标签:printf chain sha span 介绍 lse int UNC 其他
一:链表介绍
链表是有序的列表,但在内存的分部较为特殊
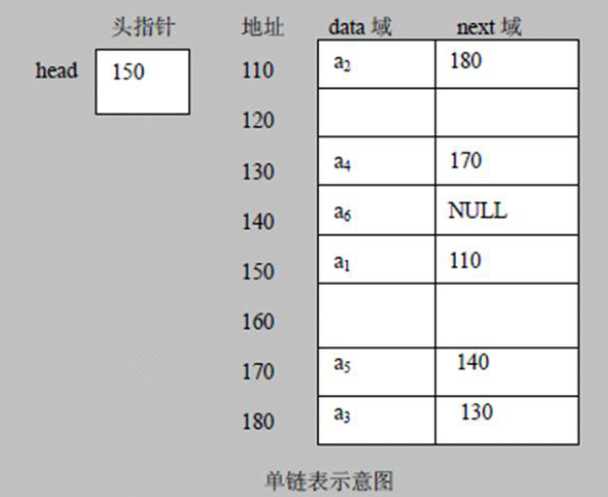
二:单链表的举例使用
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type Students struct{
num int
name string
next *Students
}
//尾部添加
func InsertStudentNode1(head *Students, student *Students){
//设置从头部开始遍历
temp := head
for {
if temp.next == nil {
break
}
temp = temp.next
}
temp.next=student
}
//有序添加
func InsertStudentNode2(head *Students, student *Students){
temp := head
for {
if temp.next == nil {
break
}else if temp.next.num > student.num {//按照有小到大添加
break
}else if temp.next.num == student.num {
fmt.Println("节点已存在")
return
}
temp = temp.next
}
student.next = temp.next
temp.next = student
}
//显示所有节点
func ShowStudentNode(head *Students){
//设置从头部开始遍历
show := head
//先判断是否为空链表
if show.next == nil {
fmt.Println("链表为空")
return
}
for {
if show.next == nil {
break
}
fmt.Printf("学生编号:%v,姓名:%v\n", show.next.num, show.next.name)
show = show.next
}
}
//删除节点
func DelStudentNode(head *Students, num int){
temp := head
if temp.next == nil {
fmt.Println("链表为空")
return
}
for {
if temp.next.num == num {
break
}else if temp.next == nil {
fmt.Println("节点不存在")
return
}
temp = temp.next
}
temp.next = temp.next.next
}
func main() {
//初始化一个头结点
head := &Students{}
//添加新节点
student1 := &Students{
num : 1,
name : "james",
}
student2 := &Students{
num : 2,
name : "kobe",
}
student5 := &Students{
num : 5,
name : "jorden",
}
student3 := &Students{
num : 3,
name : "shark",
}
// 添加节点
InsertStudentNode1(head, student1)
InsertStudentNode1(head, student2)
InsertStudentNode1(head, student5)
InsertStudentNode2(head, student3)
//获取
ShowStudentNode(head)
//删除编号为5的学生
DelStudentNode(head, 1)
fmt.Println("删除后----------------")
//获取
ShowStudentNode(head)
} 结果 [ `go run chainTable.go` | done ]
学生编号:1,姓名:james
学生编号:2,姓名:kobe
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
学生编号:5,姓名:jorden
删除后----------------
学生编号:2,姓名:kobe
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
学生编号:5,姓名:jorden
三:双向链表
①:双线链表的优点
①-1:单向链表的查找方向只能向后查找,而双线链表可以向后也可以向前;
①-2:单向链表不能自我删除,需要其他节点的协助,而双线链表可以自我删除(根据指向的前节点与指向的后节点)
②:举例说明
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type Students struct{
num int
name string
pre *Students
next *Students
}
//尾部添加
func InsertStudentNode1(head *Students, student *Students){
//设置从头部开始遍历
temp := head
for {
if temp.next == nil {
break
}
temp = temp.next
}
temp.next=student
student.pre = temp
}
//有序添加
func InsertStudentNode2(head *Students, student *Students){
temp := head
last := false
for {
if temp.next == nil {
last = true
break
}else if temp.next.num > student.num {//按照有小到大添加
break
}else if temp.next.num == student.num {
fmt.Println("节点已存在")
return
}
temp = temp.next
}
if last {
temp.next = student
student.pre = temp
}else{
student.next = temp.next
temp.next = student
student.next.pre = student
student.pre = temp
}
}
//显示所有节点
func ShowStudentNode(head *Students){
//设置从头部开始遍历
show := head
//先判断是否为空链表
if show.next == nil {
fmt.Println("链表为空")
return
}
for {
if show.next == nil {
fmt.Println("最后节点的前一个节点信息")
fmt.Printf("学生编号:%v,姓名:%v\n", show.pre.num, show.pre.name)
return
}
fmt.Printf("学生编号:%v,姓名:%v\n", show.next.num, show.next.name)
show = show.next
}
}
//删除节点
func DelStudentNode(head *Students, num int){
temp := head
if temp.next == nil {
fmt.Println("链表为空")
return
}
//用于判断是否为最后一个节点
last := false
for {
if temp.next.num == num {
//再判断一下是否为最后一个节点
if temp.next.next == nil {
last = true
