标签:存在 apply OWIN header 用户访问 The nal ror method
看了前面一节对Struts2各个模块运行有了大概了解,也对调用的函数有了一定的了解,本节希望打断点跑一个Struts2例子!
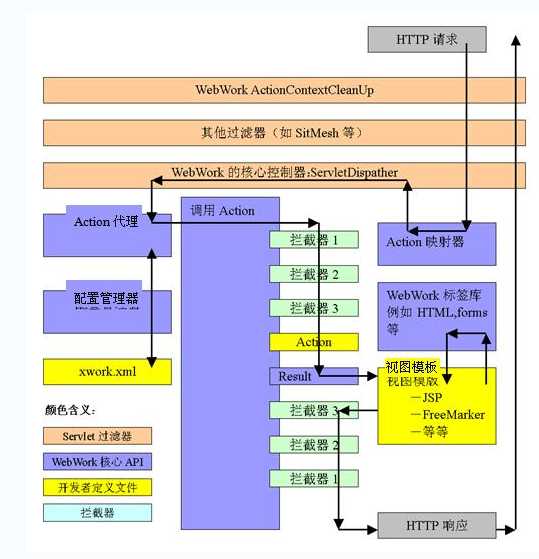
还是放在struts2结构图:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app id="WebApp_9" version="2.4" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"> 5 6 <display-name>Struts2Demo</display-name> 7 8 <filter> 9 <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> 10 <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> 11 </filter> 12 13 <filter-mapping> 14 <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> 15 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> 16 </filter-mapping> 17 18 <welcome-file-list> 19 <welcome-file>login.jsp</welcome-file> 20 </welcome-file-list> 21 </web-app>
在此研究的是StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter。
二:StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter中的方法:
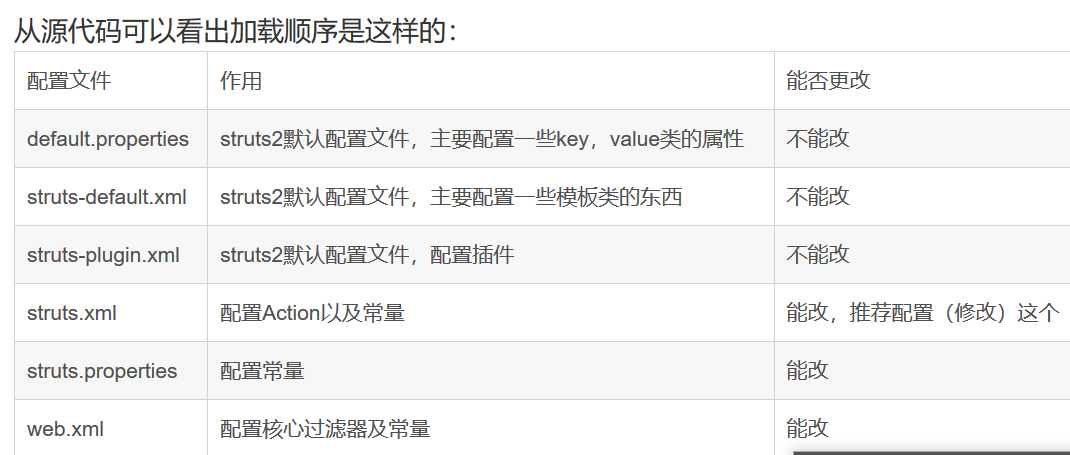
| void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) | 继承自Filter,过滤器的初始化 |
| doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) | 继承自Filter,执行过滤器 |
| void destroy() | 继承自Filter,用于资源释放 |
| void postInit(Dispatcher dispatcher, FilterConfig filterConfig) | Callback for post initialization(一个空的方法,用于方法回调初始化) |
web容器一启动,就会初始化核心过滤器StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter,并执行初始化方法,初始化方法如下:
1 public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { 2 InitOperations init = new InitOperations(); 3 Dispatcher dispatcher = null; 4 try { 5 //封装filterConfig,其中有个主要方法getInitParameterNames将参数名字以String格式存储在List 6 FilterHostConfig config = new FilterHostConfig(filterConfig); 7 //初始化struts内部日志 8 init.initLogging(config); 9 //创建dispatcher ,并初始化 10 dispatcher = init.initDispatcher(config); 11 init.initStaticContentLoader(config, dispatcher); 12 //初始化类属性:prepare 、execute 13 prepare = new PrepareOperations(dispatcher); 14 execute = new ExecuteOperations(dispatcher); 15 this.excludedPatterns = init.buildExcludedPatternsList(dispatcher); 16 //回调空的postInit方法 17 postInit(dispatcher, filterConfig); 18 } finally { 19 if (dispatcher != null) { 20 dispatcher.cleanUpAfterInit(); 21 } 22 init.cleanup(); 23 } 24 }
关于封装filterConfig,首先看下FilterHostConfig ,源码如下:
1 public class FilterHostConfig implements HostConfig { 2 3 private FilterConfig config; 4 //构造方法 5 public FilterHostConfig(FilterConfig config) { 6 this.config = config; 7 } 8 //根据init-param配置的param-name获取param-value的值 9 public String getInitParameter(String key) { 10 return config.getInitParameter(key); 11 } 12 //返回初始化参数名的迭代器 13 public Iterator<String> getInitParameterNames() { 14 return MakeIterator.convert(config.getInitParameterNames()); 15 } 16 //返回Servlet上下文 17 public ServletContext getServletContext() { 18 return config.getServletContext(); 19 } 20 }
只有短短的几行代码,getInitParameterNames是这个类的核心,将Filter初始化参数名称有枚举类型转为Iterator。此类的主要作为是对filterConfig 封装。
接下来,看下StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter中init方法中dispatcher = init.initDispatcher(config);这是初始化dispatcher的,是通过init对象的initDispatcher方法来初始化的,init是InitOperations类的对象,我们看看InitOperations中initDispatcher方法:
1 public Dispatcher initDispatcher( HostConfig filterConfig ) { 2 Dispatcher dispatcher = createDispatcher(filterConfig); 3 dispatcher.init(); 4 return dispatcher; 5 }
创建Dispatcher,会读取 filterConfig 中的配置信息,将配置信息解析出来,封装成为一个Map,然后根绝servlet上下文和参数Map构造Dispatcher :
private Dispatcher createDispatcher( HostConfig filterConfig ) { //存放参数的Map Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<String, String>(); //将参数存放到Map,这个地方就用到前面提到FilterHostConfig的转为list功能 for ( Iterator e = filterConfig.getInitParameterNames(); e.hasNext(); ) { String name = (String) e.next(); String value = filterConfig.getInitParameter(name); params.put(name, value); } //根据servlet上下文和参数Map构造Dispatcher return new Dispatcher(filterConfig.getServletContext(), params); }
这样dispatcher对象创建完成,接着就是dispatcher对象的初始化,打开Dispatcher类,看到它的init方法如下:
