标签:eva 应用 image result 打开 jpeg oat pyplot ati
上篇文章介绍了深度学习中数据增强技术的应用,及部分TensorFlow实现代码。废话不说了,这篇接着介绍:
TensorFlow实现图片数据增强
注:类似的方法放在了代码中注释的部分,实际调试时可以分别打开运行
③图像色彩调整
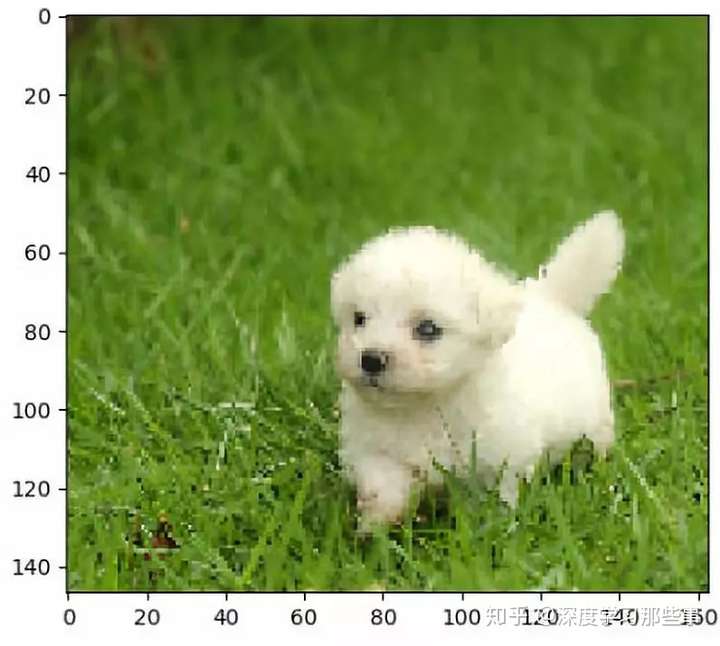
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf # 读取图片 image_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile("data/dog3.jpg", ‘br‘).read() # 4中调整图片大小的方法,实际应用中可以根据需求组合调整 with tf.Session() as sess: img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_data) plt.imshow(img_data.eval()) plt.show() # 将图片数据转换成实数类型 img_data = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data, dtype=tf.float32) # 亮度 # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_brightness(img_data,0.5) # adjusted = tf.clip_by_value(adjusted, 0.0, 1.0) # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_brightness(img_data, -0.5) # adjusted = tf.clip_by_value(adjusted, 0.0, 1.0) # adjusted = tf.image.random_brightness(img_data,0.5) # 对比度 # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_contrast(img_data,0.5) # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_contrast(img_data, 5) # adjusted = tf.image.random_contrast(img_data,0.1,5) # 色相 # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_hue(img_data,0.3) # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_hue(img_data, 0.1) # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_hue(img_data, 0.9) # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_hue(img_data, 0.6) # adjusted = tf.image.random_hue(img_data,0.5) # 饱和度 adjusted = tf.image.adjust_saturation(img_data,-5) # adjusted = tf.image.adjust_saturation(img_data, 5) # adjusted = tf.image.random_saturation(img_data,2,5) # 图像标准化 均值为0 方差变为1 # adjusted = tf.image.per_image_standardization(img_data) plt.imshow(adjusted.eval()) plt.show()
图片效果
原图:
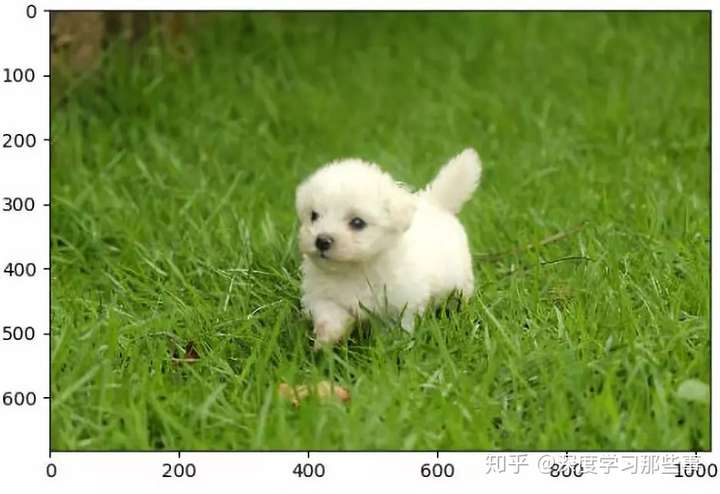

