标签:php pid [] abc clu roc base swa 顺序
1.base case(递归出口)。必须有某些基本情形,它无需递归就能解出。
2.分解 或者 分类。分解成子问题,或者每层递归分叉,也就是一个N叉树模型。
分解:按顺序每个字母是否打印,分解。
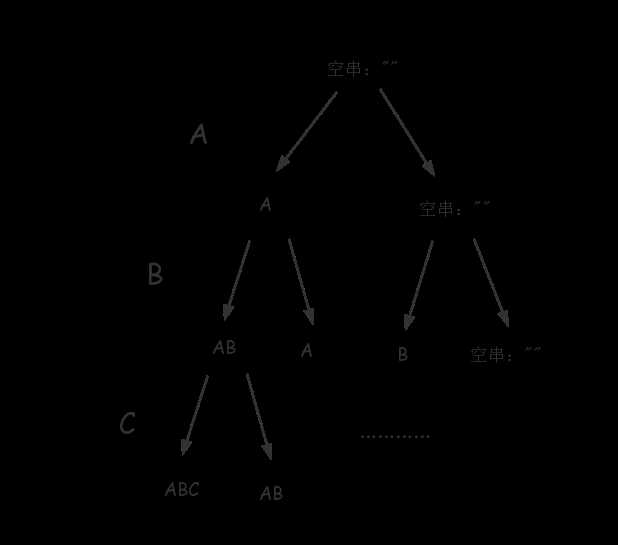
base case: 当 pos==length,分解到了最后一步
void process(char *s,int pos,int length,string res) { if (pos == length) { cout << res << endl; return; } process(s, pos + 1,length,res); process(s, pos + 1, length, res + s[pos]); } int main() { char str[] = "abc"; process(str, 0, 3,""); return 0; }
void process(string s,int n) { if (n == s.length()) { cout << s << endl; return; } for (int i = n; i < s.length(); i++) { swap(s[i],s[n]); process(s,n+1); } }
要注意带返回值的递归函数写法:
bool recur(int *a, int n,int res,int aim,int length) { if (n == length || res == aim) { return res == aim; } return recur(a, n + 1, res + a[n], aim,length)|| recur(a, n + 1, res, aim,length); }
比如:HDU 2018:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2018
两种解法,虽然递归解法要短很多,但是时间上,填表要快很多,因为递归会重复计算已经算过的值:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int a[55]; int f(int n) { if (n <= 4) return n; return f(n - 1) + f(n - 3); } int main() { int n; a[1] = 1; a[2] = 2; a[3] = 3; a[4] = 4; for (int i = 5; i < 55; i++) { a[i] = a[i - 1] + a[i - 3]; } while (cin >> n) { if (n == 0)break; cout << a[n]<< endl; } return 0; }
标签:php pid [] abc clu roc base swa 顺序
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/czc1999/p/10357290.html