1 public void init() { 2 3 if (configurationManager == null) { 4 configurationManager = createConfigurationManager(BeanSelectionProvider.DEFAULT_BEAN_NAME); 5 } 6 7 try { 8 init_FileManager(); 9 //加载org/apache/struts2/default.properties 10 init_DefaultProperties(); // [1] 11 //加载struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml 12 init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations(); // [2] 13 init_LegacyStrutsProperties(); // [3] 14 //用户自己实现的ConfigurationProviders类 15 init_CustomConfigurationProviders(); // [5] 16 //Filter的初始化参数 17 init_FilterInitParameters() ; // [6] 18 init_AliasStandardObjects() ; // [7] 19 20 Container container = init_PreloadConfiguration(); 21 container.inject(this); 22 init_CheckWebLogicWorkaround(container); 23 24 if (!dispatcherListeners.isEmpty()) { 25 for (DispatcherListener l : dispatcherListeners) { 26 l.dispatcherInitialized(this); 27 } 28 } 29 } catch (Exception ex) { 30 if (LOG.isErrorEnabled()) 31 LOG.error("Dispatcher initialization failed", ex); 32 throw new StrutsException(ex); 33 } 34 }
这里主要是加载一些配置文件的,将按照顺序逐一加载:default.properties,struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml,……关于文件是如何加载的,大家可以自己取看源文件,主要是由xwork核心类加载的,代码在xwork-core\src\main\java\com\opensymphony\xwork2\config\providers包里面。
现在,我们回到StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter类中,刚才我们分析了StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter类的init方法,该方法在web容器一启动就会调用的,当用户访问某个action的时候,首先调用核心过滤器StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter的doFilter方法,该方法内容如下:
1 public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { 2 3 HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req; 4 HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res; 5 6 try { 7 if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) { 8 chain.doFilter(request, response); 9 } else { 10 //设置编码和国际化 11 prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response); 12 //创建action上下文 13 prepare.createActionContext(request, response); 14 prepare.assignDispatcherToThread(); 15 request = prepare.wrapRequest(request); 16 ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true); 17 //如果mapping为空,则认为不是调用action,会调用下一个过滤器链,直到获取到mapping才调用action 18 if (mapping == null) { 19 boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response); 20 if (!handled) { 21 chain.doFilter(request, response); 22 } 23 } else { 24 execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping); 25 } 26 } 27 } finally { 28 prepare.cleanupRequest(request); 29 } 30 }
下面对doFilter方法中的重点部分一一讲解:
(1)prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
第8行是调用prepare对象的setEncodingAndLocale方法,prepare是PrepareOperations类的对象,PrepareOperations类是用来做请求准备工作的。我们看下PrepareOperations类中的setEncodingAndLocale方法:
1 public void setEncodingAndLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { 2 dispatcher.prepare(request, response); 3 }
在这方法里面我们可以看到它只是调用了dispatcher的prepare方法而已,下面我们看看dispatcher的prepare方法:
1 /** 2 * Prepare a request, including setting the encoding and locale. 3 * 4 * @param request The request 5 * @param response The response 6 */ 7 public void prepare(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { 8 String encoding = null; 9 if (defaultEncoding != null) { 10 encoding = defaultEncoding; 11 } 12 // check for Ajax request to use UTF-8 encoding strictly http://www.w3.org/TR/XMLHttpRequest/#the-send-method 13 if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(request.getHeader("X-Requested-With"))) { 14 encoding = "UTF-8"; 15 } 16 17 Locale locale = null; 18 if (defaultLocale != null) { 19 locale = LocalizedTextUtil.localeFromString(defaultLocale, request.getLocale()); 20 } 21 22 if (encoding != null) { 23 applyEncoding(request, encoding); 24 } 25 26 if (locale != null) { 27 response.setLocale(locale); 28 } 29 30 if (paramsWorkaroundEnabled) { 31 request.getParameter("foo"); // simply read any parameter (existing or not) to "prime" the request 32 } 33 }
我们可以看到该方法只是简单的设置了encoding 和locale ,做的只是一些辅助的工作。
(2)prepare.createActionContext(request, response)
我们回到StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter的doFilter方法,看到第10行代码:prepare.createActionContext(request, response);这是action上下文的创建,ActionContext是一个容器,这个容器主要存储request、session、application、parameters等相关信 息. ActionContext是一个线程的本地变量,这意味着不同的action之间不会共享ActionContext,所以也不用考虑线程安全问 题。其实质是一个Map,key是标示request、session、……的字符串,值是其对应的对象,我们可以看到com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext类中时如下定义的:
