标签:cas set oid 兄弟节点 标准 code insert btree private
本文将主要讲述平衡二叉树中的红黑树,红黑树是一种我们经常使用的树,相较于 AVL 树他无论是增加还是删除节点,其结构的变化都能控制在常树次;在 JDK 中的 TreeMap 同样也是使用红黑树实现的;
红黑树是在AVL 树平衡条件的基础上,进一步放宽条件,从而使得红黑树在动态变化的时候,其结构的变化在常数次;其标准大致可以表示为; 任一节点左、右子树的高度,相差不得超过两倍。
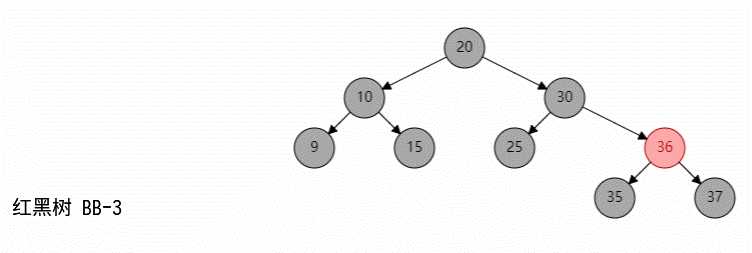
同他的名字,红黑树的节点是有颜色的,如图所示:
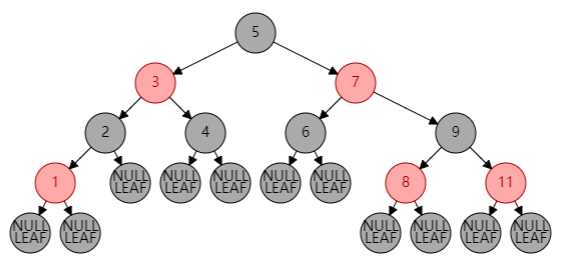
其性质如下:
(2,4)B 树,如果将红黑树的红色节点和其父节点合并为一个超级节点,则其结构和(2,4)B 树 的结构完全一样,所以在学习红黑树的时候,可以对照 B 的转换方法,帮助理解;
public class RBTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
private RBTNode<T> root; // 根结点
public class RBTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
boolean color; // 颜色
T key; // 关键字(键值)
RBTNode<T> left; // 左孩子
RBTNode<T> right; // 右孩子
RBTNode<T> parent; // 父结点
}
}因为通常情况下插入的节点会标记为红色,那么就有可能导致两个红色的节点练成父子,所以需要通过一下方法修复;
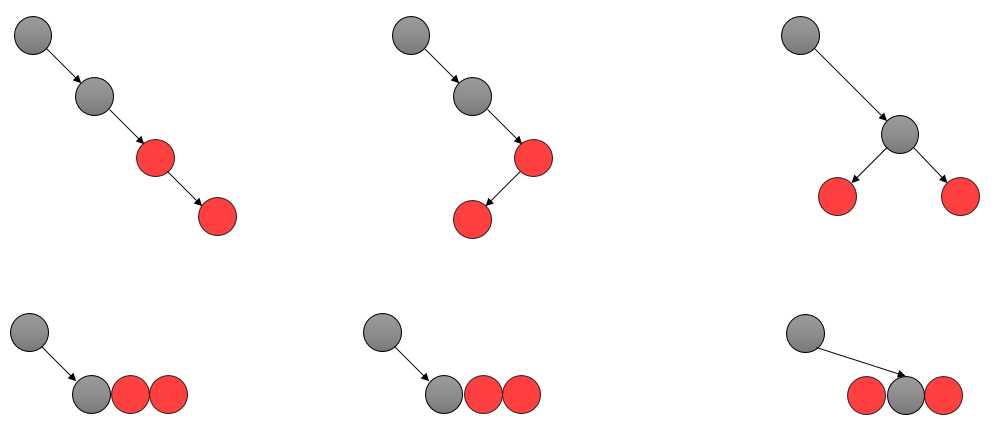
如图所示,如果插入的红色节点和父节点一起组成了3个关键码的超级节点,在 B 树的角度上则只需要重新标记颜色,使黑色节点位于中间即可;表现在红黑树中就需要进行旋转操作,如图:
双红节点同边:
双红节点异边:
其实在这里如果忽略颜色,其旋转操作就可 AVL 树是一样的;那么在实现的时候同样可以使用之前讲过的 3+4 重构;
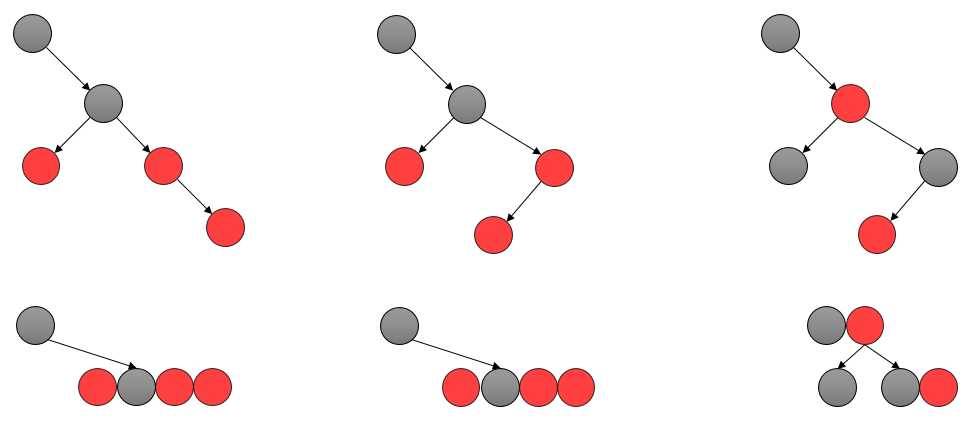
如图所示,如果红色节点上移后,同其父节点组成的超级节点是4个关键码,则发生了上溢,需要将其分裂为两个节点;但此时表现在红黑树上其结构并未发生变化,所以只需要重新染色即可;
如图所示:
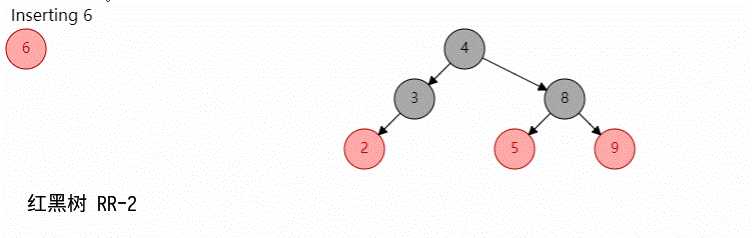
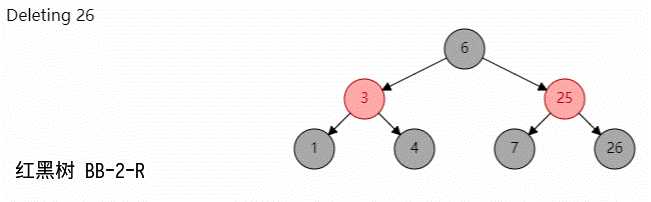
当删除黑节点的时候,会使得该分支的黑高度降低,从而不满足每个分支的黑高度相等,所以下面将删除黑节点分成几种情况进行修复;
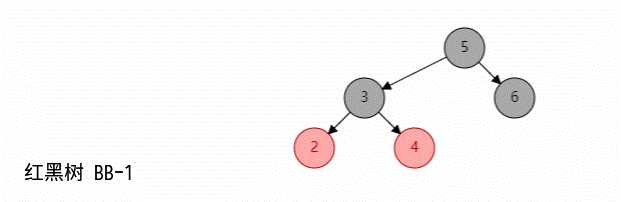
当删除的节点是黑色节点,且其兄弟节点是黑色,同时有红孩子的时候;如果转化为 (2,4)B 树:
如图所示:
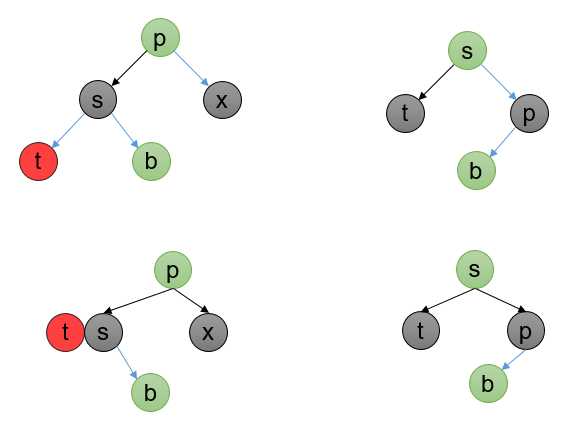
如果父节点是红色,有黑色兄弟节点,并且没有红色孩子:
转化为 (2,4)B 树:
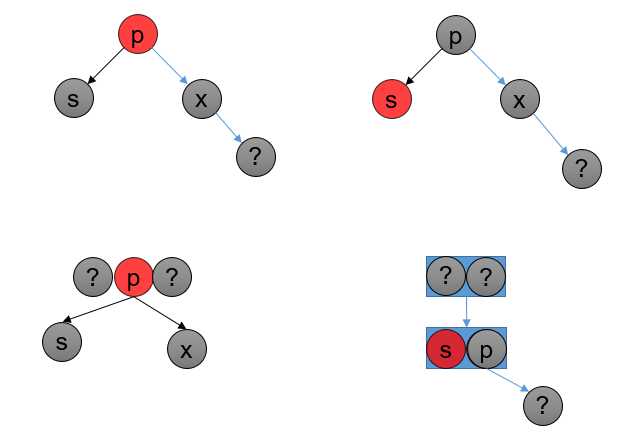
如图所示,
如果父节点是黑色,有黑色兄弟节点,并且没有红色孩子:
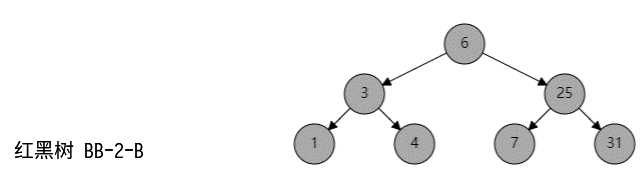
转化为 (2,4)B 树:
如图所示:
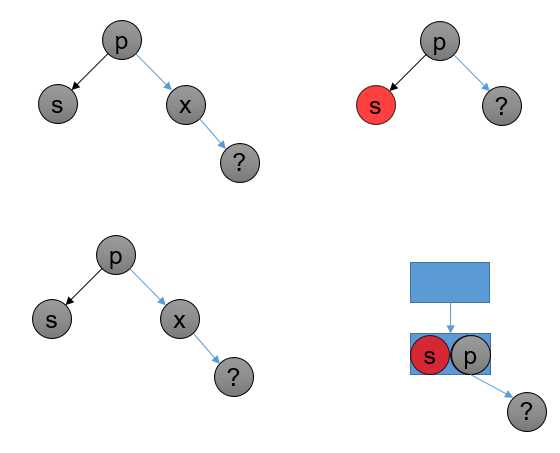
bb-2-r 一样,但是其父节点为黑色;O(logn) 次;如果父节点是黑色,有红色兄弟节点:
转化为 (2,4)B 树:
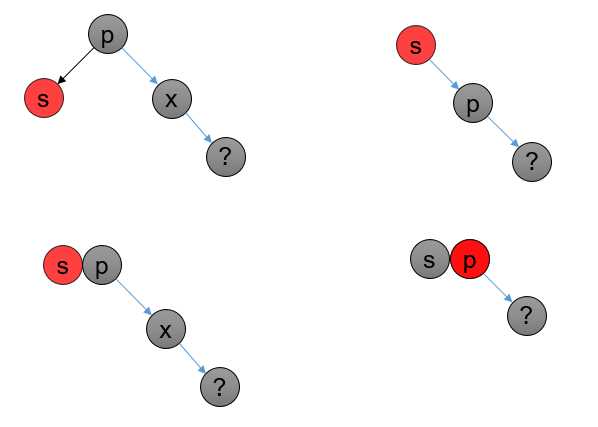
如图所示:
private RBTNode<T> search(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x == null) return x;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
return search(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
return search(x.right, key);
else
return x;
}public void insert(T key) {
insert(new RBTNode<T>(key, BLACK, null, null, null));
}
private void insert(RBTNode<T> node) {
int cmp;
RBTNode<T> y = null;
