标签:else tor eth 左右 and lse over read head
其他的神马分配其实归根结底还是靠chunk来做,只是别的操作把chunk组成大集装箱或者拆成多个小方块。
简单来说,chunk拥有着一块16MiB的地址,它利用伙伴算法拆分以8k大小的page为基准块的内存空间。
/**
Description of algorithm for PageRun/PoolSubpage allocation from PoolChunk
Notation: The following terms are important to understand the code
page - a page is the smallest unit of memory chunk that can be allocated
chunk - a chunk is a collection of pages
- in this code chunkSize = 2^{maxOrder} * pageSize
To begin we allocate a byte array of size = chunkSize
Whenever a ByteBuf of given size needs to be created we search for the first position
in the byte array that has enough empty space to accommodate the requested size and
return a (long) handle that encodes this offset information, (this memory segment is then
- marked as reserved so it is always used by exactly one ByteBuf and no more)
For simplicity all sizes are normalized according to PoolArena#normalizeCapacity method
This ensures that when we request for memory segments of size >= pageSize the normalizedCapacity
- equals the next nearest power of 2
To search for the first offset in chunk that has at least requested size available we construct a
- complete balanced binary tree and store it in an array (just like heaps) - memoryMap
- The tree looks like this (the size of each node being mentioned in the parenthesis)
depth=0 1 node (chunkSize)
depth=1 2 nodes (chunkSize/2)
..
..
depth=d 2^d nodes (chunkSize/2^d)
..
- depth=maxOrder 2^maxOrder nodes (chunkSize/2^{maxOrder} = pageSize)
- depth=maxOrder is the last level and the leafs consist of pages
With this tree available searching in chunkArray translates like this:
To allocate a memory segment of size chunkSize/2^k we search for the first node (from left) at height k
- which is unused
Algorithm:
Encode the tree in memoryMap with the notation
memoryMap[id] = x => in the subtree rooted at id, the first node that is free to be allocated
- is at depth x (counted from depth=0) i.e., at depths [depth_of_id, x), there is no node that is free
- As we allocate & free nodes, we update values stored in memoryMap so that the property is maintained
Initialization -
In the beginning we construct the memoryMap array by storing the depth of a node at each node
- i.e., memoryMap[id] = depth_of_id
Observations:
1) memoryMap[id] = depth_of_id => it is free / unallocated
2) memoryMap[id] > depth_of_id => at least one of its child nodes is allocated, so we cannot allocate it, but
some of its children can still be allocated based on their availability
3) memoryMap[id] = maxOrder + 1 => the node is fully allocated & thus none of its children can be allocated, it
- is thus marked as unusable
Algorithm: [allocateNode(d) => we want to find the first node (from left) at height h that can be allocated]
1) start at root (i.e., depth = 0 or id = 1)
2) if memoryMap[1] > d => cannot be allocated from this chunk
3) if left node value <= h; we can allocate from left subtree so move to left and repeat until found
- 4) else try in right subtree
Algorithm: [allocateRun(size)]
1) Compute d = log_2(chunkSize/size)
- 2) Return allocateNode(d)
Algorithm: [allocateSubpage(size)]
1) use allocateNode(maxOrder) to find an empty (i.e., unused) leaf (i.e., page)
2) use this handle to construct the PoolSubpage object or if it already exists just call init(normCapacity)
- note that this PoolSubpage object is added to subpagesPool in the PoolArena when we init() it
Note:
