使用TCMalloc进行堆栈分析
Author:Echo Chen(陈斌)
Email:chenb19870707@gmail.com
Blog:Blog.csdn.net/chen19870707
Date:October 10th, 2014
在前一篇译文《使用TCmalloc的堆栈检查》,介绍了Tcmalloc进行堆栈检查,今天翻译《heap-profiling using tcmalloc》,了解如何 TCmalloc进行堆栈分析。
这篇技术文档描述了如何使用C++程序来分析堆栈。可以用来做一下三条事情:
你可以对任何链接了tcmalloc的程序进行堆栈分析,并且不需要重新编译。
把tcmalloc链接到你的程序,即时你不想使用堆栈分析器来检查也是安全的。你的程序并不会运行的有任何一点缓慢,因为你没有用到任何一点堆栈分析的特性。
你可以通过LD_PRELOAD在那些不是你编译的程序中运行堆栈检查。
1: $ LD_PRELOAD="/usr/lib/libtcmalloc.so" HEAPPROFILE=...
我们不建议这种使用。
定义HEAPPROFILE环境变量来确定生成分析文件的位置,例如生成在/usr/local/nmetscape:
1: $ HEAPPROFILE=/tmp/profile /usr/local/netscape # sh
2: % setenv HEAPPROFILE /tmp/profile; /usr/local/netscape # csh
分析对子进程也是有效的:每个子进程根据自己的名字得到它自己的分析文件(由HEAPPROFILE和进程ID组成)
出于安全的原因,堆栈检查将不会写道文件里,所以对于有setuid的程序,堆栈分析是不能使用的。
如果堆程序中打开了堆栈分析,程序将会把分析文件生成到文件系统中,一系列分析文件的名字将被命名为如下:
1: <prefix>.0000.heap
2: <prefix>.0001.heap
3: <prefix>.0002.heap
4: ...
<perfix> 是HEAPPROFILE中定义的值。注意到如果没有定义文件的路径,文件将直接被生成到程序当前目录。
默认情况下,一个文件写满1GB换一个新的文件。写文件的频率可以在你的程序中调用HeapProfilerSetAllocationInterval()来控制。得出这样一个结论,每个文件的大小是一个确定的数值。
你也可以调用HeapProfile来在你程序的特定位置生成分析文件,例如:
1: extern const char* HeapProfile();
2: const char* profile = HeapProfile();
3: fputs(profile, stdout);
4: free(const_cast<char*>(profile));
这个分析系统说明了所有内存申请和释放。它保留了每次内存分配的一系列信息。内存分配定义为堆栈内活跃调用:malloc,calloc,realloc, or,
new.
可以通过把分析文件传给pprof工具来得到分析输出,pprof工具可以打印CPU和堆栈使用情况。解释如下:
这里是一些例子,这些例子假设二进制名字为gfs_master,一系列的堆栈分析文件名字如下:
profile.0001.heap profile.0002.heap ... profile.0100.heap
% pprof --gv gfs_master profile.0100.heap
这个命令将会弹出一个显示分析信息的图表的窗口,如下是一个例子:
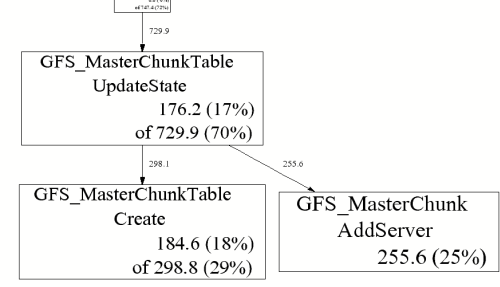
一些解释:
你经常希望跳过程序在初始化阶段的内存分配来找到内存泄漏。一个简单的方法来实现这件事情是通过比较两个分析文件,这两个文件都是从程序开始到运行了一段时间。使用—baseoption来指定第一个文件,例如:
% pprof --base=profile.0004.heap gfs_master profile.0100.heap
profile.0004.heap 中的内存使用将会见到profile.0100.heap中的内存使用,并显示出结果。
% pprof gfs_master profile.0100.heap 255.6 24.7% 24.7% 255.6 24.7% GFS_MasterChunk::AddServer 184.6 17.8% 42.5% 298.8 28.8% GFS_MasterChunkTable::Create 176.2 17.0% 59.5% 729.9 70.5% GFS_MasterChunkTable::UpdateState 169.8 16.4% 75.9% 169.8 16.4% PendingClone::PendingClone 76.3 7.4% 83.3% 76.3 7.4% __default_alloc_template::_S_chunk_alloc 49.5 4.8% 88.0% 49.5 4.8% hashtable::resize ...
如下的命令将会给出调用的图形显示,只包含了调用图中包含了DataBuffer表达式的那些路径:
% pprof --gv --focus=DataBuffer gfs_master profile.0100.heap
同样的,下面的命令将忽略所有的路径。所有匹配了DataBuffer中的表达式的都会被忽略:
% pprof --gv --ignore=DataBuffer gfs_master profile.0100.heap
所有前面的例子已经说明了如何显示出空间使用,例如:那些分配了但未释放的数量。里可以获取其它信息用如下标志:
--inuse_space |
Display the number of in-use megabytes (i.e. space that has been allocated but not freed). This is the default. |
--inuse_objects |
Display the number of in-use objects (i.e. number of objects that have been allocated but not freed). |
--alloc_space |
Display the number of allocated megabytes. This includes the space that has since been de-allocated. Use this if you want to find the main allocation sites in the program. |
--alloc_objects |
Display the number of allocated objects. This includes the objects that have since been de-allocated. Use this if you want to find the main allocation sites in the program. |
-
Echo Chen:Blog.csdn.net/chen19870707
-
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/chen19870707/article/details/40145565