标签:res ext com 个数 通过 方法 摘要 int 技术
首先我们去看看 Expressions类 ,定义了一个泛型委托类型 TDelegate:
1 // 摘要: 2 // 将强类型化的 Lambda 表达式表示为表达式树形式的数据结构。 此类不能被继承。 3 // 4 // 类型参数: 5 // TDelegate: 6 // 该委托的类型, System.Linq.Expressions.Expression`1 表示。 7 public sealed class Expression<TDelegate> : LambdaExpression
我们先来一个带返回值的委托: 其中m、n是两个Int 类型的参数
1 Func<int, int, int> func = (m, n) => m * n + 2;
//lambda实例化委托 是个方法 是实例化委托的参数
int iResult1 =func.Invoke(1,3); //调用执行
通过表达式目录树计算 m*n+2:
1 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (m, n) => m * n + 2; 2 int iResult2 = exp.Compile().Invoke(1, 2);
//Complie()方法将编译表达式树由描述为可执行代码的 lambda 表达式,并生成一个委托,表示 lambda 表达式。所以可以调用Invoke方法。
通过中间语言IL反编译查看源码 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> exp = (m, n) => m * n + 2
表达式目录树结构拆分步骤:
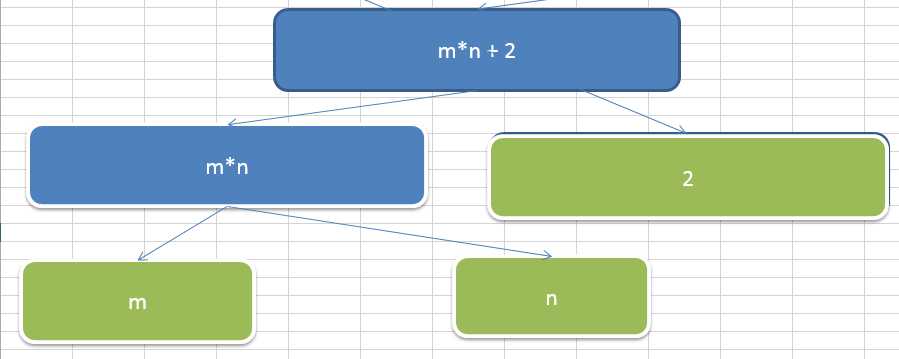
手动拼装表达式目录树 m * n + m + n + 2;
1 { 2 //Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = (m, n) => m * n + m + n + 2; 3 //int iResult = expression.Compile().Invoke(1, 2); 4 5 ParameterExpression m = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "m"); //第一个参数 M 6 ParameterExpression n = Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "n"); //第二个参数 n 7 var constant = Expression.Constant(2); //常量 2 8 9 var mutiply = Expression.Multiply(m, n); // m*n 10 var plus1 = Expression.Add(mutiply, m); // m*n+m 11 var plus2 = Expression.Add(plus1, n); //m*n+m+n 12 var plus3 = Expression.Add(plus2, constant); //m*n+m+n+2 13 Expression<Func<int, int, int>> expression = Expression.Lambda<Func<int, int, int>>(plus3, new ParameterExpression[] { m, n });
//组装表达式目录树 14 int iResult = expression.Compile().Invoke(1, 2);//调用 15 }
标签:res ext com 个数 通过 方法 摘要 int 技术
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/super-xi-xi/p/10247922.html