标签:步骤 数据 aic empty class img span failed printf
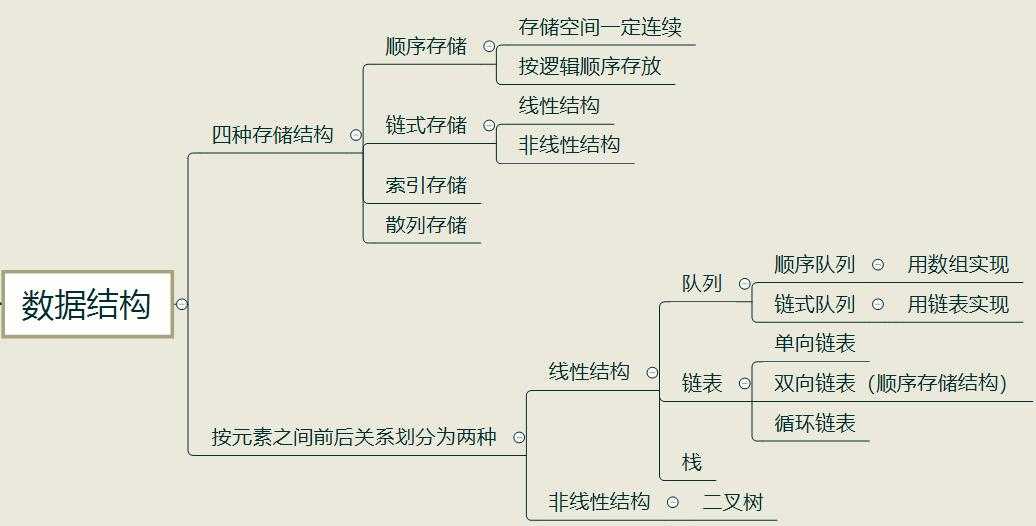
链式队列----用链表实现,链式队列就是一个操作受限的单向链表,如果读者了解单向链表的建立过程,那理解链式队列就很容易了,先回顾一下单向链表的建立过程
(不熟悉单向链表的可以先看看另一片随笔,再回来看链式队列理解起来更容易?https://www.cnblogs.com/lanhaicode/p/10304567.html)
单向链表节点的组成部分
1 struct link
2 {
3 int data;
4 struct link *next;
5 };
数据域:data----用来存储节点数据
指针域:struct link *next----用来存储下一个节点的地址
链式队列和单向链表比就多了两个指针,头指针和尾指针(这里我多加了一个length来记录队列的长度)
1 typedef struct QNode /* 声明链式队列的结点 */
2 {
3 int data;
4 struct QNode *next;
5 }Node;
6 typedef struct QueuePoint /* 声明链式队列的首尾指针 */
7 {
8 Node *front;
9 Node *rear;
10 int length; /* 记录链式队列长度 */
11 }Queue;
后面就是单向链表的建立了,这里就不再赘述了,重点分析下头指针的尾指针的移动,为了方便理解先附上main函数部分的代码
1 main()
2 {
3 int i = 0;
4 char c;
5 Queue q; //链式队列首尾指针 和 长度
6
7 q.front = q.rear = NULL; /* 首尾指针初始化 */
8 q.length = 0; /* 链式队列长度初始化 */
9 q = init(q); /* 初始化队列 */
10 printf("Do you want to append a new node(Y/N)?");
11 scanf_s(" %c", &c);
12 while (c == ‘Y‘ || c == ‘y‘)
13 {
14 q = AppendNode(q); /* 入队*/
15 DisplyNode(q); /* 按先进先出对队列进行打印 */
16 printf("Do you want to append a new node(Y/N)?");
17 scanf_s(" %c", &c);
18 }
19 printf("Do you want to delete node(Y/N)?");
20 scanf_s(" %c", &c);
21 while (c == ‘Y‘ || c == ‘y‘)
22 {
23 q = DeletNode(q);
24 DisplyNode(q);
25 printf("Do you want to delete node(Y/N)?");
26 scanf_s(" %c", &c);
27 }
28
29 return 0;
30 }
下面上图
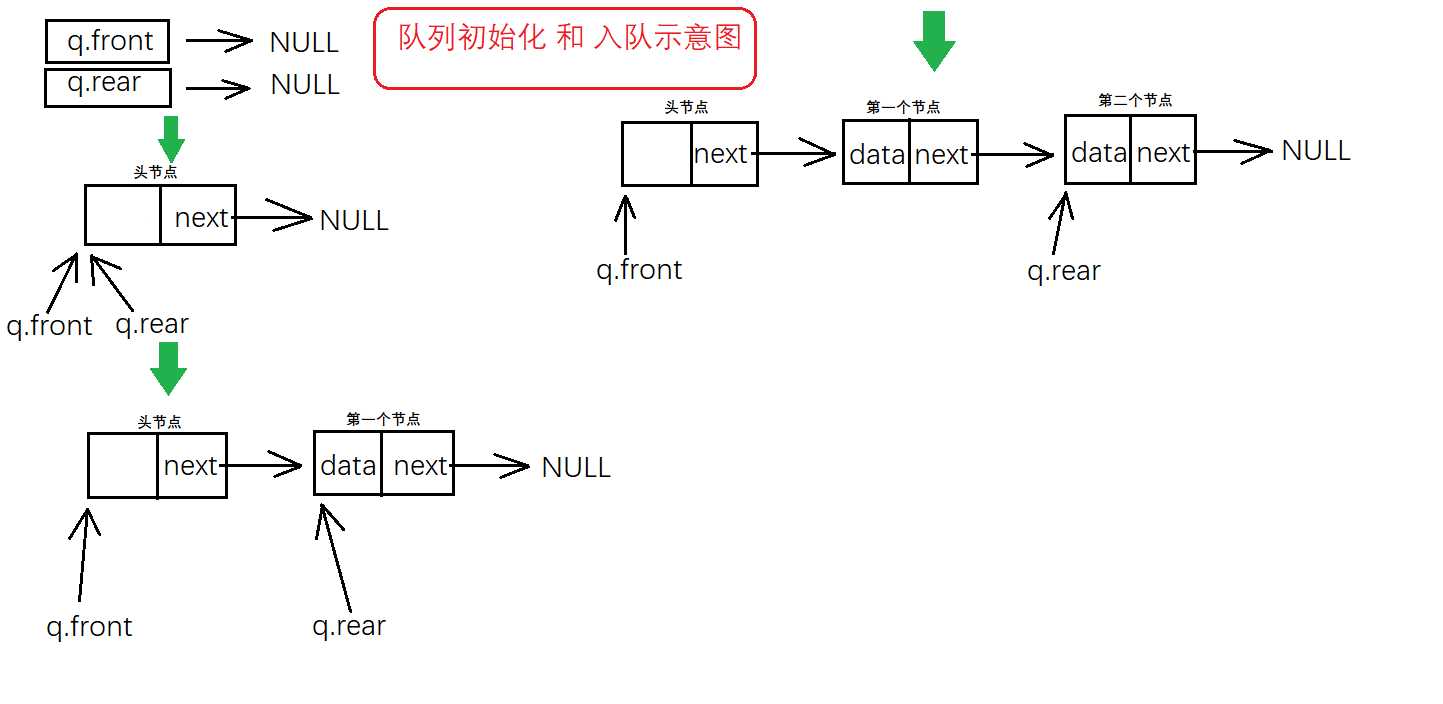
(灵魂画手已上线)
简单描述一下上图的步骤
第一步:初始化队列(就是添加一个头节点在队列中),头结点不存储数据,使队首指针和队尾指针都指向头结点
第二步:入队(添加节点),使队尾指针指向头新建的节点,队首指针不变仍然指向头结点
初始化队列和入队----实现代码
1 //函数功能:初始化队列(其实就是搞个头结点放在队列里面)
2 //单独弄个子函数来初始化队列是为了方便入队的时候判断队列是否为空
3 Queue init (Queue p)
4 {
5 p.front = p.rear = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