In the implementation for improving cache coherence,
- we store 2 pieces of information (i.e, 2 byte vals) as a short value in memoryMap
memoryMap[id]= (depth_of_id, x)
where as per convention defined above
the second value (i.e, x) indicates that the first node which is free to be allocated is at depth x (from root)
*/
id树中1-4095page基础块,2048-4095,所以1024只是2048和2049两个page合起来的空间depth树的高度0-11id,数组memoryMap存的值代表id指向的depth12,即最大高度加1,表示无空间。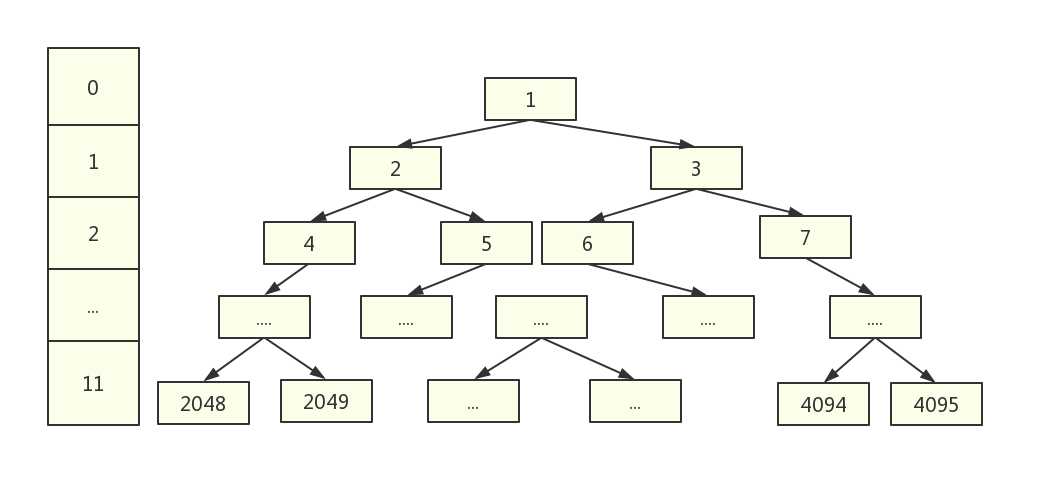
/**
* Algorithm to allocate an index in memoryMap when we query for a free node
* at depth d
*
* @param d depth
* @return index in memoryMap
*/
private int allocateNode(int d) {
int id = 1;
// 掩码,大于d的id的掩码
int initial = - (1 << d); // has last d bits = 0 and rest all = 1
byte val = value(id);
// 当前分配空间已经不满足了
if (val > d) { // unusable
return -1;
}
// 能走到这里说明接下来一定是有空间的
while (val < d || (id & initial) == 0) { // id & initial == 1 << d for all ids at depth d, for < d it is 0
// 左结点
id <<= 1;
val = value(id);
if (val > d) {
// 兄弟节点
id ^= 1;
val = value(id);
}
}
byte value = value(id);
assert value == d && (id & initial) == 1 << d : String.format("val = %d, id & initial = %d, d = %d",
value, id & initial, d);
setValue(id, unusable); // mark as unusable
// 更新父节点
updateParentsAlloc(id);
return id;
}
/**
* Update method used by allocate
* This is triggered only when a successor is allocated and all its predecessors
* need to update their state
* The minimal depth at which subtree rooted at id has some free space
*
* @param id id
*/
private void updateParentsAlloc(int id) {
while (id > 1) {
int parentId = id >>> 1;
byte val1 = value(id);
byte val2 = value(id ^ 1);
byte val = val1 < val2 ? val1 : val2;
setValue(parentId, val);
id = parentId;
}
}int initial = - (1 << d);此时的initial=1111100,后两位是00,作为掩码,显然id&initial==0的都是有效值(深度<2)。id,如图中树中1-4095,就是所谓的id,id能够反向计算出所在的层数,那么即可以知道该id节点所统管的内存空间大小。总的分配函数
long allocate(int normCapacity) {
if ((normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0) { // >= pageSize
return allocateRun(normCapacity);
} else {
return allocateSubpage(normCapacity);
}
}分配内存空间大于pageSize的函数
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {
int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts);
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
return id;
}分配内存空间小于pageSize的函数
/**
* Create/ initialize a new PoolSubpage of normCapacity
* Any PoolSubpage created/ initialized here is added to subpage pool in the PoolArena that owns this PoolChunk
*
* @param normCapacity normalized capacity
* @return index in memoryMap
*/
private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity);
synchronized (head) {
int d = maxOrder; // subpages are only be allocated from pages i.e., leaves
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages = this.subpages;
final int pageSize = this.pageSize;
freeBytes -= pageSize;
int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);
PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx];
if (subpage == null) {
subpage = new PoolSubpage<T>(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity);
subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;
} else {
subpage.init(head, normCapacity);
}
return subpage.allocate();
}
}this.subpages是一个2048长度的数组,每一个叶节点都对应一个,释放一个内存地址可以判断bitmap属性来判断是否为一个subpage,从而调用特殊的释放函数。
利用伙伴算法,分配的是以page为基准的成块的内存,如果小于page大小的调用subpage去分配
标签:else tor eth 左右 and lse over read head
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/GrimReaper/p/10385343.html