标签:sum 迭代 blog ++ 记录 name 就是 terminal 名称
jdk8出来日子不短了,jdk11都出来了,不过用的最多的不过是1.5罢了。
今年终于鼓起勇气认真对待它,在18年记录下学习stream,画上一个圆。
Java8中有两大最为重要的改变。第一个是Lambda 表达式;另外一个则是Stream API(java.util.stream.*)。
说说stream吧。前提得有lambda的基础。
Stream 是Java8 中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以指定你希望对集合进行的操作,可以执行非常复杂的查找、过滤和映射数据等操作。使用Stream API 对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用SQL 执行的数据库查询。也可以使用Stream API 来并行执行操作。简而言之,Stream API 提供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式。
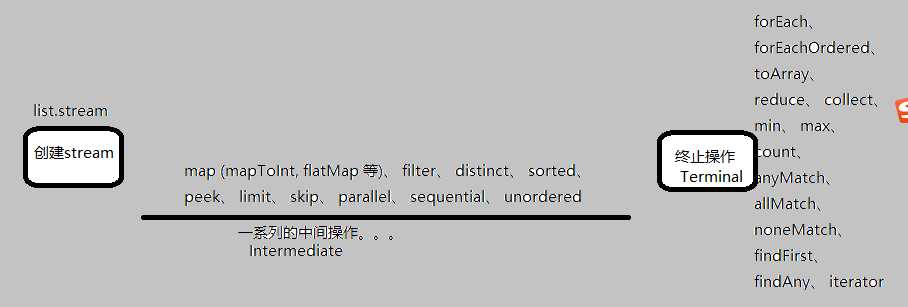
对stream的操作分为三类。
流程如下图
虽然大部分情况下stream是容器调用Collection.stream()方法得到的,但stream和collections有以下不同:
@Test
public void test5() {
List<String> collect = list.stream()
.filter(p -> p.getId() > 1)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Star::getScore))
.map(Star::getName)
.collect((Collectors.toList()));
System.out.println(collect);
}
就是这么的容易。
package com.test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import org.junit.Test;
public class DoubleColonTest {
public static void myPrint(String str) {
System.out.println("print value : " + str);
}
/**
* 不使用双冒号
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("刘德华","黎明","张学友","郭富城");
list.forEach(p -> myPrint(p));
}
/**
* 使用双冒号
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("刘德华","黎明","张学友","郭富城");
list.forEach(DoubleColonTest::myPrint);
}
/**
* 类似于双冒号
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("刘德华","黎明","张学友","郭富城");
Consumer<String> methodParam = DoubleColonTest::myPrint;
list.forEach(methodParam);
}
/**
* 类似于双冒号
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("刘德华","黎明","张学友","郭富城");
Consumer<String> methodParam = DoubleColonTest::myPrint;
list.forEach(p -> methodParam.accept(p));
}
}
完整代码实例
package com.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestStream {
List<Star> list = null;
@Before
public void before() {
list = new ArrayList<Star>() {
{
add(new Star(1, "张学友", 11.3));
add(new Star(3, "刘德华", 4.3));
add(new Star(2, "黎明", 13.3));
add(new Star(5, "郭富城", 22.3));
add(new Star(4, "范冰冰", 2.3));
}
};
}
/**
* 遍历方式
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("第一种---------");
for (Star Star : list) {
System.out.println(Star);
}
System.out.println("第二种---------");
list.forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
System.out.println("第三种---------");
list.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("第四种---------");
Iterator<Star> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("第五种---------");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("第六种---------");
for (Iterator<Star> it = list.iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("第七种---------");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size();) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
i++;
}
}
/**
* 普通排序
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Star>() {
@Override
public int compare(Star o1, Star o2) {
return o1.getScore().compareTo(o2.getScore());
}
});
list.forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
}
/**
* lambda排序
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
Collections.sort(list, (p1, p2) -> p1.getScore().compareTo(p2.getScore()));
list.forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
}
/**
* streame排序
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
Stream<Star> stream = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Star::getScore));// .forEach(p ->
stream.forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
// list.forEach(p -> System.out.println(p));
}
/**
* 进行过滤操作
*/
@Test
public void test5() {
List<String> collect = list.stream()
.filter(p -> p.getId() > 1)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(p -> p.getScore()))
// .sorted(Comparator.comparing(Star::getScore))
.map(Star::getName)
.collect((Collectors.toList()));
System.out.println(collect);
}
}
class Star {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double score;
public Double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Star() {
super();
}
public Star(Integer id, String name, Double score) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Star [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", score=" + score + "]";
}
}
OK,到位,入个门。。。
标签:sum 迭代 blog ++ 记录 name 就是 terminal 名称
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/c-h-y/p/10127884.html