RBTNode<T> x = this.root;
// 1. 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点添加到二叉查找树中。
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
node.parent = y;
if (y != null) {
cmp = node.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0)
y.left = node;
else
y.right = node;
} else {
this.root = node;
}
// 2. 设置节点的颜色为红色
node.color = RED;
// 3. 将它重新修正为一颗二叉查找树
insertFixUp(node);
}
private void insertFixUp(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> parent, gparent;
// 若“父节点存在,并且父节点的颜色是红色”
while (((parent = parentOf(node)) != null) && isRed(parent)) {
gparent = parentOf(parent);
//若“父节点”是“祖父节点的左孩子”
if (parent == gparent.left) {
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.right;
if ((uncle != null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// Case 2条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子
if (parent.right == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
leftRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子。
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
rightRotate(gparent);
} else { //若“z的父节点”是“z的祖父节点的右孩子”
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.left;
if ((uncle != null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// Case 2条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子
if (parent.left == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
rightRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子。
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
leftRotate(gparent);
}
}
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* px px
* / /
* x y
* / \ --(左旋)-. / \ #
* lx y x ry
* / \ / * ly ry lx ly
*
*
*/
private void leftRotate(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 设置x的右孩子为y
RBTNode<T> y = x.right;
// 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”;
// 如果y的左孩子非空,将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子的父亲”
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null)
y.left.parent = x;
// 将 “x的父亲” 设为 “y的父亲”
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.root = y; // 如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将y设为根节点
} else {
