标签:pmu 预测 定义 改变 mit vuejs getter 开发环境 apm
当我们的应用遇到多个组件共享状态时,会需要多个组件依赖于同一状态抑或是来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态。以前的解决办法:
a.将数据以及操作数据的行为都定义在父组件;
b.将数据以及操作数据的行为传递给需要的各个子组件(有可能需要多级传递)
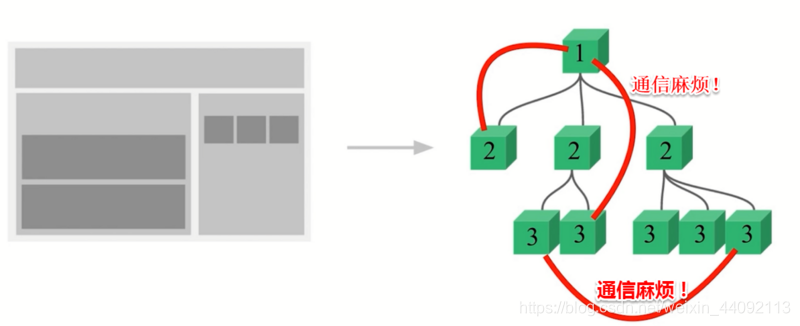
传参的方法对于多层嵌套的组件将会非常繁琐,并且对于兄弟组件间的状态传递无能为力。在搭建下面页面时,你可能会对 vue 组件之间的通信感到崩溃 ,特别是非父子组件之间通信。此时就应该使用vuex,轻松可以搞定组件间通信问题。
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。这里的关键在于集中式存储管理。简单来说,对 vue 应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写)。
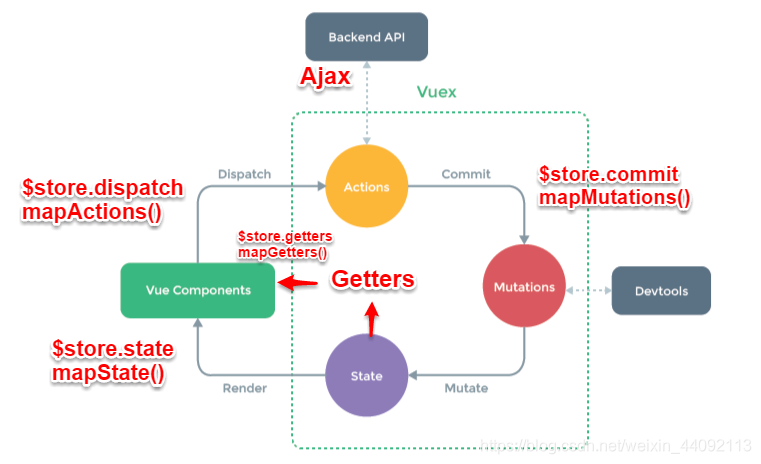
Vuex实现了一个单向数据流,在全局拥有一个State存放数据,当组件要更改State中的数据时,必须通过Mutation进行,Mutation同时提供了订阅者模式供外部插件调用获取State数据的更新。而当所有异步操作(常见于调用后端接口异步获取更新数据)或批量的同步操作需要走Action,但Action也是无法直接修改State的,还是需要通过Mutation来修改State的数据。最后,根据State的变化,渲染到视图上。
$store.dispatch(‘action 名称‘, data1)来触发。然后由commit()来触发mutation的调用 , 间接更新 state。负责处理Vue Components接收到的所有交互行为。包含同步/异步操作,支持多个同名方法,按照注册的顺序依次触发。向后台API请求的操作就在这个模块中进行,包括触发其他action以及提交mutation的操作。该模块提供了Promise的封装,以支持action的链式触发。commit(‘mutation 名称‘)来触发。是Vuex修改state的唯一推荐方法。该方法只能进行同步操作,且方法名只能全局唯一。操作之中会有一些hook暴露出来,以进行state的监控等。虽然 Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,但也附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。
如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex,因为使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。一个简单的 global event bus 就足够您所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
首先要安装vue-cli脚手架,对于大陆用户,建议将npm的注册表源设置为国内的镜像(淘宝镜像),可以大幅提升安装速度。
npm config set registry https://[registry.npm.taobao.org](http://registry.npm.taobao.org/)
npm config get registry//配置后可通过下面方式来验证是否成功
npm install -g cnpm --registry=[https://registry](https://registry/).npm.taobao.org
//cnpm安装脚手架
cnpm install -g vue-cli
vue init webpack my-vue
cd my-vue
cnpm install
cnpm run dev脚手架安装好后,再安装vuex
cnpm install vuex --save### 1.如何通过Vue来实现如下效果?