static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal<ActionContext>();
我们看下PrepareOperations类的createActionContext方法:
1 /** 2 * Creates the action context and initializes the thread local 3 */ 4 public ActionContext createActionContext(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { 5 ActionContext ctx; 6 Integer counter = 1; 7 Integer oldCounter = (Integer) request.getAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER); 8 if (oldCounter != null) { 9 counter = oldCounter + 1; 10 } 11 //此处是从ThreadLocal中获取此ActionContext变量 12 ActionContext oldContext = ActionContext.getContext(); 13 if (oldContext != null) { 14 // detected existing context, so we are probably in a forward 15 ctx = new ActionContext(new HashMap<String, Object>(oldContext.getContextMap())); 16 } else { 17 ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack(); 18 stack.getContext().putAll(dispatcher.createContextMap(request, response, null)); 19 //stack.getContext()返回的是一个Map<String,Object>,根据此Map构造一个ActionContext
ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext()); 20 } 21 request.setAttribute(CLEANUP_RECURSION_COUNTER, counter); 22 ActionContext.setContext(ctx); //将ActionContext存到ThreadLocal 23 return ctx; 24 }
上面第18行代码中dispatcher.createContextMap,如何封装相关参数:
1 /** 2 * Create a context map containing all the wrapped request objects 3 * 4 * @param request The servlet request 5 * @param response The servlet response 6 * @param mapping The action mapping 7 * @return A map of context objects 8 * 9 * @since 2.3.17 10 */ 11 public Map<String,Object> createContextMap(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, 12 ActionMapping mapping) { 13 14 // request map wrapping the http request objects 15 Map requestMap = new RequestMap(request); 16 17 // parameters map wrapping the http parameters. ActionMapping parameters are now handled and applied separately 18 Map params = new HashMap(request.getParameterMap()); 19 20 // session map wrapping the http session 21 Map session = new SessionMap(request); 22 23 // application map wrapping the ServletContext 24 Map application = new ApplicationMap(servletContext); 25 26 Map<String,Object> extraContext = createContextMap(requestMap, params, session, application, request, response); 27 28 if (mapping != null) { 29 extraContext.put(ServletActionContext.ACTION_MAPPING, mapping); 30 } 31 return extraContext; 32 }
(3)request = prepare.wrapRequest(request)
我们再次回到StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter的doFilter方法中,看到第15行:request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);这一句是对request进行包装的,我们看下prepare的wrapRequest方法:
1 /** 2 * Wraps the request with the Struts wrapper that handles multipart requests better 3 * @return The new request, if there is one 4 * @throws ServletException 5 */ 6 public HttpServletRequest wrapRequest(HttpServletRequest oldRequest) throws ServletException { 7 HttpServletRequest request = oldRequest; 8 try { 9 // Wrap request first, just in case it is multipart/form-data 10 // parameters might not be accessible through before encoding (ww-1278) 11 request = dispatcher.wrapRequest(request); 12 ServletActionContext.setRequest(request); 13 } catch (IOException e) { 14 throw new ServletException("Could not wrap servlet request with MultipartRequestWrapper!", e); 15 } 16 return request; 17 }
由第11行我们可以看到它里面调用的是dispatcher的wrapRequest方法,我们看下dispatcher的wrapRequest:
1 public HttpServletRequest wrapRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException { 2 // don‘t wrap more than once 3 if (request instanceof StrutsRequestWrapper) { 4 return request; 5 } 6 7 String content_type = request.getContentType();
