标签:mod efault objects inux运维 return from res max 例子
在网上看到 django ORM 有一个 content_type 字段表的应用,这张表不是我们通过建立model类添加的,而是django自动帮我们生成的,具体的作用先简单的举个例子给大家介绍一下。
首先,创业初期,老板有一个需求,只做线上课程,根据学习周期不同,建立对应价格。
1.没啥好说的,建立两张表,一个课程可以有多个价格套餐,一个价格套餐可以对应多个课程,课程表Course和价格表PriceStrategy(后面简称PS).
class Course(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class PriceStrategy(models.Model):
price = models.IntegerField(verbose_name=‘课程价格‘,default=3000)
period = models.IntegerField(verbose_name=‘学习周期‘,default=30)
course = models.ManyToManyField(to=‘Course‘,related_name=‘ps‘)
2.在数据库中录入相关字段:
对于课程:
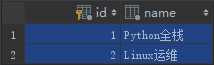
对于价格套餐:
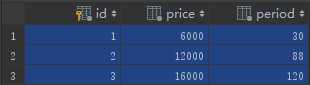
两张表的对应关系(自动生成的):
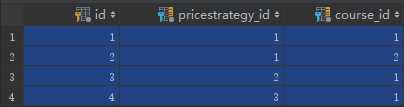
3.这样我就可以根据需求来执行相关ORM操作:
比如,取出python全栈这门课程的价格套餐:
course_obj = models.Course.objects.filter(id=1).first() res = course_obj.ps.all() for item in res: price = item.price period = item.period print(price,period)
或者,套餐价格12000的课程有哪些:
ps_obj = models.PriceStrategy.objects.filter(price=12000).first()
course = ps_obj.course.first()
这样是没有问题的,但是后期,公司扩大了规模,老板发展了线下课程,要求重建一张OfflineCourse表,绑定价格策略。这样,Course表和OfflineCourse表都要和PS表保持多对多关系,我们知道,ManytoMany只能关联一张表,要想关联两张表,我们必须重新添加一个字段,再用Many2Many关联,这样可以做,但如果后期老板后期又提出了新需求开发了新课程,这样又要添加表,显得比较麻烦。
Django 自动生成的content_type表帮我们解决了这个麻烦:
models.py
from django.db import models from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey,GenericRelation class Course(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) price = GenericRelation(to=‘PriceStrategy‘) class OfflineCourse(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=32) price = GenericRelation(to=‘PriceStrategy‘) class PriceStrategy(models.Model): price = models.IntegerField() period = models.IntegerField() content_type = models.ForeignKey(ContentType,on_delete=models.CASCADE) object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField() content_obj = GenericForeignKey(‘content_type‘,‘object_id‘)
我们通过ORM语句,利用视图函数录入数据资料,发现PS表:
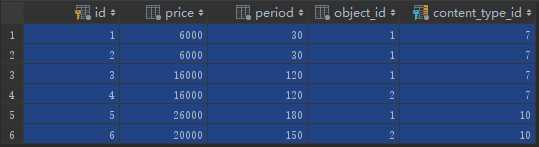
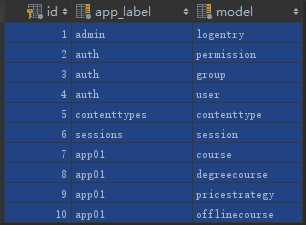
最后一列,content_type_id 对应的是 content_type表中的id 取对应的model表,object_id是取到的表中数据的id:
需求一:根据价格套餐,找到对应的课程
比如上图中的第4行,content_type_id = 7,取course表,object_id=2,取course表中的id为2的数据,是linux运维课程。
我们来验证一下结果:
views.py:
def test(request): ps_obj = models.PriceStrategy.objects.get(id=4) print(ps_obj.content_obj) return HttpResponse(‘...‘)
打印结果正确!
需求二:查找该课程所有的价格套餐
views.py:
def test(request): course_obj = models.Course.objects.get(id=1) for item in course_obj.price.all(): print(item.price, item.period) return HttpResponse(‘...‘)
总结:
content_type表的作用,其实就相当于一张地图,根据content_type_id,找到你需要的表,再根据object_id,找到表中你要的数据。这样,无论你老板后来需要加多少表,多少个价格套餐,都可以不用改表结构可以完成。
所以,在例子中PS建立表结构时,额外录入三个字段:
1:content_type 外键关联到django自动生成的content_type表;
2:object_id:正整数,取表中数据的id;
3:content_obj:取哪张表,GenericForeignKey(‘content_type‘,‘object_id‘),不会生成额外的列,用来帮助查找数据。
已经有了1,2两个字段,直接点语法取第三个字段,就自然找到了你想要的数据。
同时,反向查找的话,直接点语法取关联字段即可,非常方便,前提是关联字段必须用GenericRelation来关联:
price = GenericRelation(to=‘PriceStrategy‘)。
以上就是我作为django菜鸟对于content_type的理解,如有错误,欢迎指正。
标签:mod efault objects inux运维 return from res max 例子
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jimmyhe/p/10284642.html