标签:log more prim nodevalue nbsp 复杂 bigger not 解决
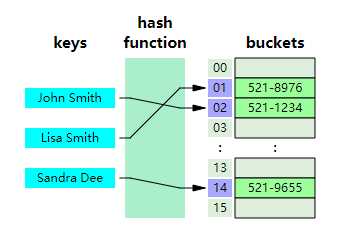
在计算中, 一个哈希表(hash table 或hash map) 是一种实现关联数组(associative array) 的抽象数据类型, 该结构可以将 键映射到值。
哈希表使用 哈希函数/散列函数 来计算一个值在数组或桶(buckets)中或槽(slots)中对应的索引,可使用该索引找到所需的值。
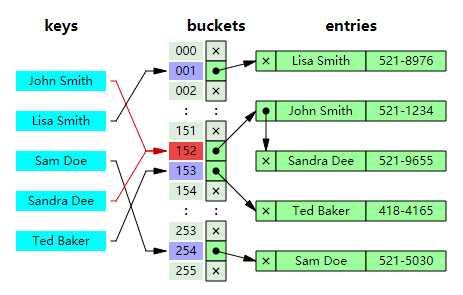
理想情况下,散列函数将为每个键分配给一个唯一的桶(bucket),但是大多数哈希表设计采用不完美的散列函数,这可能会导致"哈希冲突(hash collisions)",也就是散列函数为多个键(key)生成了相同的索引,这种碰撞必须 以某种方式进行处理。
通过单独的链接解决哈希冲突
复杂度
时间复杂度
获取:O(1)
查询:O(1)
插入:O(1)
删除:O(1)
空间复杂度
O(n)
HashTable:
import LinkedList from ‘../linked-list/LinkedList‘; // Hash table size directly affects on the number of collisions. // The bigger the hash table size the less collisions you‘ll get. // For demonstrating purposes hash table size is small to show how collisions // are being handled. //哈希表的size直接影响冲突的次数。 //哈希表size越大,冲突越少。 //因为示范的目的这里size设置的很小以便展示如何处理冲突 const defaultHashTableSize = 32; export default class HashTable { /** * @param {number} hashTableSize */ constructor(hashTableSize = defaultHashTableSize) {//构造函数,hashTableSize是哈希表的size // Create hash table of certain size and fill each bucket with empty linked list. //创建确定大小的哈希表,然后每个bucket填充一个空的链表 //先创建一个hashTableSize大小的数组,然后里面每个元素填充为null,然后里面每一个元素都是一个链表 this.buckets = Array(hashTableSize).fill(null).map(() => new LinkedList()); // Just to keep track of all actual keys in a fast way. //keys属性存放键,只是为了快速追踪所有实际key this.keys = {}; } /** * Converts key string to hash number. * * @param {string} key * @return {number} */ hash(key) {//将键字符串转换成哈希值 // For simplicity reasons we will just use character codes sum of all characters of the key // to calculate the hash. //为了让程序简单一点,我们只将键字符串的字符编码求和后的总值计算哈希值 // But you may also use more sophisticated approaches like polynomial string hash to reduce the // number of collisions: //你也可以使用更复杂的方法比如多项式字符串哈希值来减小冲突的次数 // hash = charCodeAt(0) * PRIME^(n-1) + charCodeAt(1) * PRIME^(n-2) + ... + charCodeAt(n-1) // // where charCodeAt(i) is the i-th character code of the key, n is the length of the key and // PRIME is just any prime number like 31. //charCodeAt(i)是第i个字符的编码,n是key的长度,PRIME是自定义的任意数字 const hash = Array.from(key).reduce( (hashAccumulator, keySymbol) => (hashAccumulator + keySymbol.charCodeAt(0)), 0, ); //将键字符串的每一个字符的编码累加求总和后的数作为哈希值 // Reduce hash number so it would fit hash table size. //hash和哈希表size取余,减小hash让它与之符合 return hash % this.buckets.length; } /** * @param {string} key * @param {*} value */ set(key, value) {//给哈希表里存新的键值 const keyHash = this.hash(key);//用hash处理key生成key的哈希值 this.keys[key] = keyHash;//在keys对象里存下key: keyHash const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[keyHash];//keyHash对应的buckets链表 const node = bucketLinkedList.find({ callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key }); //调用链表的find方法查找看链表里有没有相同的key的节点 if (!node) {//如果没有,在链表的结尾插入新节点,节点的值是键值对的对象{key: key, value: value} // Insert new node. bucketLinkedList.append({ key, value }); } else {//如果已经有相同的key了,就只修改这个节点的value // Update value of existing node. node.value.value = value; } } /** * @param {string} key * @return {*} */ delete(key) {//删除key对应的节点 const keyHash = this.hash(key);//根据key计算出key哈希值 delete this.keys[key];//从keys对象里删除key: keyHash const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[keyHash];//keyHash对应的buckets链表 const node = bucketLinkedList.find({ callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key }); //调用链表的find方法查找链表里相同的key的节点 if (node) {//如果找到了,就将这个节点从链表里删除,并返回被删的节点 return bucketLinkedList.delete(node.value); } return null;//没有对应key返回null } /** * @param {string} key * @return {*} */ get(key) {//获取key对应的value const bucketLinkedList = this.buckets[this.hash(key)];//keyHash对应的buckets链表 const node = bucketLinkedList.find({ callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key }); //调用链表的find方法查找链表里相同的key的节点 return node ? node.value.value : undefined;//找到了就返回value,没找到就返回undefined } /** * @param {string} key * @return {boolean} */ has(key) {//看哈希表里有没有对应的key return Object.hasOwnProperty.call(this.keys, key); } /** * @return {string[]} */ getKeys() {//获取所有key组成的数组 return Object.keys(this.keys); } }
note:
0.对于getKeys的Object.keys说明
getKeys() { return Object.keys(this.keys); }
Object.keys举例:
// simple array var arr = [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘]; console.log(Object.keys(arr)); // console: [‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘] // array like object var obj = { 0: ‘a‘, 1: ‘b‘, 2: ‘c‘ }; console.log(Object.keys(obj)); // console: [‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘] // array like object with random key ordering var anObj = { 100: ‘a‘, 2: ‘b‘, 7: ‘c‘ }; console.log(Object.keys(anObj)); // console: [‘2‘, ‘7‘, ‘100‘]
1.hash表包括关键字以及拉链法所组成的链表,所包含的数据结构为:
this.buckets = Array(hashTableSize).fill(null).map(() => new LinkedList()); this.keys = {};
2.对元素值的累加代码为:
const hash = Array.from(key).reduce( (hashAccumulator, keySymbol) => (hashAccumulator + keySymbol.charCodeAt(0)), 0, );
3.拉链法链表的查找:
const node = bucketLinkedList.find({ callback: nodeValue => nodeValue.key === key });
4.找到以后,拉链法链表的修改,改关键字对应的哈希值:
if (!node) {
// Insert new node.
bucketLinkedList.append({ key, value });
} else {
// Update value of existing node.
node.value.value = value;
}
标签:log more prim nodevalue nbsp 复杂 bigger not 解决
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Archer-Fang/p/10234614.html