//如果content_type是multipart/form-data类型,则将request包装成MultiPartRequestWrapper对象,否则包装成StrutsRequestWrapper对象 8 if (content_type != null && content_type.contains("multipart/form-data")) { 9 MultiPartRequest mpr = getMultiPartRequest(); 10 LocaleProvider provider = getContainer().getInstance(LocaleProvider.class); 11 request = new MultiPartRequestWrapper(mpr, request, getSaveDir(), provider, disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup); 12 } else { 13 request = new StrutsRequestWrapper(request, disableRequestAttributeValueStackLookup); 14 } 15 16 return request; 17 }
此次包装根据请求内容的类型不同,返回不同的对象,如果为multipart/form-data类型,则返回MultiPartRequestWrapper类型的对象,该对象服务于文件上传,否则返回StrutsRequestWrapper类型的对象,MultiPartRequestWrapper是StrutsRequestWrapper的子类,而这两个类都是HttpServletRequest接口的实现。
(4)ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true)
包装request后,通过ActionMapper的getMapping()方法得到请求的Action,Action的配置信息存储在ActionMapping对象中,如StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter的doFilter方法中第16行:ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);我们找到prepare对象的findActionMapping方法:
1 public ActionMapping findActionMapping(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, boolean forceLookup) { 2 //首先从request对象中取mapping对象,看是否存在 3 ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping) request.getAttribute(STRUTS_ACTION_MAPPING_KEY); 4 //不存在就创建一个 5 if (mapping == null || forceLookup) { 6 try { 7 //首先创建ActionMapper对象,通过ActionMapper对象创建mapping对象 8 mapping = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ActionMapper.class).getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager()); 9 if (mapping != null) { 10 request.setAttribute(STRUTS_ACTION_MAPPING_KEY, mapping); 11 } 12 } catch (Exception ex) { 13 if (dispatcher.isHandleException() || dispatcher.isDevMode()) { 14 dispatcher.sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 19 return mapping; 20 }
下面是ActionMapper接口的实现类DefaultActionMapper的getMapping()方法的源代码:
1 public ActionMapping getMapping(HttpServletRequest request, ConfigurationManager configManager) { 2 ActionMapping mapping = new ActionMapping(); 3 //获得请求的uri,即请求路径URL中工程名以后的部分,如/userAction.action 4 String uri = RequestUtils.getUri(request); 5 //修正url的带;jsessionid 时找不到的bug 6 int indexOfSemicolon = uri.indexOf(‘;‘); 7 uri = (indexOfSemicolon > -1) ? uri.substring(0, indexOfSemicolon) : uri; 8 //删除扩展名,如.action或者.do 9 uri = dropExtension(uri, mapping); 10 if (uri == null) { 11 return null; 12 } 13 //从uri中分离得到请求的action名、命名空间。 14 parseNameAndNamespace(uri, mapping, configManager); 15 //处理特殊的请求参数 16 handleSpecialParameters(request, mapping); 17 //如果允许动态方法调用,即形如/userAction!getAll.action的请求,分离action名和方法名 18 return parseActionName(mapping); 19 }
下面对getMapping方法中的重要部分一一讲解:
①:parseNameAndNamespace(uri, mapping, configManager)
我们主要看下第14行的parseNameAndNamespace(uri, mapping, configManager);这个方法的主要作用是分离出action名和命名空间:
1 protected void parseNameAndNamespace(String uri, ActionMapping mapping, ConfigurationManager configManager) { 2 String namespace, name; 3 int lastSlash = uri.lastIndexOf("/"); //最后的斜杆的位置 4 if (lastSlash == -1) { 5 namespace = ""; 6 name = uri; 7 } else if (lastSlash == 0) { 8 // ww-1046, assume it is the root namespace, it will fallback to 9 // default 10 // namespace anyway if not found in root namespace. 11 namespace = "/"; 12 name = uri.substring(lastSlash + 1); 13 //允许采用完整的命名空间,即设置命名空间是否必须进行精确匹配 14 } else if (alwaysSelectFullNamespace) { 15 // Simply select the namespace as everything before the last slash 16 namespace = uri.substring(0, lastSlash); 17 name = uri.substring(lastSlash + 1); 18 } else { 19 // Try to find the namespace in those defined, defaulting to "" 20 Configuration config = configManager.getConfiguration(); 21 String prefix = uri.substring(0, lastSlash); //临时的命名空间,将会用来进行匹配 22 namespace = "";//将命名空间暂时设为"" 23 boolean rootAvailable = false;//rootAvailable作用是判断配置文件中是否配置了命名空间"/" 24 // Find the longest matching namespace, defaulting to the default 25 for (Object cfg : config.getPackageConfigs().values()) { //循环遍历配置文件中的package标签 26 String ns = ((PackageConfig) cfg).getNamespace(); //获取每个package标签的namespace属性 27 //进行匹配 28 if (ns != null && prefix.startsWith(ns) && (prefix.length() == ns.length() || prefix.charAt(ns.length()) == ‘/‘)) { 29 if (ns.length() > namespace.length()) { 30 namespace = ns; 31 } 32 } 33 if ("/".equals(ns)) { 34 rootAvailable = true; 35 } 36 } 37 38 name = uri.substring(namespace.length() + 1); 39 40 // Still none found, use root namespace if found 41 if (rootAvailable && "".equals(namespace)) { 42 namespace = "/"; 43 } 44 } 45 46 if (!allowSlashesInActionNames) { 47 int pos = name.lastIndexOf(‘/‘); 48 if (pos > -1 && pos < name.length() - 1) { 49 name = name.substring(pos + 1); 50 } 51 } 52 //将分离后的acion名和命名空间保存到mapping对象 53 mapping.setNamespace(namespace); 54 mapping.setName(cleanupActionName(name)); 55 }
