标签:while lld ++ lse string ddb width 左右 win
As shown in the following figure, If another lighthouse is in gray area, they can beacon each other.
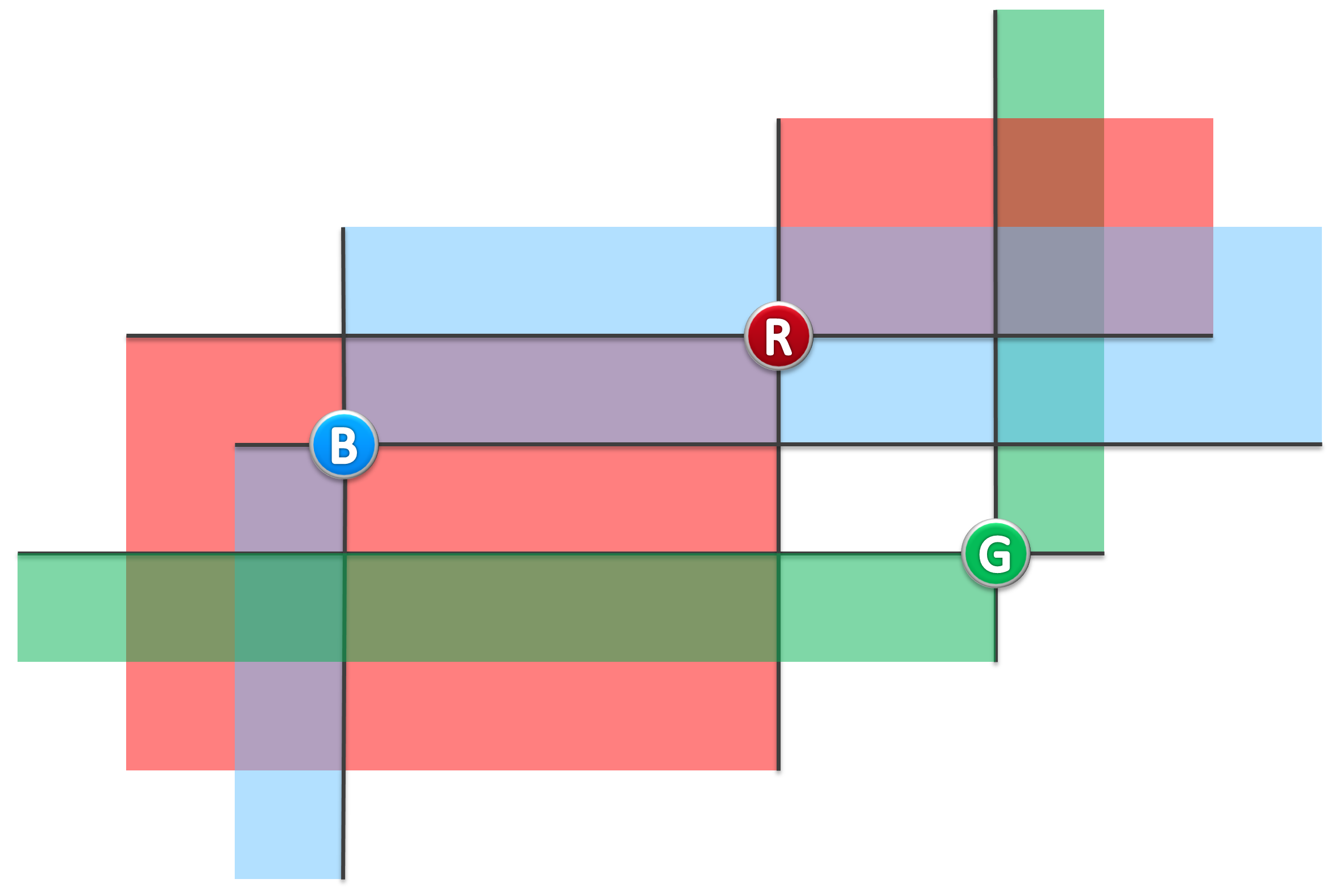
For example, in following figure, (B, R) is a pair of lighthouse which can beacon each other, while (B, G), (R, G) are NOT.
1st line: N
2nd ~ (N + 1)th line: each line is X Y, means a lighthouse is on the point (X, Y).