6 if (p.front == NULL && p.rear == NULL)
7 {
8 printf("initialization failed");
9 exit(0);
10 }
11 p.front->next = NULL;
12
13 return p;
14 }
15 //函数功能:新建节点并添加到队列中,记录队列长度
16 Queue AppendNode (Queue p)
17 {
18 int data;
19 Node *q;
20
21 q = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
22 if (q == NULL) /* 判断分配内存是否失败 */
23 {
24 printf("No enough memory to allocate");
25 exit(0);
26 }
27 p.rear->next = q; /* 最后一个节点的指针指向新建节点*/
28 p.rear = q; /* 队尾指针指向新建节点*/
29
30 printf("Input node data\n");
31 scanf("%d", &data);
32 p.rear->data = data;
33 p.rear->next = NULL;
34 p.length++;
35 return p;
36
37 }
后面来分析下出队时首尾指针的变化,因为后面出队时要用到判断队列是否为空的一个子函数,这里先附上子函数代码
1 int IsemptyQueue(Queue p)
2 {
3 if (p.front == p.rear) /* 队首指针和队尾指针重合队列为空 */
4 {
5 return Empty;
6 }
7 else
8 {
9 return NoEmpty;
10 }
11 }
出队时队首指针的位置是不变的,队首指针始终指向头节点,出队时头节点的指针域指向出队节点的后一节点,并将出队的节点用free()函数释放掉,为了方便读者理解下面上图
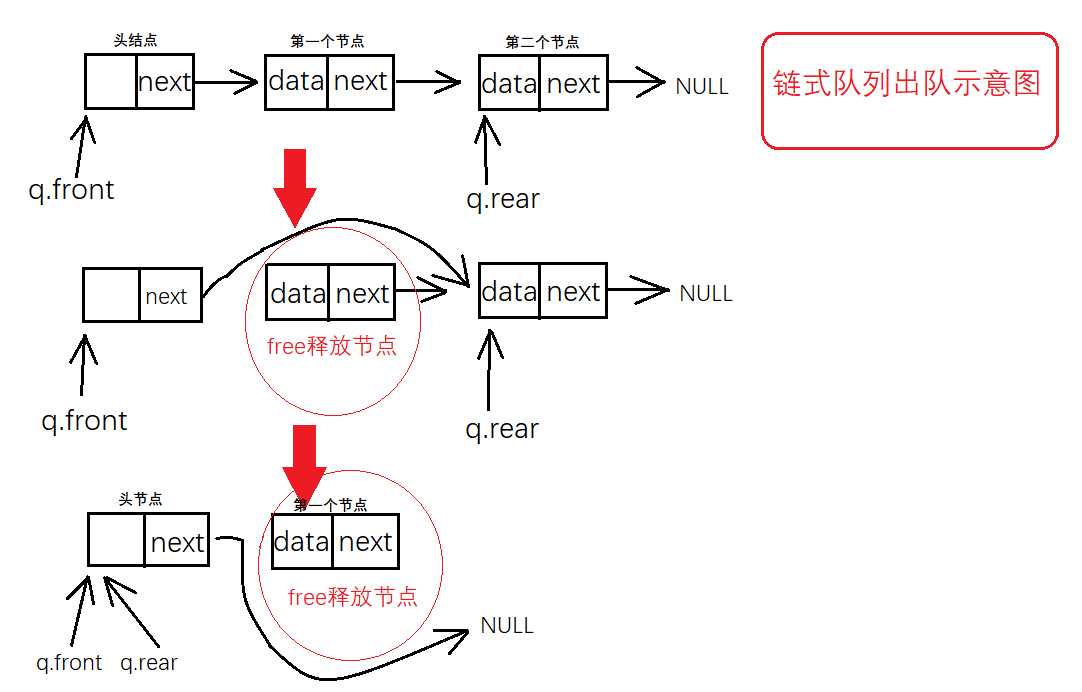
出队实现代码
1 Queue DeletNode (Queue p)
2 {
3 Node *del;
4
5 if (IsemptyQueue(p) == Empty) /* 判断队列是否为空*/
6 {
7 printf("队列为空,无法出队 ");
8 return p;
9 }
10 else /* 队列不为空 */
11 {
12 if (p.front->next == p.rear) /* 如果出队的节点为最后一个节点 */
13 {
14 printf("出队节点的数据为%d----", p.rear->data);
15 free(p.rear); /* 释放最后一一个节点*/
16 p.rear = p.front; /* 队首指针和队尾指针都指向头节点 */
17 p.front->next = NULL;
18 p.length--;
19 }
20 else
21 {
22 del = p.front->next;
23 printf("出队节点的数据为%d----", del->data);
24 p.front->next = p.front->next->next; /* 使头节点的指针域指向出队节点的下一个节点 */
25 free(del); /* 释放出队的节点 */
26 p.length--;
27 }
28
29 return p;
30 }
31 }
1.顺序队列是用数组实现的,首指针在出队的时候移动,尾指针在入队的时候移动,需要考虑队列为空和队列为满的两种情况
2.链式队列是用链表实现的,首指针不移动始终指向头节点,尾指针在入队的时候移动,只考虑队列为空的情况(不用考虑满是因为链表长度在程序运行过程中可以不断增加,只要存储空间够malloc就能申请内存空间来存放节点)