看到上面代码的第14行,参数alwaysSelectFullNamespace我们可以通过名字就能大概猜出来"允许采用完整的命名空间",即设置命名空间是否必须进行精确匹配,true必须,false可以模糊匹配,默认是false。进行精确匹配时要求请求url中的命名空间必须与配置文件中配置的某个命名空间必须相同,如果没有找到相同的则匹配失败。这个参数可通过struts2的"struts.mapper.alwaysSelectFullNamespace"常量配置,如:<constant name="struts.mapper.alwaysSelectFullNamespace" value="true" />。当alwaysSelectFullNamespace为true时,将uri以lastSlash为分割,左边的为namespace,右边的为name。如:http://localhost:8080/myproject/home/actionName!method.action,此时uri为/home/actionName!method.action(不过前面把后缀名去掉了,变成/home/actionName!method),lastSlash的,当前值是5,这样namespace为"/home", name为actionName!method。
我们再看到上面代码第18行到第44行:当上面的所有条件都不满足时,其中包括alwaysSelectFullNamespace 为false(命名空间进行模糊匹配),将由此部分处理,进行模糊匹配。第1句,通过configManager.getConfiguration()从配置管理器中获得配置对象Configuration,Configuration中存放着struts2的所有配置,形式是将xml文档的相应元素封装为java bean,如<package>元素被封装到PackageConfig类中,这个一会儿会用到。第2句按lastSlash将uri截取出prefix,这是一个临时的命名空间,之后将会拿prefix进行模糊匹配。第3句namespace = "",将命名空间暂时设为""。第4句创建并设置rootAvailable,rootAvailable作用是判断配置文件中是否配置了命名空间"/",true为配置了,false未配置,下面for语句将会遍历我们配置的所有包(<package>),同时设置rootAvailable。第5句for,通过config.getPackageConfigs()获得所有已经配置的包,然后遍历。String ns = ((PackageConfig) cfg).getNamespace()获得当前包的命名空间ns,之后的if句是进行模糊匹配的核心,我摘出来单独说,如下:
1 if (ns != null && prefix.startsWith(ns) && (prefix.length() == ns.length() || prefix.charAt(ns.length()) == ‘/‘)) { 2 if (ns.length() > namespace.length()) { 3 namespace = ns; 4 } 5 }
ns != null && prefix.startsWith(ns)这部分判断当ns不等于空并且ns是prefix的前缀。prefix.length() == ns.length()当二者长度相等时,结合前面部分就是ns是prefix的前缀并且二者长度相等,最终结论就是ns和prefix相等。如果前面的条件不成立,则说明prefix的长度大于ns。prefix.charAt(ns.length()) == ‘/‘)意思是prefix中与ns不相等的字符中的第一个字符必须是"/",也就是说,在命名空间采用斜杠分级的形式中,ns必须是prefix的某一子集,如:/common/home 是用户配置的命名空间,则在http的请求url中,/common/home/index1、/common/home/index2、/common/home/index/aaa 都是正确的,都可以成功的匹配到/common/home,而/common/homeaa、/common/homea/aaa都是错误的。接着if (ns.length() > namespace.length()) 句,目的是找出字符长度最长的。因为命名空间采用的是分级的,则长度越长所表示的越精确,如/common/home/index比/common/home精确。之后将namespace = ns。
我们接着往下看if ("/".equals(ns)) 当我们配置了"/"这个命名空间时,将rootAvailable = true。name = uri.substring(namespace.length() + 1)句不涉及到命名空间就不说了。if (rootAvailable && "".equals(namespace))如果通过上面的for循环没有找到匹配的命名空间即namespace的值仍然是当初设置的"",但却配置了"/"时,将命名空间设为"/"。
我们再看到第46到51行那个if语句:
1 if (!allowSlashesInActionNames) { 2 int pos = name.lastIndexOf(‘/‘); 3 if (pos > -1 && pos < name.length() - 1) { 4 name = name.substring(pos + 1); 5 } 6 }
allowSlashesInActionNames代表是否允许"/"出现在Action的名称中,默认为false,如果不允许"/"出现在Action名中,并且这时的Action名中有"/",则取"/"后面的部分。
下面是命名空间匹配规则的总结:
(1). 如果请求url中没有命名空间时,将采用"/"作为命名空间。
(2). 当我们将常量 struts.mapper.alwaysSelectFullNamespace设为true时,那么请求url的命名空间必须和配置文件配置的完全相同才能匹配。
当将常量 struts.mapper.alwaysSelectFullNamespace设为false时,那么请求url的命名空间和配置文件配置的可按模糊匹配。规则:
a.如果配置文件中配置了/common 而url中的命名空间/common、/common/home、/common/home/index等等都是可匹配的,即子命名空间可匹配父命名空间。
b.如果对于某个url请求中的命名空间同时匹配了俩个或俩个以上的配置文件中配置的命名空间,则选字符最长的,如:当前请求的命名空间为/common/home/index/aaaa, 而我们在配置时同时配置了/common/home、/common/home/index 则将会匹配命名空间最长的,即/common/home/index。
(3).最后,如果请求的命名空间在配置中没有匹配到时,将采用""作为命名空间。如果没有设置为""的命名空间将抛出404错误。
②:parseActionName(mapping)
好了,到这里parseNameAndNamespace方法已经分析完了,我们再次回到getMapping方法中去,看到16行:handleSpecialParameters(request, mapping);好像是处理特殊参数的函数吧,里面有点看不懂,暂时就不管,以后有时间再研究。我们看到18行:return parseActionName(mapping);主要是用来处理形如/userAction!getAll.action的请求,分离action名和方法名:
1 protected ActionMapping parseActionName(ActionMapping mapping) { 2 if (mapping.getName() == null) { 3 return null; 4 } 5 if (allowDynamicMethodCalls) { //如果允许动态方法调用 6 // handle "name!method" convention. 7 String name = mapping.getName(); 8 int exclamation = name.lastIndexOf(‘!‘); 9 if (exclamation != -1) { //如果包含"!"就进行分离 10 mapping.setName(name.substring(0, exclamation)); //分离出action名 11 12 mapping.setMethod(name.substring(exclamation + 1)); //分离出方法名 13 } 14 } 15 return mapping; 16 }
到此为止getMapping方法已经分析结束了!
(5)execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping)
上面我们分析完了mapping的获取,继续看doFilter方法:
1 //如果mapping为空,则认为不是调用action,会调用下一个过滤器链,直到获取到mapping才调用action 2 if (mapping == null) { 3 boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response); 4 if (!handled) { 5 chain.doFilter(request, response); 6 } 7 } else { 8 //执行action 9 execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping); 10 }
如果mapping对象不为空,则会执行action,我们看到上面代码第9行:execute是ExecuteOperations类的对象,ExecuteOperations类在包org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng下面,我们找到它里面的executeAction方法:
1 public void executeAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException { 2 dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, mapping); 3 }
我们可以看到它里面只是简单的调用了dispatcher的serviceAction方法:我们找到dispatcher的serviceAction方法:
1 /** 2 * Load Action class for mapping and invoke the appropriate Action method, or go directly to the Result. 3 * <p/> 4 * This method first creates the action context from the given parameters, 5 * and then loads an <tt>ActionProxy</tt> from the given action name and namespace. 6 * After that, the Action method is executed and output channels through the response object. 7 * Actions not found are sent back to the user via the {@link Dispatcher#sendError} method, 8 * using the 404 return code. 9 * All other errors are reported by throwing a ServletException. 10 * 11 * @param request the HttpServletRequest object 12 * @param response the HttpServletResponse object 13 * @param mapping the action mapping object 14 * @throws ServletException when an unknown error occurs (not a 404, but typically something that 15 * would end up as a 5xx by the servlet container) 16 * 17 * @since 2.3.17 18 */ 19 public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping) 20 throws ServletException { 21 //封转上下文环境,主要将requestMap、params、session等Map封装成为一个上下文Map 22 Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping); 23 24 // If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action 25 ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY); 26 boolean nullStack = stack == null; 27 if (nullStack) { 28 ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext(); 29 if (ctx != null) { 30 stack = ctx.getValueStack(); 31 } 32 } 33 if (stack != null) { 34 extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack)); 35 } 36 37 String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher"; 38 try { 39 UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey); 40 String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();//从mapping对象获取命名空间 41 String name = mapping.getName();//获取请求的action名 42 String method = mapping.getMethod();//获取请求方法 43 //根据执行上下文参数,命名空间,名称等创建用户自定义Action的代理对象 44 ActionProxy proxy = getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy( 45 namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false); 46 47 request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack()); 48 //如果配置文件中执行的这个action配置了result,就直接转到result 49 // if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it! 50 if (mapping.getResult() != null) { 51 Result result = mapping.getResult(); 52 result.execute(proxy.getInvocation()); 53 } else { 54 proxy.execute(); 55 } 56 57 // If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request 58 if (!nullStack) { 59 request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack); 60 } 61 } catch (ConfigurationException e) { 62 logConfigurationException(request, e); 63 sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e); 64 } catch (Exception e) { 65 if (handleException || devMode) { 66 sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e); 67 } else { 68 throw new ServletException(e); 69 } 70 } finally { 71 UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey); 72 } 73 }
最后通过Result完成页面跳转!
