标签:http 定义变量 mamicode sts 输出 通过 shell 情况 技术
变量名应该由数字、字母、或者下划线组成,变量名需要以字母开头,ansible内置的关键词不能作为变量名使用。
可以使用vars在playbook中定义变量
---
- hosts: all
vars:
testvar1: testfile
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: task1
file:
path: /{{ testvar1 }}
state: touch
也可以直接定义多个变量。
定义变量时还可以使用以类似“属性”的方式定义变量。
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx:
conf80: /tmp/80.conf
conf8080: /tmp/8080.conf
tasks:
- name: task1
file:
path: "{{nginx.conf80}}"
state: touch
- name: task2
file:
path: "{{nginx.conf8080}}"
state: touch
当我们需要引用这两个变量时,有两种方式引用:
语法一:
"{{nginx.conf80}}"
语法二:
"{{nginx[‘conf8080‘]}}"
当我们运行playbook时,默认会运行一个[Gathering Facts]的任务,ansible通过这个任务收集远程主机的系统信息(IP、操作系统、配置信息等),其实这些收集的主机被存放在相应的变量中。
想要查看这些被收集的信息,我们需要setup模块。
ansible all -m setup
ad-hoc命令表示收集主机的相关信息,执行完上述命令后,相关信息会输出到ansible的主机控制台上,返回的信息是json格式。
返回的信息很多,如果你想要某一项信息,可以对信息进行过滤。
ansible all -m setup -a ‘filter=ansible_memory_mb‘
支持通配符进行模糊过滤。
ansible all -m setup -a ‘filter=*mb*‘
ansible在执行模块的过程中其实是有返回值的,在默认情况下这些返回值是不会在控制台显示的,我们可以把这些返回值写入到变量中,然后通过引用变量的方式来查看这些返回值,将模块的返回值写入变量的方式叫做变量注册。
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test shell
shell: "echo test > /var/testshellfile"
register: testvar
- name: shell module return values
debug:
var: testvar
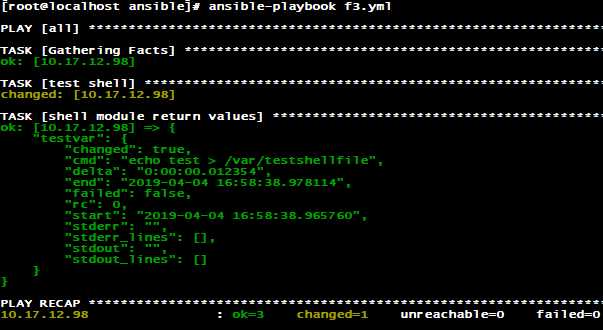
返回值是json格式的,返回结果中包含一些键值对,如果你想要获取结果中的某一项特定值,需要指定键值对中的key。
语法一
- name: shell module return values
debug:
msg: "{{testvar.cmd}}"
语法二
- name: shell module return values
debug:
msg: "{{testvar[‘cmd‘]}}"
标签:http 定义变量 mamicode sts 输出 通过 shell 情况 技术
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jinyuanliu/p/10655850.html