这个小demo很容易用vue实现,核心代码如下:
<div class="hello">
<p>click {{count}} times,count is {{evenOrOdd}}</p>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<button @click="incrementIfOdd">increment if odd</button>
<button @click="incrementAsync">increment async</button>
</div>
......
export default {
name: "HelloWorld",
data() {
return {
count: 0
};
},
computed: {
evenOrOdd() {
return this.count % 2 === 0 ? "偶数" : "奇数";
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.count = this.count + 1;
},
decrement() {
this.count = this.count - 1;
},
// 只有是奇数才加1
incrementIfOdd() {
if (this.count % 2 === 1) {
this.count = this.count + 1;
}
},
// 过两秒才加1
incrementAsync() {
setInterval(() => {
this.count = this.count + 1;
}, 2000);
}
}
}
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {// 包含了多个直接更新state函数的对象
INCREMENT(state) {
state.count = state.count + 1;
},
DECREMENT(state) {
state.count = state.count - 1;
}
},
getters: { // 当读取属性值时自动调用并返回属性值
evenOrOdd(state) {
return state.count % 2 === 0 ? "偶数" : "奇数";
}
},
actions: { // 包含了多个对应事件回调函数的对象
incrementIfOdd({ commit, state }) { // 带条件的action
if (state.count % 2 === 1) {
commit('INCREMENT')
}
},
incrementAsync({ commit }) { //异步的action
setInterval(() => {
commit('INCREMENT')
}, 2000);
}
}
})
export default store //用export default 封装代码,让外部可以引用
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,//注册上vuex的store: 所有组件对象都多一个属性$store
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
<template>
<div class="hello">
<p>click {{count}} times,count is {{evenOrOdd}}</p>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<button @click="incrementIfOdd">increment if odd</button>
<button @click="incrementAsync">increment async</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "HelloWorld",
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count;
},
evenOrOdd() {
return this.$store.getters.evenOrOdd;
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.$store.commit("INCREMENT");
},
decrement() {
this.$store.commit("DECREMENT");
},
// 只有是奇数才加1
incrementIfOdd() {
this.$store.dispatch("incrementIfOdd"); //触发store中对应的action调用
},
// 过两秒才加1
incrementAsync() {
this.$store.dispatch("incrementAsync");
}
}
};
</script>由于 store 中的状态是响应式的,当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。在组件中调用 store 中的状态简单到仅需要在计算属性中返回即可。改变store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutations。
import { mapActions, mapGetters, mapState, mapMutations } from "vuex";
...
computed: {
...mapState(["count"]),
...mapGetters(["evenOrOdd"])
}
methods: {
...mapActions(["incrementIfOdd", "incrementAsync"]),
...mapMutations(["increment", "decrement"])
}有点必须要注意:HelloWorld.vue文件中increment函数名称要跟store.js文件mutations中一致,才可以写成 ...mapMutations(["increment", "decrement"]),同样的道理,incrementIfOdd和incrementAsync也要和store.js文件actions保持一致。
先store.js文件里给add方法加上一个参数n
mutations: {
INCREMENT(state,n) {
state.count+=n;
},
DECREMENT(state){
state.count--;
}
}然后在HelloWorld.vue里修改按钮的commit( )方法传递的参数
increment() {
return this.$store.commit("INCREMENT",2);
},
decrement() {
return this.$store.commit("DECREMENT");
}getters从表面是获得的意思,可以把他看作在获取数据之前进行的一种再编辑,相当于对数据的一个过滤和加工。getters就像计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
例如:要对store.js文件中的count进行操作,在它输出前,给它加上100。
首先要在store.js里Vuex.Store()里引入getters
getters:{
count:state=>state.count+=100
}然后在HelloWorld.vue中对computed进行配置,在vue 的构造器里边只能有一个computed属性,如果你写多个,只有最后一个computed属性可用,所以要用展开运算符”…”对上节写的computed属性进行一个改造。
computed: {
...mapGetters(["count"])
}actions和上面的Mutations功能基本一样,不同点是,actions是异步的改变state状态,而Mutations是同步改变状态。
同步的意义在于这样每一个 mutation 执行完成后都可以对应到一个新的状态(和 reducer 一样),这样 devtools 就可以打个 snapshot 存下来,然后就可以随便 time-travel 了。如果你开着 devtool 调用一个异步的 action,你可以清楚地看到它所调用的 mutation 是何时被记录下来的,并且可以立刻查看它们对应的状态----尤雨溪
ps:如果想访问源代码,请猛戳git地址
如果觉得文章对你有些许帮助,欢迎在我的GitHub博客点赞和关注,感激不尽!
来源:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016768961
标签:pmu 预测 定义 改变 mit vuejs getter 开发环境 apm
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/datiangou/p/10126821.html