if (x.parent.left == x)
x.parent.left = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
else
x.parent.right = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
y.left = x;
// 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
x.parent = y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(y)进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行左旋):
* py py
* / /
* y x
* / \ --(右旋)-. / \ #
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \ #
* lx rx rx ry
*
*/
private void rightRotate(RBTNode<T> y) {
// 设置x是当前节点的左孩子。
RBTNode<T> x = y.left;
// 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”;
// 如果"x的右孩子"不为空的话,将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right != null)
x.right.parent = y;
// 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲”
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null) {
this.root = x; // 如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
} else {
if (y == y.parent.right)
y.parent.right = x; // 如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的右孩子”
else
y.parent.left = x; // (y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
x.right = y;
// 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
y.parent = x;
}public void remove(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node;
if ((node = search(root, key)) != null)
remove(node);
}
private void remove(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> child, parent;
boolean color;
// 被删除节点的"左右孩子都不为空"的情况。
if ((node.left != null) && (node.right != null)) {
// 被删节点的后继节点。(称为"取代节点")
// 用它来取代"被删节点"的位置,然后再将"被删节点"去掉。
RBTNode<T> replace = node;
// 获取后继节点
replace = replace.right;
while (replace.left != null)
replace = replace.left;
// "node节点"不是根节点(只有根节点不存在父节点)
if (parentOf(node) != null) {
if (parentOf(node).left == node)
parentOf(node).left = replace;
else
parentOf(node).right = replace;
} else {
// "node节点"是根节点,更新根节点。
this.root = replace;
}
// child是"取代节点"的右孩子,也是需要"调整的节点"。
// "取代节点"肯定不存在左孩子!因为它是一个后继节点。
child = replace.right;
parent = parentOf(replace);
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = colorOf(replace);
// "被删除节点"是"它的后继节点的父节点"
if (parent == node) {