}
break
}else if temp.next == nil {
fmt.Println("节点不存在")
return
}
temp = temp.next
}
if last {
temp.next = nil
}else{
temp.next = temp.next.next
temp.next.pre = temp
}
}
func main() {
//初始化一个头结点
head := &Students{}
//添加新节点
student1 := &Students{
num : 1,
name : "james",
}
student2 := &Students{
num : 2,
name : "kobe",
}
student5 := &Students{
num : 5,
name : "jorden",
}
student3 := &Students{
num : 3,
name : "shark",
}
// 添加节点
InsertStudentNode1(head, student1)
InsertStudentNode1(head, student2)
InsertStudentNode1(head, student5)
InsertStudentNode2(head, student3)
//获取
ShowStudentNode(head)
//删除编号为5的学生
DelStudentNode(head, 1)
fmt.Println("删除后----------------")
//获取
ShowStudentNode(head)
}
结果
[ `go run doubleChainTable.go` | done ]
学生编号:1,姓名:james
学生编号:2,姓名:kobe
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
学生编号:5,姓名:jorden
最后节点的前一个节点信息
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
删除后----------------
学生编号:2,姓名:kobe
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
学生编号:5,姓名:jorden
最后节点的前一个节点信息
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
四:环形单向链表
①:介绍,参考环形数组队列
②:环形单向链表与单向链表和双向链表不同之处在于,head也要存放数据
③:使用举例
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type Students struct{
num int
name string
next *Students
}
//尾部添加
func InsertStudentNode1(head *Students, student *Students){
temp := head
//先判断头部是否为空
if temp.next == nil {
temp.num = student.num
temp.name = student.name
//自环
temp.next = temp
return
}
for {
if temp.next == head {
break
}
temp = temp.next
}
student.next = head
temp.next=student
}
//显示所有节点
func ShowStudentNode(head *Students){
//设置从头部开始遍历
show := head
//先判断是否为空链表
if show.next == nil {
fmt.Println("链表为空")
return
}
for {
fmt.Printf("学生编号:%v,姓名:%v\n", show.num, show.name)
if show.next == head {
break
}
show = show.next
}
}
//删除节点
func DelStudentNode(head *Students, num int) *Students{
temp := head
helper := head//帮助节点跳过将要删除的节点
if temp.next == nil {
fmt.Println("链表为空")
return head
}
//判断是否只有一个节点
if temp.next == head {
if temp.num == num {
temp.next = nil
}else{
fmt.Println("节点不存着")
}
return head
}
//将helper定位到最后一个节点
for {
if helper.next == head{
break
}
helper = helper.next
}
//当节点有多个时
flag := true
for{
if temp.next == head{
break
}
if temp.num == num {
if temp == head{//判断是否删除头节点
head = head.next
}
helper.next = temp.next
fmt.Println("num=",num)
flag = false
break
}
temp = temp.next
helper = helper.next
}
if flag {
if temp.num == num {
//说明要删除的节点是最后一个,这时temp已经指向最后一个节点
helper.next = temp.next
}else{
fmt.Println("节点不存在")
}
}
//防止要删除的节点是头部,返回最新的头部位置
return head
}
func main() {
//初始化一个头结点
head := &Students{}
//添加新节点
student1 := &Students{
num : 1,
name : "james",
}
student2 := &Students{
num : 2,
name : "kobe",
}
student3 := &Students{
num : 3,
name : "shark",
}
student4 := &Students{
num : 4,
name : "shark",
}
// 添加节点
InsertStudentNode1(head, student1)
InsertStudentNode1(head, student2)
InsertStudentNode1(head, student3)
InsertStudentNode1(head, student4)
// 获取
ShowStudentNode(head)
//删除编号为5的学生
head = DelStudentNode(head, 1)
fmt.Println("删除后----------------")
//获取
ShowStudentNode(head)
}
结果
[ `go run circleChainTable.go` | done ]
学生编号:1,姓名:james
学生编号:2,姓名:kobe
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
学生编号:4,姓名:shark
num= 1
删除后----------------
学生编号:2,姓名:kobe
学生编号:3,姓名:shark
学生编号:4,姓名:shark
标签:printf chain sha span 介绍 lse int UNC 其他
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/louis181214/p/10419136.html