标签:格式 ace 方法 申请 names ase col 就是 bubuko
ybt1365:FBI树(fbi)
[题目描述]
我们可以把由“0”和“1”组成的字符串分为三类:全“0”串称为B串,全“1”串称为I串,既含“0”又含“1”的串则称为F串。
FBI树是一种二叉树,它的结点类型也包括F结点,B结点和I结点三种。由一个长度为2N的“01”串S可以构造出一棵FBI树T,递归的构造方法如下:
T的根结点为R,其类型与串S的类型相同;
若串S的长度大于1,将串S从中间分开,分为等长的左右子串S1和S2;由左子串S1构造R的左子树T1,由右子串S2构造R的右子树T2。
现在给定一个长度为2N的“01”串,请用上述构造方法构造出一棵FBI树,并输出它的后序遍历序列。
[输入格式]
第一行是一个整数N(0 ≤ N ≤ 10),第二行是一个长度为2N的“01”串。
[输出格式]
一行,这一行只包含一个字符串,即FBI树的后序遍历序列。
[输入样例]
3
10001011
[输出样例]
IBFBBBFIBFIIIFF
[解法1(常规建树)]
请看任天祥大佬代码:
1 #include<cstdio> 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 5 #include<cstring> 6 7 #include<cstdlib> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 int N; 12 13 struct FBI 14 15 { 16 17 FBI *l,*r; 18 19 char R; 20 21 }*root; 22 23 void build(string c,FBI **pr) //新建节点的串与该节点位置 24 25 { 26 27 FBI *d; 28 29 d=(FBI *)malloc(sizeof(FBI)); //位置申请空间 30 31 32 33 if(c.length()==1) //边界 34 35 { 36 37 switch (c[0]) 38 39 { 40 41 case ‘0‘: d->R=‘B‘;//识别 42 43 break; 44 45 case ‘1‘: d->R=‘I‘; 46 47 break; 48 49 } 50 51 *pr=d; 52 53 d->l=NULL; //这两句贼重要,要不然输出无边界。 54 55 d->r=NULL; 56 57 return; 58 59 } 60 61 62 63 int mid=c.length()/2; //串分两半 64 65 string s1,s2; //串分两半 66 67 s1=c.substr(0,mid); 68 69 s2=c.substr(mid,mid); //指针指空 70 71 FBI *dl,*dr; 72 73 build(s1,&(d->l)); //递归建树 74 75 build(s2,&(d->r)); 76 77 dl=d->l; 78 79 dr=d->r; 80 81 if((dl)->R==‘B‘&&(dr)->R==‘B‘) 82 83 { 84 85 d->R=‘B‘; 86 87 *pr=d; 88 89 return; 90 91 } 92 93 if((dl)->R==‘I‘&&(dr)->R==‘I‘) 94 95 { 96 97 d->R=‘I‘; 98 99 *pr=d; 100 101 return; 102 103 } 104 105 else d->R=‘F‘; 106 107 *pr=d; 108 109 return; 110 111 } 112 113 114 115 void backprin(FBI *a) 116 117 { 118 119 if(a) 120 121 { 122 123 backprin(a->l); 124 125 backprin(a->r); 126 127 printf("%c",a->R); 128 129 return; 130 131 } 132 133 134 135 } 136 137 int main () 138 139 { 140 141 freopen("in.in","r",stdin); 142 143 freopen("std.out","w",stdout); 144 145 scanf("%d",&N); 146 147 string x; 148 149 cin>>x; 150 151 build(x,&root); 152 153 backprin(root); 154 155 return 0; 156 157 }
[解法2(递归骚代码)]
仔细观察我们就会发现对于一部分01串[l,r]对应节点i的fbi只与它左右两个子节点的fbi决定,而左右两个子节点对应的01串分别就是[l,(r+l)/2]和[(r+l)/2+1,r]由此我们可以得到递归式:
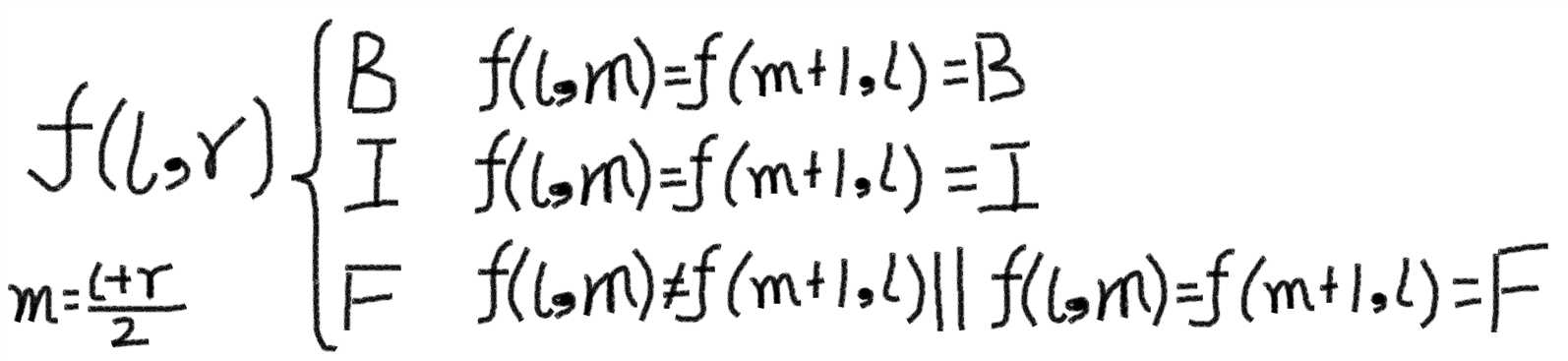
递归终点就是l=r直接返回这个01串对应值就好。如此我们得到了一下代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cmath> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 using namespace std; 8 bool fbi[1056]; 9 char dfs(int left,int right){ 10 if(left==right){ 11 if(fbi[left]){ 12 printf("I"); 13 return ‘I‘; 14 } 15 else{ 16 printf("B"); 17 return ‘B‘; 18 } 19 } 20 char l=dfs(left,left+(right-left)/2); 21 char r=dfs(left+(right-left)/2+1,right); 22 if(l==‘F‘||r==‘F‘){ 23 printf("F"); 24 return ‘F‘; 25 } 26 if(l==r){ 27 printf("%c",l); 28 return l; 29 } 30 else { 31 printf("F"); 32 return ‘F‘; 33 } 34 } 35 int main(){ 36 int n; 37 scanf("%d",&n); 38 n=pow(2,n); 39 char temp; 40 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ 41 scanf("\n%c",&temp); 42 fbi[i]=temp-‘0‘; 43 } 44 dfs(1,n); 45 return 0; 46 }
2019-01-06 22:57:10
标签:格式 ace 方法 申请 names ase col 就是 bubuko
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zjd-ac/p/10230883.html