标签:span info 其它 ima .com memset tor dfs argv
小明参加了学校的趣味运动会,其中的一个项目是:跳格子。
地上画着一些格子,每个格子里写一个字,如下所示:(也可参见p1.jpg)
从我做起振
我做起振兴
做起振兴中
起振兴中华
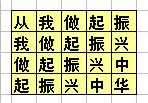
比赛时,先站在左上角的写着“从”字的格子里,可以横向或纵向跳到相邻的格子里,但不能跳到对角的格子或其它位置。
一直要跳到“华”字结束。 要求跳过的路线刚好构成“从我做起振兴中华”这句话。 请你帮助小明算一算他一共有多少种可能的跳跃路线呢?
答案是一个整数,请通过浏览器直接提交该数字。
注意:不要提交解答过程,或其它辅助说明类的内容。
分析:
思路一:dfs深搜
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 // int dfs(int x,int y,int step){ 8 // if(step==7){ 9 // if(x==5&&y==4) return 1; 10 // else return 0; 11 // } 12 // else{ 13 // return dfs(x+1,y,step+1)+dfs(x,y+1,step+1); 14 // } 15 // } 16 int cnt=0; 17 void dfs(int x,int y,int step){ 18 if(step==7){ 19 if(x==5&&y==4) cnt++; 20 else return ; 21 } 22 else{ 23 dfs(x+1,y,step+1); 24 dfs(x,y+1,step+1); 25 } 26 27 } 28 29 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 30 { 31 // cout<<dfs(1,1,0)<<endl; 32 dfs(1,1,0); 33 cout<<cnt<<endl; 34 return 0; 35 }
思路二:
dp思想,先说一下近似dp的思想的做法
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int f(int x,int y){ 8 if(x==5||y==4) return 1;/*走到边界的地方那么他就一定是一条路径,类似dp*/ 9 else{ 10 return f(x+1,y)+f(x,y+1); 11 } 12 } 13 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 14 { 15 cout<<f(1,1)<<endl; 16 return 0; 17 }
下面是正宗dp做法:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 using namespace std; 5 int main(){ 6 int dp[6][5]; 7 memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); 8 dp[1][1]=1; 9 for( int x=1; x<=5; x++ ){ 10 for( int y=1; y<=4; y++ ){ 11 /*[x][y]位置要么从[x-1][y]向右走,要么从[x][y-1]向下走*/ 12 dp[x][y]+=dp[x-1][y]+dp[x][y-1]; 13 // printf("dp[%d][%d]=%d\n",x,y,dp[x][y]); 14 } 15 } 16 cout<<dp[5][4]<<endl; 17 return 0; 18 }
标签:span info 其它 ima .com memset tor dfs argv
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Bravewtz/p/10447813.html