下面我们来看看ActionInvocation是如何工作的:
ActionInvocation是Xworks 中Action 调度的核心。而对Interceptor 的调度,也正是由ActionInvocation负责。ActionInvocation 是一个接口,而DefaultActionInvocation 则是Webwork 对ActionInvocation的默认实现。
总计struts的步骤就是以下步骤
Struts流程:
一、 Tomcat服务器启动
1. 服务器启动,加载自身config/web.xml, 以及webapps下所有项目的web.xml
2. 创建过滤器对象
创建struts核心过滤器实例
3. 初始化
执行过滤器init()方法
---> 加载默认Properties配置文件
---> 加载xml
struts-default.xml, 【所有需要创建的bean、默认的包(结果类型、所有拦截器、默认的拦截器栈)】
struts-plugin.xml, 【插件配置】
struts.xml 【自定义配置】
二、 用户访问
用户每次访问,执行doFilter()方法:
1. 每次访问struts,都会创建ActionContext对象 【 prepare.createActionContext(request, response);】
1.1 然后,创建ValuStack值栈对象
ValueStack 结构
|-- root 根元素数据
|-- context 非根元素(map)
1.2 给ValustStack封装数据, 所有的map数据都放入值栈
--> 把代表request/session/application的map、以及HttpServletRequest等对象都放入值栈中
1.3 把值栈的map数据,拷贝一份给ActionContext!
所以,我们可以通过ActionContext获取struts运行的数据!
2. ActionMapping
struts把请求的参数(路径等信息), 封装为一个ActionMapping对象!
判断:
---> 如果请求静态资源(jsp), 就放行
---> 如果请求的是action,才执行Action(的过程)
3. 如果访问的是struts的action, 执行:execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
(Action创建、拦截器的调用)