How many pairs of lighthourses can beacon each other
( For every lighthouses, X coordinates won‘t be the same , Y coordinates won‘t be the same )
Input
3
2 2
4 3
5 1
Output
1
For 90% test cases: 1 <= n <= 3 * 105
For 95% test cases: 1 <= n <= 106
For all test cases: 1 <= n <= 4 * 106
For every lighthouses, X coordinates won‘t be the same , Y coordinates won‘t be the same.
1 <= x, y <= 10^8
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
The range of int is usually [-231, 231 - 1], it may be too small.
解题思路:将灯塔按照x轴由大到小排序,即将问题转化为求y的逆序对的个数。求解逆序对可以利用归并排序的思路实现。
如下图:在某次归并的时候,左右两个数组已经排好顺序,如果遇到a[i] > a[j],则,a[j] 与a[i] 到a[n]的所有元素均构成逆序对。
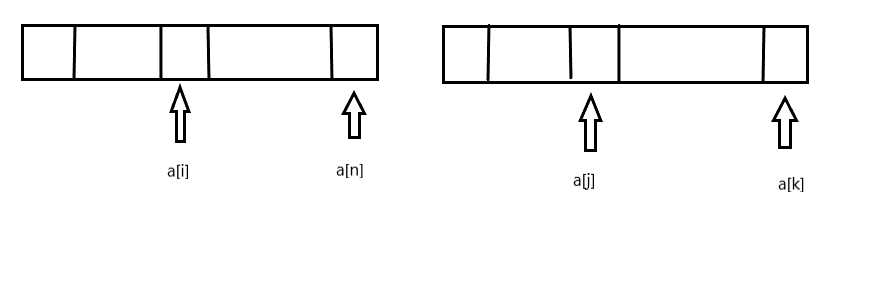
在归并排序的时候顺便统计一下逆序对的个数。
注意,要统计的逆序对个数可能很大。
代码如下

#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #define MAXN 4000005 #define ll long long using namespace std; struct node{ ll x; ll y; } tower[MAXN]; ll des[MAXN]; struct node des1[MAXN]; int N; ll num; void merg(int l, int mid, int r) { int i, j; int k; i = l; k = l; j = mid + 1; while(i <= mid && j <= r){ if(tower[i].x < tower[j].x){ des1[k].x = tower[i].x; des1[k++].y = tower[i++].y; } else{ des1[k].x = tower[j].x; des1[k++].y = tower[j++].y; } } while(i <= mid){ des1[k].x = tower[i].x; des1[k++].y = tower[i++].y; } while(j <= r){ des1[k].x = tower[j].x; des1[k++].y = tower[j++].y; } for (i = l; i <= r; i++){ tower[i].x = des1[i].x; tower[i].y = des1[i].y; } } void msort(int l, int r){ if(l >= r - 1) { if(tower[l].x > tower[r].x){ int x, y; x = tower[l].x; y = tower[l].y; tower[l].x = tower[r].x; tower[l].y = tower[r].y; tower[r].x = x; tower[r].y = y; } return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; msort(l, mid); msort(mid + 1, r); merg(l, mid, r); } void merge1(int l, int mid, int r) { int i, j; ll cnt = 0; int k = l; i = l; j = mid + 1; while(i <= mid && j <= r){ if(tower[i].y < tower[j].y){ des[k++] = tower[i++].y; cnt += r - j + 1; } else{ des[k++] = tower[j++].y; } } while(i <= mid) des[k++] = tower[i++].y; while(j <= r) des[k++] = tower[j++].y; for (i = l; i <= r; i++){ tower[i].y = des[i]; } num += cnt; } void get_num(int l, int r) { if(l >= r - 1){ if(tower[l].y < tower[r].y){ num++; } else{ int temp = tower[l].y; tower[l].y = tower[r].y; tower[r].y = temp; } return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; get_num(l, mid); get_num(mid + 1, r); merge1(l, mid, r); } int main() { scanf("%d", &N); num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { scanf("%lld %lld", &tower[i].x, &tower[i].y); } msort(0, N - 1); get_num(0, N - 1); printf("%lld\n", num); return 0; }
标签:while lld ++ lse string ddb width 左右 win
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Ido-911/p/10732504.html