标签:模块化 image The 修改 map 扩展 report 需求分析 任务
1.程序需要读入至少一个词,可读入任意英文文本。
2.至少可以统计10万词及以上的文本。
3.用户可以同时查询多个单词的统计,并显示出其个数和柱状图。
4.用户可以筛选单词频数大于n的单词,进行降序显示其单词及其频数。
5.统计文本所以单词及其词频,并在文本文件中按字典序进行显示。1.基本功能:对输入的大于等于一个单词的英文,
实现其一个或多个单词的单词和词频统计并以柱状图的形式显示出来,
可以对多个单词进行条件查询并对其按降序或字典序进行显示。
2.扩展功能:对输入的英文文本,筛选出包含某个单词的句子。
(在英语单词的学习过程中,最好是结合真题去学习。那么就可以把历年真题进行扫描录入,然后筛选包含某个单词的句子。)1.模块划分及其功能:
扑获内容:把文件或网页中的文本抓取出来,对其进行分割后用于统计。
统计词频:对相应的词通过for循环进行词频统计。
绘制柱状图:对统计来的数据做出直观表达。
按字典序排序:把统计来的数据按字典序排序,并显示词及其频数。
输出为文本:统计结果输出为文本文件。
2.模块之间的关系:捕获内容模块从源文件中捕获数据,对其进行分割后用于词频统计模块 的数据源,绘制柱状图模块把统计的来的数据直观展示,字典序排序模块对统计的单词按字典序排列显示。各模块之间相互依赖,前者为后者提供源数据。
3.重要的函数(必要时画出流程图):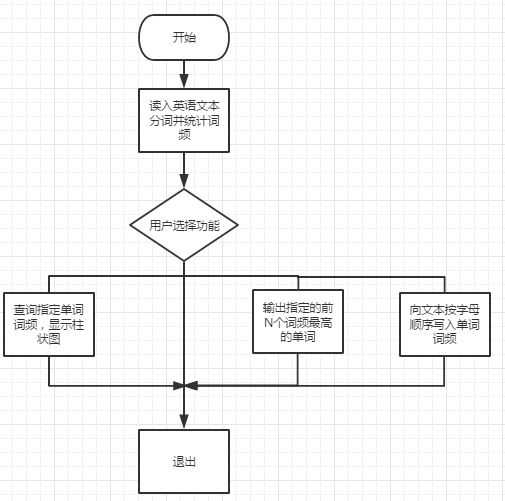
4.函数之间的关系:
前者给后者提供源数据,模块与模块之间相互依赖互相区别。
1.显示单词词频和柱状图
2.输出前K个高频词
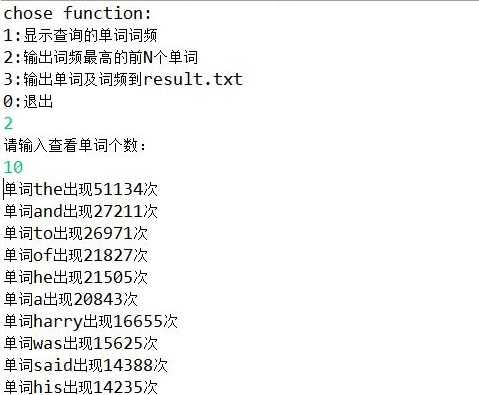
1.文件读入并统计词频// 读取要处理的文件 BufferedReader b = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src/HarryPotter.txt")); //<单词:词频> Map<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(); String value= b.readLine(); while (value!= null) { //处理标点符号 String[] words = value.split("[【】、.。,\"!--;:?\‘\\] ]"); for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) { //将大写字母转换为小写字母 String key = words[i].toLowerCase(); if (key.length() > 0) { if (!map.containsKey(key)) { map.put(key, 1); } else { int k = map.get(key)+1;// 如果不是第一次出现,就把k值++ map.put(key, k); } } } value = b.readLine(); }
2.按词频或字母排序
Set<Entry<String,Integer>> m= map.entrySet();
LinkedList<Entry<String, Integer>> List = new LinkedList<Entry<String,Integer>>(m);
//按值排序
if(a==2) {
Collections.sort(List, new Comparator<Entry<String,Integer>>() {
public int compare(Entry<String, Integer> a, Entry<String, Integer> b) {
return b.getValue().compareTo(a.getValue());
}
});
//按键排序
else if(a==3) {
Collections.sort(List, new Comparator<Entry<String,Integer>>() {
public int compare(Entry<String, Integer> a, Entry<String, Integer> b) {
return a.getKey().compareTo(b.getKey());
}
});
}
//排序后存入Map中
for(Entry<String,Integer> entry: List) {
Map.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
} 3.向文件写入单词词频 File file = new File("result.txt");
//向文件写入
FileWriter f = new FileWriter(file.getAbsoluteFile());
for(Entry<String,Integer> w: Map.entrySet()) {
f.write(w.getKey() + "/" + w.getValue()+" ");
}
f.close();
System.out.println("结束!");1.按功能用函数实现了模块化。
2.最开始读数据打算用数组,后面发现处理起来有点麻烦,就选择了目前这种方式。
3.柱状图绘制时,把统计和绘制放在了一起。| PSP2.1 | 任务内容 | 计划共完成需要的时间(min) | 实际完成需要的时间(min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 42 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间,并规划大致工作步骤 | 30 | 42 |
| Development | 开发 | 700 | 1088 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 150 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 50 | 50 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 20 | 15 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 30 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 120 | 60 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 240 | 600 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 60 | 80 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 120 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 55 | 100 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 20 | 32 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结 ,并提出过程改进计划 | 25 | 60 |
总结:大部分环节都有超时现象,只要原因是因为自己对开发过程的不熟悉,对使用语言没有系统的学习过。标签:模块化 image The 修改 map 扩展 report 需求分析 任务
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaxiangming/p/10528177.html