4. ConfigurationManager 配置管理器类,管理各配置文件
5. 根据配置管理器对象, 创建Action的代理 , 通过Action的代理,创建Action实例!
6. 再依次默认的18个拦截器
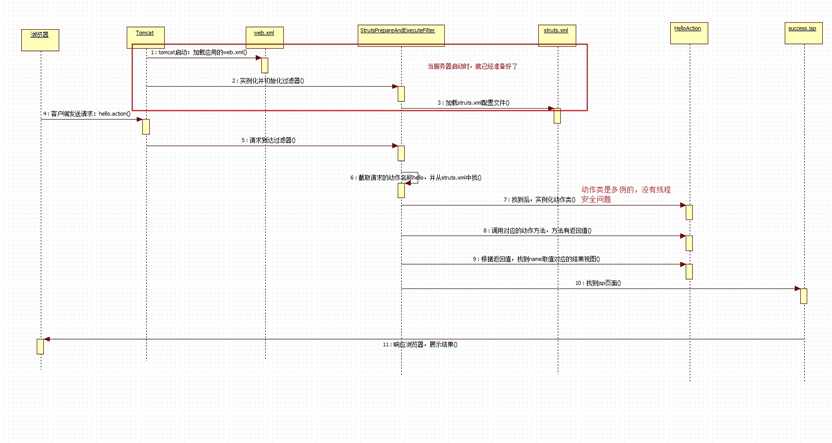
提几个比较好的流程图:
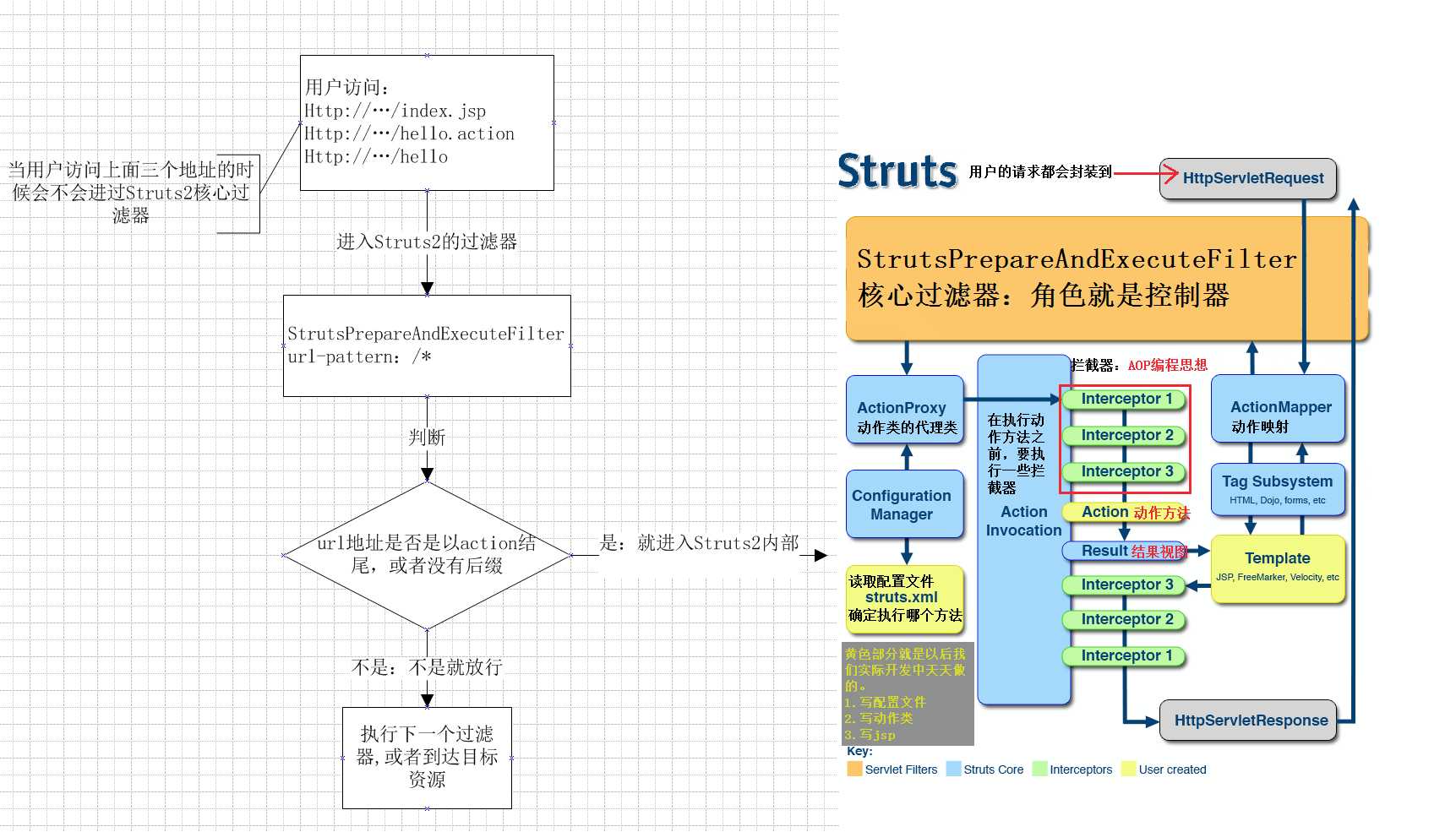
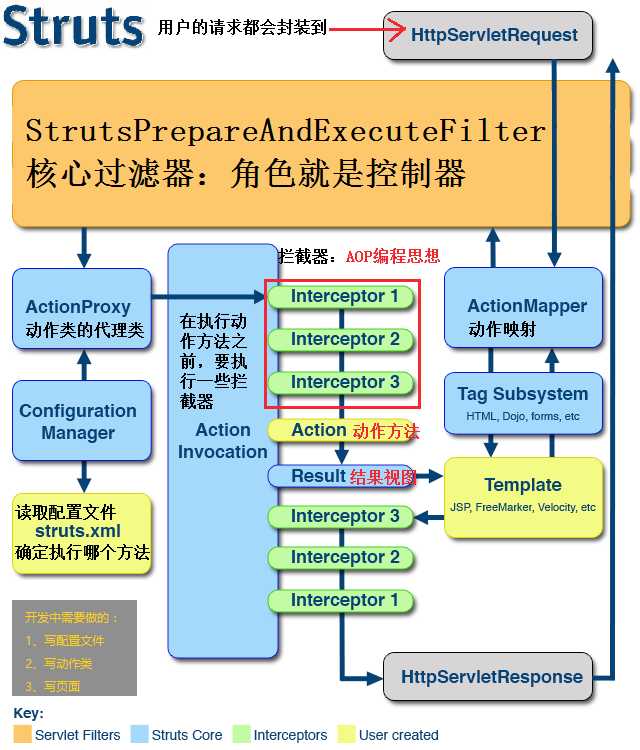
步骤:
1、客户端请求,生成相应的HttpServletRequest对象
2、Struts2核心过滤器,StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter进行拦截,(如果满足要求,进行拦截,不满足要求,放行)
3、ActionMapper动作映射类,将请求的路径与struts.xml中的配置进行对比,找到匹配的动作类
4、经过核心过滤器,然后创建匹配的动作类的代理类对象,进行一系列的配置,(读取配置文件struts.xml,确定执行那个方法)
5、通过一些拦截器,对数据进行预处理,比如说请求参数的封装就是在这进行
6、进入动作方法,进行业务处理
7、动作方法返回结果视图的名字,到ActionMapper找到对应的结果视图,进行结果视图预处理
8、反向经过5中的拦截器
9、生成HttpServletResponse对象,返回给客户端。
https://blog.csdn.net/q547550831/article/details/53267815----不错
https://blog.csdn.net/chainiao_zhang/article/details/76825171----面试题
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40234548/article/details/81359958
https://www.cnblogs.com/duanxz/p/5441342.html----------主要参考
标签:存在 apply OWIN header 用户访问 The nal ror method
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/beilou310/p/10552883.html