parent = replace;
} else {
// child不为空
if (child != null)
setParent(child, parent);
parent.left = child;
replace.right = node.right;
setParent(node.right, replace);
}
replace.parent = node.parent;
replace.color = node.color;
replace.left = node.left;
node.left.parent = replace;
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
return;
}
if (node.left != null) {
child = node.left;
} else {
child = node.right;
}
parent = node.parent;
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = node.color;
if (child != null)
child.parent = parent;
// "node节点"不是根节点
if (parent != null) {
if (parent.left == node)
parent.left = child;
else
parent.right = child;
} else {
this.root = child;
}
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
}
private void removeFixUp(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
RBTNode<T> other;
while ((node == null || isBlack(node)) && (node != this.root)) {
if (parent.left == node) {
other = parent.right;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
leftRotate(parent);
other = parent.right;
}
if ((other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right == null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.right == null || isBlack(other.right)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.left);
setRed(other);
rightRotate(other);
other = parent.right;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.right);
leftRotate(parent);
node = this.root;
break;
}
} else {
other = parent.left;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
rightRotate(parent);
other = parent.left;
}
if ((other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right == null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.left == null || isBlack(other.left)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.right);
setRed(other);
leftRotate(other);
other = parent.left;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.left);
rightRotate(parent);
node = this.root;
break;
}
}
}
if (node != null) setBlack(node);
}标签:cas set oid 兄弟节点 标准 code insert btree private
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sanzao/p/10509626.html