处理后:
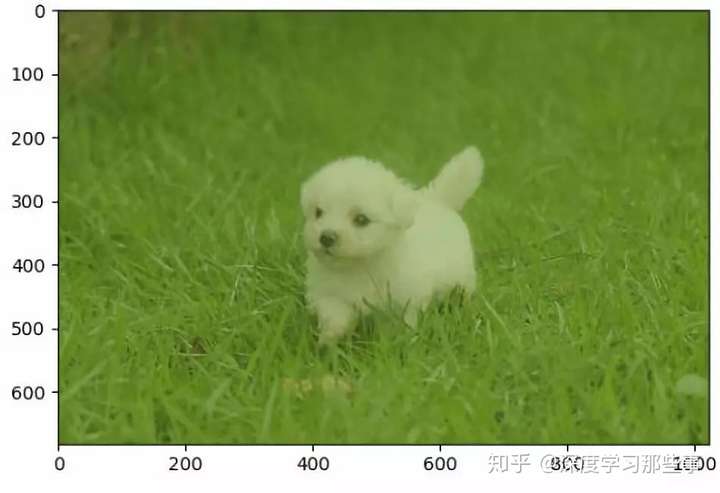
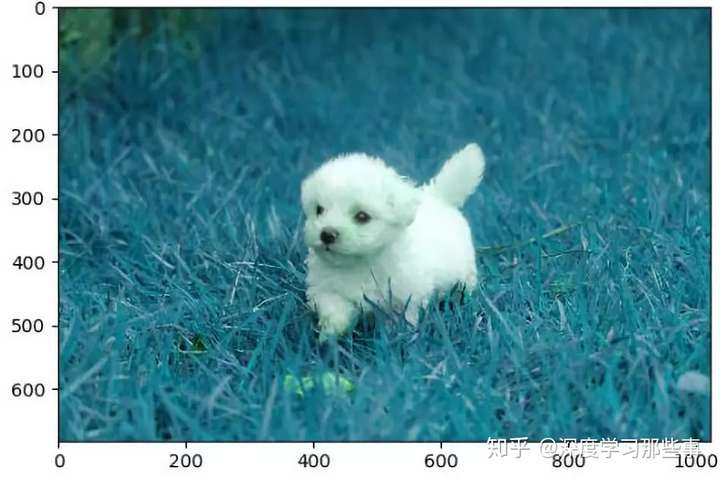




④标注、裁剪
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf # 读取图片 image_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile("data/dog3.jpg", ‘br‘).read() # with tf.Session() as sess: img_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_data) plt.imshow(img_data.eval()) plt.show() # 将图片数据转换成实数类型 img_data = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data, dtype=tf.float32) # 将图片缩小一些,这样可视化能让标注框更加清楚 img_data = tf.image.resize_images(img_data,[180,267],method=1) batched = tf.expand_dims(tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data,tf.float32),0) boxes = tf.constant([[[0.05,0.05,0.9,0.7],[0.28,0.36,0.62,0.56]]]) result = tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(batched,boxes=boxes) plt.imshow(result[0].eval()) plt.show() # print(result) # 随机截取图片 begin,size,bbox_for_draw =tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(tf.shape(img_data),bounding_boxes=boxes,min_object_covered=0.4) batched = tf.expand_dims(tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img_data,tf.float32),0) image_with_box = tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(batched,bbox_for_draw) distored_image = tf.slice(img_data,begin,size=size) plt.imshow(distored_image.eval()) plt.show()
图片效果
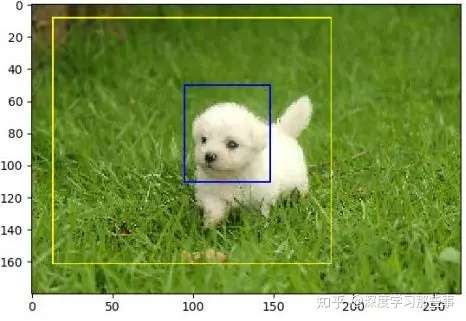
关注公众号“从机器学习到深度学习那些事”获取更多最新资料
代码整合总结
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ‘‘‘ 给定一张图片,随机调整图像的色彩。因为调整亮度、对比度、饱和度和色相的顺序会影响最后得到的结果,所以可以定义多种不同的顺序。 具体使用哪一种顺序可以在训练数据预处理时随机的选择一种。这样可以进一步降低无关因素对模型的影响 ‘‘‘ def distort_color(image, color_ordering=0): if color_ordering == 0: image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255) image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) elif color_ordering == 1: image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2) elif color_ordering == 2: image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2) image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255) # 还可以添加其他的排列 else: image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255) image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2) image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5) return tf.clip_by_value(image, 0.0, 1.0) def preprocess_for_train(image, height, width, bbox): # 如果没有提供标准框,则认为整个图像就是需要关注的部分 if bbox is None: bbox = tf.constant([0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 1, 4]) # 转换图像张量的类型: if image.dtype != tf.float32: image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32) # 随机截取图像,减少需要关注的物体大小对图像识别算法的影响 # 为图像生成一个随机distorted的边框,Generate a single randomly distorted bounding box for an image bbox_begin, bbox_size, _ = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(tf.shape(image), bounding_boxes=bbox,min_object_covered=0.4) distorted_image = tf.slice(image, bbox_begin, bbox_size) # 将随机截取的图像调整为神经网络输入层的大小。大小调整的算法是随机选择的。 distorted_image = tf.image.resize_images(distorted_image, [height, width], method=np.random.randint(4)) # 随机左右翻转图像 distorted_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(distorted_image) # 使用一种随机的顺序处理图像的色彩 distorted_image = distort_color(distorted_image, np.random.randint(2)) return distorted_image image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile("./data/dog1.jpg", ‘br‘).read() with tf.Session() as sess: image_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data) bboxes = tf.constant([[[0.05, 0.05, 0.9, 0.7], [0.35, 0.47, 0.5, 0.56]]]) # 运行6次获得6中不同的图片,展示出来 for i in range(6): result = preprocess_for_train(image_data, 299, 299, bboxes) plt.imshow(result.eval()) plt.show()
参考资料
21个项目玩转深度学习
TensorFlow实战Google深度学习框架

标签:eva 应用 image result 打开 jpeg oat pyplot ati
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ziyan09/p/10412722.html