标签:|| struct else return get 出栈 情况 oid http
这里顺序栈和链栈的基本操作和差别在之前的线性表操作中是一样的,目前栈对我而言在实际使用中使用哪一种差别并没有很大,顺序栈用起来会方便一点
顺序栈
>>ADT:
typedef struct { DataType data[StackSize]; int top;//栈顶位置,栈顶元素在数组中的下标 }SeqStack;
>>入栈:
int Push(SeqStack *S, DataType x) { if (S->top==StackSize-1) return 0; S->data[++S->top] = x; return 1; }
>>出栈:
int Pop(SeqStack *S, DataType *ptr) { if (S->top==-1) return 0;//表示栈空的情况 *ptr = S->data[S->top--]; return 1; }
链栈
>>入栈:
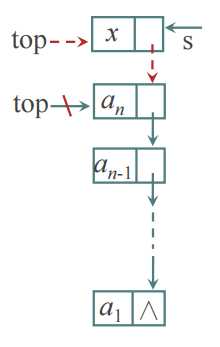
void Push(Node *top, DataType x) { Node *s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); s->data = x; s->next = top; top = s; }
>>出栈:
int Pop(Node *top, DataType *ptr) { if (top==NULL) return 0;//top==NULL表示空栈 *ptr = top->data; top = top->next; free(p); return 1; }
栈的应用
1. 进制转化
思路:用短除法(具体原理可以去看数学证明)求余数时,结果要逆序输出,利用栈的先进后出特点可以满足这个要求
#include <cstdio> #include <stack> using namespace std; int main() { int num, d; scanf("%d%d", &num, &d); stack<int> s; while (num>0) { int x = num%d; s.push(x); num = num/d; } while (!s.empty()) { printf("%d", s.top()); s.pop(); } return 0; }
2. 括号匹配
#include <cstdio> #include <stack> using namespace std; int main() { char str[1000]; gets(str); stack<int> s; for(int i = 0; str[i]!=‘\0‘; i++) { if (str[i]==‘(‘||str[i]==‘[‘||str[i]==‘{‘) s.push(str[i]); else if (str[i]==‘)‘||str[i]==‘]‘||str[i]==‘}‘){ if(s.empty()) { printf("No"); return 0; } else { int x = s.top(); if (x==‘(‘&&str[i]==‘)‘||x==‘[‘&&str[i]==‘]‘||x==‘{‘&&str[i]==‘}‘) s.pop(); else { printf("No"); return 0; } } } } if (s.empty()) printf("Yes"); else printf("No"); return 0; }
标签:|| struct else return get 出栈 情况 oid http
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wizarderror/p/10639687.html