标签:adl next 如何 += 数据结构 gre nts rate ali

问题如上图,下面为中文描述:
有容量限制的设施地址问题:假设有n个设施和m个顾客,我们可以作以下操作:
①开启设施 ②分配顾客到某设施
上述两个操作都有各自的成本,我们希望总成本最低,且分配到某设施的总需求不能超过其容量。
为了方便问题的解决,我们首先建立模型,更具体地说,我们为设施、顾客创建一个具有相应属性的类。
我们以一个实例来更好地了解如何构建一个类:
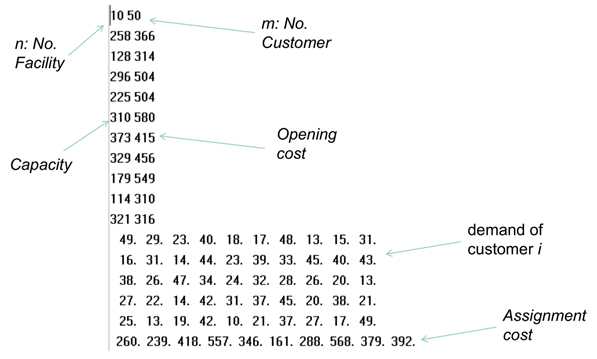
由上图可知,设施有容量、开启费用、是否开启、服务某个顾客的费用四个属性;顾客有需求、被哪个设施服务两个属性。为了区分每个设施和顾客,我们用ID区分他们,由此建立Facility,Customer两个类:

public class Facility { int facilityId; int capacity; int cost; boolean open; // 从customerId -> cost的映射 Map<Integer, Integer> assignmentCost; public int getFacilityId() { return facilityId; } public void setFacilityId(int facilityId) { this.facilityId = facilityId; } public int getCapacity() { return capacity; } public void setCapacity(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; } public int getCost() { return cost; } public void setCost(int cost) { this.cost = cost; } public Map<Integer, Integer> getAssignmentCost() { return assignmentCost; } public void setAssignmentCost(Map<Integer, Integer> assignmentCost) { this.assignmentCost = assignmentCost; } public boolean isOpen() { return open; } public void setOpen(boolean open) { this.open = open; } public Facility(Facility faci) { super(); this.facilityId = faci.facilityId; this.capacity = faci.capacity; this.cost = faci.cost; this.open = faci.open; this.assignmentCost = faci.assignmentCost; } public Facility() {} }

1 public class Customer { 2 int customerId; 3 int demand; 4 int assignedTo; // 去哪个设施 5 public int getCustomerId() { 6 return customerId; 7 } 8 public void setCustomerId(int customerId) { 9 this.customerId = customerId; 10 } 11 public int getDemand() { 12 return demand; 13 } 14 public void setDemand(int demand) { 15 this.demand = demand; 16 } 17 public int getAssignedTo() { 18 return assignedTo; 19 } 20 public void setAssignedTo(int assignedTo) { 21 this.assignedTo = assignedTo; 22 } 23 public Customer(Customer cust) { 24 super(); 25 this.customerId = cust.customerId; 26 this.demand = cust.demand; 27 this.assignedTo = cust.assignedTo; 28 } 29 public Customer() {} 30 }
在解决问题前,我们需要得到数据,以方便测试。一个样例的数据格式和第二部分的第一张图一样,输出结果的格式如下图:

我们为样例也构造一个类,格式如下:

1 public class Instance { 2 int result; 3 int time; 4 String id; 5 List<Boolean> openList; 6 List<Integer> assignmentList; 7 public int getResult() { 8 return result; 9 } 10 public void setResult(int result) { 11 this.result = result; 12 } 13 public int getTime() { 14 return time; 15 } 16 public void setTime(int time) { 17 this.time = time; 18 } 19 public List<Boolean> getOpenList() { 20 return openList; 21 } 22 public void setOpenList(List<Boolean> openList) { 23 this.openList = openList; 24 } 25 public List<Integer> getAssignmentList() { 26 return assignmentList; 27 } 28 public void setAssignmentList(List<Integer> assignmentList) { 29 this.assignmentList = assignmentList; 30 } 31 public String getId() { 32 return id; 33 } 34 public void setId(String id) { 35 this.id = id; 36 } 37 38 }
我们用List保存每个顾客、每个设施、每个实例,以及记录他们的数量:

建立好数据结构后,我们编写读取文件和初始化每个对象的代码:

1 //读取文件内容,默认文件内容格式正确,不做检查 2 public void ReadFileAndInit(String path) { 3 File file = new File(path); 4 //System.out.println(path); 5 BufferedReader bReader = null; 6 try { 7 // 字符串相关 8 String str; 9 List<Integer> intList = null; 10 bReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); 11 12 // 读取设施和顾客数量 13 str = bReader.readLine(); 14 intList = getNumberFromLine(str); 15 facilityNum = intList.get(0).intValue(); 16 customerNum = intList.get(1).intValue(); 17 18 // 读取设施容量和开销 19 for (int i = 0; i < facilityNum; i++) { 20 str = bReader.readLine(); 21 intList = getNumberFromLine(str); 22 Facility faci = new Facility(); 23 faci.setCapacity(intList.get(0).intValue()); 24 faci.setCost(intList.get(1).intValue()); 25 faci.setOpen(false); 26 faci.setFacilityId(i); 27 faci.setAssignmentCost(new HashMap<Integer, Integer>()); 28 facilityList.add(faci); 29 } 30 // 读取顾客的需求 31 for (int i = 0; i < customerNum; ) { 32 str = bReader.readLine(); 33 intList = getNumberFromLine(str); 34 for (Integer tmp : intList) { 35 Customer cust = new Customer(); 36 cust.setAssignedTo(-1); 37 cust.setCustomerId(i); 38 cust.setDemand(tmp); 39 customerList.add(cust); 40 i++; 41 } 42 } 43 // 读取每个顾客到设施的开销 44 for (int i = 0; i < facilityNum; i++) { 45 for (int j = 0; j < customerNum; ) { 46 str = bReader.readLine(); 47 intList = getNumberFromLine(str); 48 Facility faci = facilityList.get(i); 49 for (Integer tmp : intList) { 50 faci.getAssignmentCost().put(new Integer(j), tmp); 51 j++; 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 } catch(Exception e) { 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 } finally { 58 if (bReader != null) { 59 try { 60 bReader.close(); 61 } catch(Exception ex) { 62 ex.printStackTrace(); 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 }
再编写用于展示的代码:

1 public void GenerateTable() { 2 if (instanceList == null) { 3 return; 4 } 5 System.out.println("\t"+"result"+ " " + "Time(s)"); 6 7 for (Instance ins : instanceList) { 8 System.out.print(ins.getId() + " "); 9 System.out.print(ins.getResult()); 10 System.out.print(" "); 11 // 转化为毫秒 12 System.out.print((double)ins.getTime()/1000); 13 System.out.print("\n"); 14 } 15 } 16 public void DisplayInstance() { 17 if (instanceList == null) { 18 return; 19 } 20 for (Instance ins : instanceList) { 21 System.out.println(ins.getResult()); 22 for (Boolean bool : ins.getOpenList()) { 23 System.out.print(bool ? 1 : 0); 24 System.out.print(" "); 25 } 26 System.out.println(""); 27 for (Integer tmp : ins.getAssignmentList()) { 28 System.out.print(tmp.intValue()); 29 System.out.print(" "); 30 } 31 System.out.println(""); 32 } 33 }
编写用于生成实例的代码:

1 public Instance GenerateInstance(String id) { 2 Instance ins = new Instance(); 3 long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 4 //int result = Greedy(); 5 int result = SimulateAnneal(); 6 long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); 7 List<Boolean> openList = new ArrayList<Boolean>(); 8 List<Integer> assignmentList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 9 for (Facility faci : facilityList) { 10 openList.add(faci.isOpen()); 11 } 12 for (Customer cust : customerList) { 13 assignmentList.add(cust.getAssignedTo()); 14 } 15 ins.setId(id); 16 ins.setResult(result); 17 ins.setTime((int)(t2-t1)); 18 ins.setOpenList(openList); 19 ins.setAssignmentList(assignmentList); 20 21 return ins; 22 }
比较简单的解决办法是贪心算法,虽然不能够得到最优解,但它的思路最直接、最简单,实现起来简单,且时间复杂度不算高,下面说下贪心算法在该问题下的运用。
N个用户,编号为1-N,首先编号1选择服务费用最低的且容量足够的设施,编号2一样,只不过在1选择之后选择,以此类推,这并没有考虑到设施的开启费用,这是因为顾客的数量一般比设施多,所以如果设施开启的费用相对服务顾客的费用比较低的话,设施开启的费用是个次要矛盾,因为服务费用占的比例会大很多,当然,如果这个前提不成立的话,贪心算法的效果会差很多。
根据上面所说,我们编写代码:

1 public int Greedy() { 2 int result = 0; 3 for (Customer cust : customerList) { 4 int demand = cust.getDemand(); 5 int cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 6 int faciId = -1; 7 for (Facility faci : facilityList) { 8 Map<Integer, Integer> assignmentMap = faci.getAssignmentCost(); 9 int assignmentCost = assignmentMap.get(cust.getCustomerId()); 10 if (assignmentCost < cost && faci.getCapacity() >= demand) { 11 cost = assignmentCost; 12 faciId = faci.getFacilityId(); 13 } 14 } 15 cust.setAssignedTo(faciId); 16 if (faciId >= 0) { 17 Facility faci = facilityList.get(faciId); 18 result += cost; 19 if (!faci.isOpen()) { 20 faci.setOpen(true); 21 result += faci.getCost(); 22 } 23 faci.setCapacity(faci.getCapacity()-demand); 24 } 25 26 } 27 return result; 28 }
具体效果在最后一同展示。
模拟退火算法来源于固体退火原理,是一种基于概率的算法,将固体加温至充分高,再让其徐徐冷却,加温时,固体内部粒子随温升变为无序状,内能增大,而徐徐冷却时粒子渐趋有序,在每个温度都达到平衡态,最后在常温时达到基态,内能减为最小。
根据热力学规律并结合计算机对离散数据的处理, 我们定义: 如果当前温度为T, 当前状态与新状态之间的能量差为ΔE , 则发生状态转移的概率为:
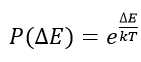
伪代码如下图(来自一篇博客):
http://www.cnblogs.com/heaad/archive/2010/12/20/1911614.html#!comments
1 /* 2 * J(y):在状态y时的评价函数值 3 * Y(i):表示当前状态 4 * Y(i+1):表示新的状态 5 * r: 用于控制降温的快慢 6 * T: 系统的温度,系统初始应该要处于一个高温的状态 7 * T_min :温度的下限,若温度T达到T_min,则停止搜索 8 */ 9 while( T > T_min ) 10 { 11 dE = J( Y(i+1) ) - J( Y(i) ) ; 12 13 if ( dE >=0 ) //表达移动后得到更优解,则总是接受移动 14 Y(i+1) = Y(i) ; //接受从Y(i)到Y(i+1)的移动 15 else 16 { 17 // 函数exp( dE/T )的取值范围是(0,1) ,dE/T越大,则exp( dE/T )也 18 if ( exp( dE/T ) > random( 0 , 1 ) ) 19 Y(i+1) = Y(i) ; //接受从Y(i)到Y(i+1)的移动 20 } 21 T = r * T ; //降温退火 ,0<r<1 。r越大,降温越慢;r越小,降温越快 22 /* 23 * 若r过大,则搜索到全局最优解的可能会较高,但搜索的过程也就较长。若r过小,则搜索的过程会很快,但最终可能会达到一个局部最优值 24 */ 25 i ++ ; 26 }
在该问题下,如果想得到新的状态Y(i+1),还不是十分清晰。换句话说,我们需要考虑如何得到邻近解,我采用的策略有两个:一是将两个顾客位置调换,即挑两个顾客出来,让一个顾客去另一个顾客的设施,另一个顾客去该顾客的设施。二是让一个顾客去另一个设施。顾客都是随机挑选的,两个策略在某个时刻时仅会执行一个。另外如果执行策略时,发现某些不合法的行为,就不会执行,直接放弃,例如某个设施容量不足。因为策略和顾客都是随机挑选的,且执行策略的次数会很大,所以放弃执行某次策略并不会影响整体效果。
综上,我们执行模拟退火的步骤如下:
①为了方便,状态初始化为贪心算法里的结果,设定初始温度,终止温度,温度下降率。
②开始循环,在某个温度时(内循环),根据上述两种策略得到临近解,然后将得到的临近解和当前解进行比较,采取状态转移的步骤,由公式得到概率,决定是否向较差的情况转移。内循环结束后,将当前解与最优解比较,更新最优解。开始降温。
③当温度降至终止温度时,结束循环。得到该算法下最有解。
代码如下:

1 public int SimulateAnneal() { 2 double temper = 100000; //初始温度 3 double minTemper = 0.001; //终止温度 4 double coolRate = 0.99; 5 double count = 1000; 6 // 初始状态,为了方便选用贪婪算法的解 7 int bestVal = Greedy(); 8 int curVal = bestVal; 9 int nextVal = bestVal; 10 List<Facility> facilityListBestCopy = new ArrayList<Facility>(); 11 List<Customer> customerListBestCopy = new ArrayList<Customer>(); 12 for (Facility faci : facilityList) { 13 facilityListBestCopy.add(new Facility(faci)); 14 } 15 for (Customer cust : customerList) { 16 customerListBestCopy.add(new Customer(cust)); 17 } 18 while (temper > minTemper) { 19 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 20 //拷贝,用于还原 21 List<Facility> facilityListCopy = new ArrayList<Facility>(); 22 List<Customer> customerListCopy = new ArrayList<Customer>(); 23 for (Facility faci : facilityList) { 24 facilityListCopy.add(new Facility(faci)); 25 } 26 for (Customer cust : customerList) { 27 customerListCopy.add(new Customer(cust)); 28 } 29 nextVal = GetNextResult(curVal); 30 double delta = nextVal - curVal; 31 if (delta < 0) { 32 curVal = nextVal; 33 } else { 34 if (Math.exp(-delta/temper) > Math.random()) { 35 curVal = nextVal; 36 } else { 37 facilityList = facilityListCopy; 38 customerList = customerListCopy; 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 if (curVal < bestVal) { 44 bestVal = curVal; 45 facilityListBestCopy = facilityList; 46 customerListBestCopy = customerList; 47 } 48 temper *= coolRate; 49 } 50 facilityList = facilityListBestCopy; 51 customerList = customerListBestCopy; 52 return bestVal; 53 }
设施开启状态和顾客去了哪个设施的结果可以在https://github.com/thougr/CFLP/tree/master/src/docs查看。
下面展示每个实例的运算时间和问题的结果(时间精度为毫秒):
|
result(SA) |
Time(s) |
result(Greedy) |
Time(s) |
|
|
p1 |
8958 |
2.738 |
9440 |
0.001 |
|
p2 |
8010 |
2.187 |
8126 |
0 |
|
p3 |
9389 |
1.974 |
10126 |
0.001 |
|
p4 |
10714 |
1.978 |
12126 |
0 |
|
p5 |
9142 |
1.966 |
9375 |
0 |
|
p6 |
7809 |
1.985 |
8061 |
0.007 |
|
p7 |
9577 |
1.971 |
10061 |
0.001 |
|
p8 |
11173 |
1.931 |
12061 |
0 |
|
p9 |
8742 |
2.074 |
9040 |
0.001 |
|
p10 |
7617 |
2.045 |
7726 |
0.002 |
|
p11 |
9077 |
2.508 |
9726 |
0.002 |
|
p12 |
10132 |
2.066 |
11726 |
0 |
|
p13 |
8492 |
2.418 |
12032 |
0 |
|
p14 |
7526 |
2.391 |
9180 |
0.002 |
|
p15 |
8937 |
2.512 |
13180 |
0 |
|
p16 |
10764 |
2.458 |
17180 |
0.001 |
|
