标签:sum nis value range float bubuko rand init oms
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Jan 19 16:59:35 2019
@author: Administrator
"""
import tensorflow as tf
from numpy.random import RandomState
batch_size=8
w1=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2,3],stddev=1,seed=1))
w2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3,1],stddev=1,seed=1))
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(None,2),name=‘x-input‘)
y_=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(None,1),name=‘y-input‘)
a=tf.matmul(x,w1)
y=tf.matmul(a,w2)
y=tf.sigmoid(y)
cross_entropy=-tf.reduce_mean(
y_*tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(y,1e-10,1.0))
+(1-y_)*tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(1-y,1e-10,1.0)))
train_step=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cross_entropy)
rdm=RandomState(1)
dataset_size=128
X=rdm.rand(dataset_size,2)
Y=[[int(x1+x2<1)] for (x1,x2) in X]
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
print( sess.run(w1))
print( sess.run(w2))
‘‘‘
w1=[[-0.81131822,1.48,0.06]
[-0.44,0.09,0.59]]
w2=[[-0.8,1.4,0.06]]
‘‘‘
STEPS=5000
for i in range(STEPS):
start=(i*batch_size)%dataset_size
end=min(start+batch_size,dataset_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:X[start:end],y_:Y[start:end]})
if i%1000==0:
total_cross_entropy=sess.run(
cross_entropy,feed_dict={x:X,y_:Y})
print("After %d training step(s),cross entropy on all data is %g"%
(i,total_cross_entropy))
print( sess.run(w1))
print( sess.run(w2))
sess.close()
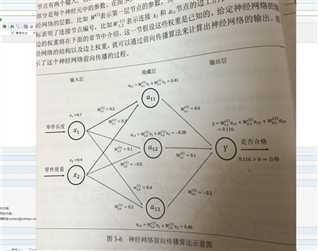
损失函数:交叉熵
tf.clip_by_value的用法
tf.clip_by_value(A, min, max):输入一个张量A,把A中的每一个元素的值都压缩在min和max之间。小于min的让它等于min,大于max的元素的值等于max。
例如:
[python] view plain copy
import tensorflow as tf;
import numpy as np;
A = np.array([[1,1,2,4], [3,4,8,5]])
with tf.Session() as sess:
print sess.run(tf.clip_by_value(A, 2, 5))
输出:
[[2 2 2 4]
[3 4 5 5]]
---------------------
tf.reduce_mean 函数用于计算张量tensor沿着指定的数轴(tensor的某一维度)上的的平均值,主要用作降维或者计算tensor(图像)的平均值。
reduce_mean(input_tensor,
axis=None,
keep_dims=False,
name=None,
reduction_indices=None)
第一个参数input_tensor: 输入的待降维的tensor;
第二个参数axis: 指定的轴,如果不指定,则计算所有元素的均值;
第三个参数keep_dims:是否降维度,设置为True,输出的结果保持输入tensor的形状,设置为False,输出结果会降低维度;
第四个参数name: 操作的名称;
第五个参数 reduction_indices:在以前版本中用来指定轴,已弃用;
以一个维度是2,形状是[3,3]的tensor举例:
import tensorflow as tf
x = [[1,2,3],
[1,2,3]]
xx = tf.cast(x,tf.float32)
mean_all = tf.reduce_mean(xx, keep_dims=False)
mean_0 = tf.reduce_mean(xx, axis=0, keep_dims=False)
mean_1 = tf.reduce_mean(xx, axis=1, keep_dims=False)
with tf.Session() as sess:
m_a,m_0,m_1 = sess.run([mean_all, mean_0, mean_1])
print m_a # output: 2.0
print m_0 # output: [ 1. 2. 3.]
print m_1 #output: [ 2. 2.]
如果设置保持原来的张量的维度,keep_dims=True ,结果:
print m_a # output: [[ 2.]]
print m_0 # output: [[ 1. 2. 3.]]
print m_1 #output: [[ 2.], [ 2.]]
类似函数还有:
tf.reduce_sum :计算tensor指定轴方向上的所有元素的累加和;
tf.reduce_max : 计算tensor指定轴方向上的各个元素的最大值;
tf.reduce_all : 计算tensor指定轴方向上的各个元素的逻辑和(and运算);
tf.reduce_any: 计算tensor指定轴方向上的各个元素的逻辑或(or运算);
标签:sum nis value range float bubuko rand init oms
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhanying999666/p/10292666.html