标签:数据 ++ int 位置 现在 first deque data 随机
要学习LinkedList,首先得了解链表结构。上篇介绍ArrayList的文章中介绍了底层是数组结构,查询快的问题,但是删除时,需要将删除位置后面的元素全部左移,因此效率比较低。
链表则是这种机制:
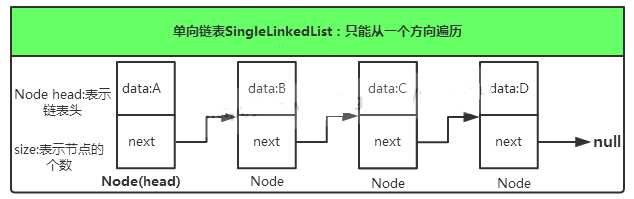
此图展示的是一个单向列表,单向链表只能向一个方向遍历。链表中存在一系列的节点(node),每个node中维护了一个data以及一个next链,data则保存当前node所需要保存的数据,而next链指向下一个元素,最后一个node的next指向null。
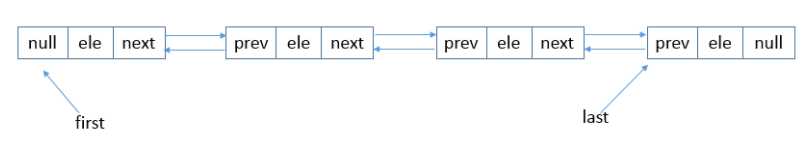
这个则是个典型的双向链表,双向链表中一共存在pre、data以及next三部分,data以及next跟单向链表则是一致的。pre则是代表前一个元素是啥,这样就可以双方向的去遍历元素。
一、LinkedList类定义、成员变量
//AbstractSequentialList提供了一个对list的骨架型的实现。该类实现了一个按次序访问的功能。如果要实现随机访问,应该先使用AbstractList。该类与实现随机访问的方法不同,它不支持随机访问。Deque表示是一个双端队列。 public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable //实际元素个数 transient int size = 0; //头结点 transient Node<E> first; //尾结点 transient Node<E> last; //内部类 private static class Node<E> { //存放数据 E item; //next链,指向下一个元素 Node<E> next; //prev链,指向前一个元素 Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
二、构造函数
public LinkedList() { } //此方法就是将collection全部加入到原linkedList中去。 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); }
三、主要方法
1、add()
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } void linkLast(E e) { //首先获取到当前的最后一个节点 final Node<E> l = last; //将新add进来的元素转换为node,因为linkedList都是节点,第一个入参是prev,第二个参数则是具体的元素,next链则为null final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //最后加进来的的当然为last last = newNode; 如果last元素为null,说明之前的linkedList为空。因此新加的元素自然也是first元素 if (l == null) first = newNode; else //将之前的last元素的next设置为新加的元素 l.next = newNode; //长度增加 size++; modCount++; }
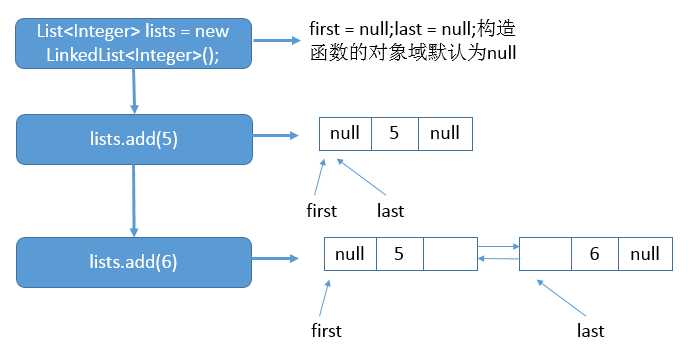
举个例子吧:
List<Integer> lists = new LinkedList<Integer>(); lists.add(5); lists.add(6);
假如你在执行上面的代码,
2、addAll()
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); } public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //判断index是否在0-size内 checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; //pred代表prev链,succ代表next链 Node<E> pred, succ; //如果插入的index==size,说明在原linkedList的last节点后插入数据 if (index == size) { //next链自然为null succ = null; //prev链自然就是当前的最后一个节点 pred = last; } else { //找到该index对应的节点,在此节点之前将所有元素插入完毕。将next链指向此节点 succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); //pred为null,说明此时是第一个位置 if (pred == null) first = newNode; else //需要将prev链的节点的next设置为新创建的节点 pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } //如果next链为null,说明当前节点就是last节点 if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; }
3、add(int index, E element)
public void add(int index, E element) { //校验index是否<0或>size checkPositionIndex(index); //index==size,说明在最后加 if (index == size) linkLast(element); else //找到index对应的节点, linkBefore(element, node(index)); } //这方法前面已经介绍了 void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { //取当前index节点的prev链以及next链 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; //创建新节点,当前节点的prev成为新节点的prev,当前节点变成新节点的next。其实想想插队的场景就明白了 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } //关于node()方法也有个骚操作 Node<E> node(int index) { //index是否<size的一半大小,小于一半,顺着遍历;如果大于一半,则逆着遍历,谁让它是双向的呢! if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
4、remove方法相关
//默认删除第一个节点 public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); } private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { //取当前节点的item,并用final修饰,不能更改引用地址。主要为了后面使用 final E element = f.item; final Node<E> next = f.next; //将item以及next都设为Null,有利于垃圾回收 f.item = null; f.next = null; // help GC //正是由于前面用final修饰,这里的next才不会一直为Null first = next; if (next == null) last = null; else next.prev = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { //循环找到null的元素,然后调用unlink方法 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { //为null调用equals()报错,所以上面先进行判断 if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; } //删除某个节点 E unlink(Node<E> x) { final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; //prev说明是第一个元素,因此next变为第一个元素 if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { //联想下插队场景,你前面的那个人后面排的是插队的人了 prev.next = next; //将x的prev设为null x.prev = null; } //如果next为null,说明x为最后一个节点,现在他没了,将他的prev设为last if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { //路人甲、你、路人乙三个人按顺序排队,你走了,路人乙的prev就是路人甲了 next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } //最后将item设为null,为了更好的进行垃圾回收 x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); }
public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l);}
5、clear()
public void clear() { //循环所有节点,将每个节点的prev、item、next全设为null。目的就是为了更好的垃圾回收 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; }
6、getFirst()、getLast()
//取第一个节点的item public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; } //取最后一个节点的item public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; }
标签:数据 ++ int 位置 现在 first deque data 随机
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/alimayun/p/10714066.html