下面附上完整代码

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #define Empty 0 /* 队列为空 */ 5 #define NoEmpty 1 /* 队列不为空*/ 6 7 typedef struct QNode /* 声明链式队列的结点 */ 8 { 9 int data; 10 struct QNode *next; 11 }Node; 12 typedef struct QueuePoint /* 声明链式队列的首尾指针 */ 13 { 14 Node *front; 15 Node *rear; 16 int length; /* 记录链式队列长度 */ 17 }Queue; 18 19 void DisplyNode (Queue p); /* 打印队列 */ 20 Queue init (Queue p); /* 初始化队列 */ 21 Queue AppendNode (Queue p); /* 入队 */ 22 Queue DeletNode (Queue p); /* 出队 */ 23 int IsemptyQueue (Queue p); /* 判断队列是否为空*/ 24 main() 25 { 26 int i = 0; 27 char c; 28 Queue q; //链式队列首尾指针 和 长度 29 30 q.front = q.rear = NULL; /* 首尾指针初始化 */ 31 q.length = 0; /* 链式队列长度初始化 */ 32 q = init(q); /* 初始化队列 */ 33 printf("Do you want to append a new node(Y/N)?"); 34 scanf_s(" %c", &c); 35 while (c == ‘Y‘ || c == ‘y‘) 36 { 37 q = AppendNode(q); /* 入队 */ 38 DisplyNode(q); /* 按先进先出对队列进行打印 */ 39 printf("Do you want to append a new node(Y/N)?"); 40 scanf_s(" %c", &c); 41 } 42 printf("Do you want to delete node(Y/N)?"); 43 scanf_s(" %c", &c); 44 while (c == ‘Y‘ || c == ‘y‘) 45 { 46 q = DeletNode(q); /* 出队 */ 47 DisplyNode(q); /* 按先进先出对队列进行打印 */ 48 printf("Do you want to delete node(Y/N)?"); 49 scanf_s(" %c", &c); 50 } 51 52 return 0; 53 } 54 int IsemptyQueue(Queue p) 55 { 56 if (p.front == p.rear) /* 队首指针和队尾指针重合队列为空 */ 57 { 58 return Empty; 59 } 60 else 61 { 62 return NoEmpty; 63 } 64 } 65 Queue DeletNode (Queue p) 66 { 67 Node *del; 68 69 if (IsemptyQueue(p) == Empty) /* 判断队列是否为空*/ 70 { 71 printf("队列为空,无法出队 "); 72 return p; 73 } 74 else /* 队列不为空 */ 75 { 76 if (p.front->next == p.rear) /* 如果出队的节点为最后一个节点 */ 77 { 78 printf("出队节点的数据为%d----", p.rear->data); 79 