p17 |
8378 |
2.335 |
12032 |
0.002 |
|
p18 |
7152 |
2.351 |
9180 |
0.002 |
|
p19 |
9042 |
2.406 |
13180 |
0 |
|
p20 |
11071 |
2.417 |
17180 |
0 |
|
p21 |
8667 |
2.427 |
12032 |
0 |
|
p22 |
7194 |
2.402 |
9180 |
0.001 |
|
p23 |
8746 |
2.434 |
13180 |
0 |
|
p24 |
11483 |
2.394 |
17180 |
0 |
|
p25 |
13191 |
5.039 |
19197 |
0.002 |
|
p26 |
11022 |
4.95 |
16131 |
0.002 |
|
p27 |
13037 |
4.919 |
21531 |
0.002 |
|
p28 |
16410 |
4.925 |
26931 |
0.002 |
|
p29 |
13289 |
4.96 |
19305 |
0.001 |
|
p30 |
12171 |
4.893 |
16239 |
0.001 |
|
p31 |
14228 |
4.937 |
21639 |
0.001 |
|
p32 |
15903 |
5.005 |
27039 |
0.001 |
|
p33 |
12220 |
4.973 |
19055 |
0.002 |
|
p34 |
11004 |
5.006 |
15989 |
0.001 |
|
p35 |
13637 |
4.926 |
21389 |
0 |
|
p36 |
15004 |
4.929 |
26789 |
0 |
|
p37 |
11935 |
4.946 |
19055 |
0 |
|
p38 |
10984 |
4.933 |
15989 |
0.001 |
|
p39 |
12984 |
4.944 |
21389 |
0.001 |
|
p40 |
14984 |
4.951 |
26789 |
0 |
|
p41 |
7103 |
2.932 |
7226 |
0 |
|
p42 |
6678 |
3.201 |
9957 |
0 |
|
p43 |
6758 |
3.038 |
12448 |
0 |
|
p44 |
7128 |
2.848 |
7585 |
0 |
|
p45 |
7478 |
3.102 |
9848 |
0 |
|
p46 |
6160 |
3.044 |
12639 |
0 |
|
p47 |
6257 |
2.865 |
6634 |
0 |
|
p48 |
6642 |
3.069 |
9044 |
0 |
|
p49 |
5658 |
3.048 |
12420 |
0 |
|
p50 |
9239 |
3.12 |
10062 |
0 |
|
p51 |
7920 |
3.451 |
11351 |
0.001 |
|
p52 |
9247 |
3.042 |
10364 |
0 |
|
p53 |
9319 |
3.43 |
12470 |
0 |
|
p54 |
9034 |
3.028 |
10351 |
0 |
|
p55 |
7938 |
3.451 |
11970 |
0 |
|
p56 |
22710 |
6.109 |
23882 |
0.001 |
|
p57 |
29464 |
6.079 |
32882 |
0.001 |
|
p58 |
43765 |
6.105 |
53882 |
0 |
|
p59 |
32854 |
6.113 |
39121 |
0.001 |
|
p60 |
23086 |
6.144 |
23882 |
0.001 |
|
p61 |
30093 |
6.193 |
32882 |
0.002 |
|
p62 |
41891 |
6.261 |
53882 |
0.001 |
|
p63 |
31788 |
6.32 |
39121 |
0.001 |
|
p64 |
22443 |
6.136 |
23882 |
0.003 |
|
p65 |
29279 |
6.15 |
32882 |
0.001 |
|
p66 |
44219 |
6.124 |
53882 |
0.001 |
|
p67 |
32471 |
7.23 |
39671 |
0 |
|
p68 |
23024 |
6.149 |
23882 |
0.001 |
|
p69 |
30318 |
6.145 |
32882 |
0.017 |
|
p70 |
43835 |
6.152 |
53882 |
0 |
|
p71 |
32071 |
6.128 |
39121 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
由上面的运算结果可以看出,贪心算法运算的很快,但相对来说结果没有那么好,模拟退火算法运算时间上升了很多,但结果优化了很多。
完整代码可以在 https://github.com/thougr/CFLP 看到。
标签:adl next 如何 += 数据结构 gre nts rate ali
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/thougr/p/10166441.html