标签:递归 前序遍历 while 位置 构建 ret 树的遍历 n+1 遍历
??题目描述:
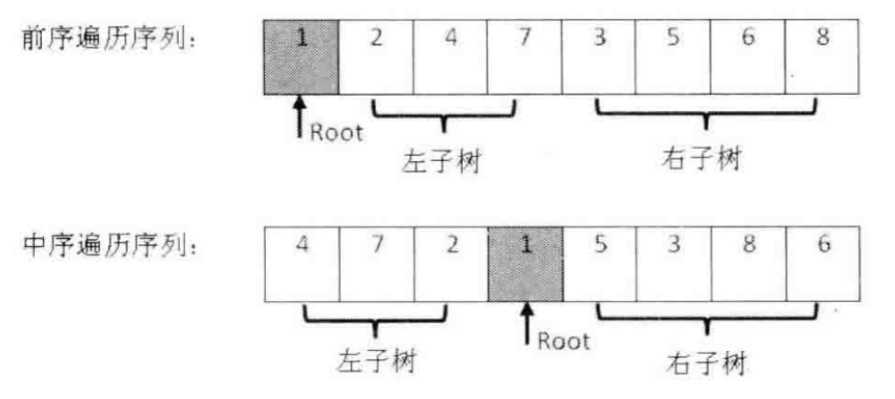
??输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回根结点。
??解题思路:
??树的遍历有三种:分别是前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。本题是根据前序和中序遍历序列重建二叉树,我们可以通过一个具体的实例来发现规律,不难发现:前序遍历序列的第一个数字就是树的根结点。在中序遍历序列中,可以扫描找到根结点的值,则左子树的结点都位于根结点的左边,右子树的结点都位于根结点的右边。
??这样,我们就通过这两个序列找到了树的根结点、左子树结点和右子树结点,接下来左右子树的构建可以进一步通过递归来实现。
??举例:
??编程实现(Java):
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
/*根据前序遍历和中序遍历确定一棵二叉树*/
//递归实现
if(pre==null||in==null||pre.length==0)
return null;
return reConstructBinaryTree(pre,in,0,pre.length-1,0,in.length-1);
}
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in,int pre_begin,
int pre_end,int in_begin,int in_end)
{
////前序序列:从pre_begin到pre_end, 中序序列:从in_begin到in_end
//递归结束条件
if(pre_begin>pre_end || in_begin>in_end)
return null;
int rootValue=pre[pre_begin];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootValue); //第一个节点就是根节点
if(pre_begin==pre_end || in_begin==in_end)
return root;
//在中序序列中,找到root,前面的就是左子树,右边的就是右子树
int rootIn=in_begin; //root在中序序列中的位置
while(rootIn<=in_end && in[rootIn]!=rootValue)
rootIn++;
int left_count=rootIn-in_begin; //左子树节点个数
root.left=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,in,pre_begin+1,pre_begin+left_count,
in_begin,rootIn-1);
root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,in,pre_begin+left_count+1,
pre_end,rootIn+1,in_end);
return root;
}标签:递归 前序遍历 while 位置 构建 ret 树的遍历 n+1 遍历
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gzshan/p/10730338.html