetRoot(); } //返回根节点的外部接口 }; #endif //TEST1_MYBST_H
bstNode.h
#ifndef TEST1_BSTNODE_H #define TEST1_BSTNODE_H template <typename T> class bstNode{ public: T data; bstNode* left; bstNode* right; bstNode(){ data = 0; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } bstNode(T val){ data = val; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; #endif //TEST1_BSTNODE_H
main.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "myBST.h" #include "bstNode.h" using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> in = {7,6,5,13,17,22,10,3,2,1}; myBST<int> bst(in); bst.Delete(5); bst.Insert(4); bool found = bst.search(4); if(!found) cout<<"not found!"<<endl; else cout<<"found!"<<endl; vector<int> result; cout<<"InorderTravelsal: "; bst.InorderTraversal(result); cout<<endl<<"PreorderTravelsal: "; bst.PreorderTraversal(result); cout<<endl<<"PostorderTraversal: "; bst.PostorderTraversal(result); cout<<endl<<"BFTraversal: "; bst.BFTraversal(result); cout<<endl<<"Graph:"<<endl; bstNode<int>* pointer = bst.GetRoot(); bst.Graph(0,pointer); return 0; }
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangxiao93/article/details/51459743
标签:traversal rap code bst poi eem define 接口 bubuko
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cyrio/p/10125546.html