free(p.rear); /* 释放最后一一个节点*/ 80 p.rear = p.front; /* 队首指针和队尾指针都指向头节点 */ 81 p.front->next = NULL; 82 p.length--; 83 } 84 else 85 { 86 del = p.front->next; 87 printf("出队节点的数据为%d----", del->data); 88 p.front->next = p.front->next->next; /* 使头节点的指针域指向出队节点的下一个节点 */ 89 free(del); /* 释放出队的节点 */ 90 p.length--; 91 } 92 93 return p; 94 } 95 } 96 //函数功能:初始化队列(其实就是搞个头结点放在队列里面) 97 //单独弄个子函数来初始化队列是为了方便入队的时候判断队列是否为空 98 Queue init (Queue p) 99 { 100 p.front = p.rear = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 101 if (p.front == NULL && p.rear == NULL) 102 { 103 printf("initialization failed"); 104 exit(0); 105 } 106 p.front->next = NULL; 107 108 return p; 109 } 110 //函数功能:新建节点并添加到队列中,记录队列长度 111 Queue AppendNode (Queue p) 112 { 113 int data; 114 Node *q; 115 116 q = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 117 if (q == NULL) /* 判断分配内存是否失败 */ 118 { 119 printf("No enough memory to allocate"); 120 exit(0); 121 } 122 p.rear->next = q; /* 最后一个节点的指针指向新建节点*/ 123 p.rear = q; /* 队尾指针指向新建节点*/ 124 125 printf("Input node data\n"); 126 scanf("%d", &data); 127 p.rear->data = data; 128 p.rear->next = NULL; 129 p.length++; 130 return p; 131 132 } 133 //函数功能:按照先进先出原则对队列进行打印 134 void DisplyNode (Queue p) 135 { 136 if (IsemptyQueue(p) == Empty) 137 { 138 printf("队列为空,无法打印\n"); 139 } 140 else 141 { 142 p.front = p.front->next; 143 printf("当前队列中的%d个节点[", p.length); 144 while (p.front != NULL) 145 { 146 printf("%d->", p.front->data); 147 p.front = p.front->next; 148 } 149 putchar(‘]‘); 150 putchar(‘\n‘); 151 } 152 }
程序试运行结果:
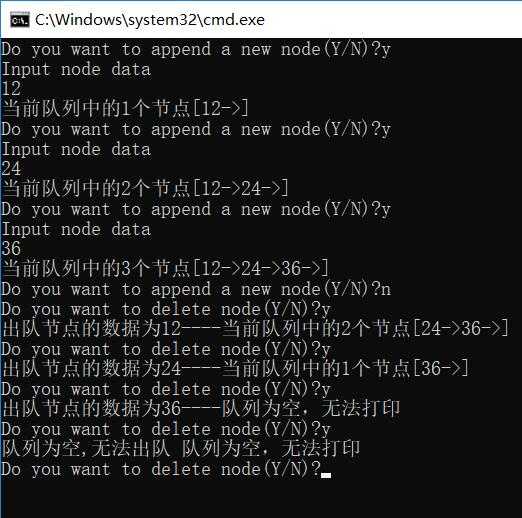
标签:步骤 数据 aic empty class img span failed printf
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lanhaicode/p/10432004.html