标签:情况下 env 报错 好的 multi testing 执行命令 over 增加
脚本程序需要能与运行脚本程序的人员进行交互,bash shell提供了一些不同的方法来从用户处获取数据,这些方法包括命令行参数、命令行选项和直接读取键盘输入;
向shell脚本传递数据的基本方式是使用命令行参数(command line parameters)。使用命令行参数可以在执行脚本时向命令行中添加数据值
./addem 10 30 #向addem脚本传入 10 30 两个参数
bash shell将在命令行中输入所有参数复制给一些特殊变量,这些变量称之为位置参数(positional parameter)。
$0为程序名称
$1为第一个参数
$2为第二个参数
依次类推;
#!/bin/bash # using one command line paramter factorial=1 for (( number = 1; number <= $1; number++ )) do factorial=$[ $factorial * $number ] done echo The factorial of $1 is $factorial
./test1 5
如果需要输入更多的命令行参数,那么必须在命令行中使用空格分隔每个参数;
#!/bin/bash # testing two command line parameters total=$[ $1 * $2 ] echo The first parameter is $1. echo The second parameter is $2. echo The total value is $total.
./test2 2 5
输入参数,除了数值外,依然可以输入文本字符串
#!/bin/bash # testing string parameters echo Hello $1,glad to meet you.
./test3 Rich
如果输入的参数包含空格,则必须用引号引起来;
如果脚本输入的参数多余9个,第十个参数就要将10用花括号括起来--${10}
#!/bin/bash # handling lots of parameters total=$[ ${10} * ${11} ] echo The tenth parameter is ${10} echo The eleventh parameter is ${11} echo The total is $total
./test4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
通过$0来提取shell脚本的名称
#!/bin/bash # testing the $0 parameter echo The command entered is: $0
传递给$0的是完整的路径,而不是相对路径;
但是我们希望只是获取脚本名称,不要路径;这时候我们通过basename命令可以;
#!/bin/bash # using basename with the $0 parameter name=`basename $0` echo The command entered is: $name
这时候只会留下脚本名字;
这样的话,就可以利用这个名称来编写一些特定功能脚本;
#!/bin/bash # testing a multi-function script name=`basename $0` if [ $name = "addem" ] then total=$[ $1 + $2 ] elif [ $name = "mutlem" ] then total=$[ $1 * $2 ] fi echo The calculated value is $total
chmod u+x test6 cp test6 addem ln -s test6 multem ls -l ./addem 2 5
./multem 2 5
如果缺少参数,则会报错:会提示语法错误
./addme: line 8: 2 + : syntax error: operand expected (error token is " ")
当脚本变量认为里面有数据时,但是实际上没有参数,这样就会出现很多不好的情况。
#!/bin/bash # testing parameters before use if [ -n "$1" ] then echo Hello $1,glad to meet you. else echo "Sorry,you didn‘t identify yourself." fi
./test7 Rich
./test7 Rich
Sorry, you didn‘t identify youself. #这样的提示就会好一些
在bash shell脚本中有一些特殊的参数
$? 可以统计输入参数变量的数量;
#!/bin/bash # getting the number of parameters echo There were $# parameters supplied
./test8 ./test8 1 2 3 4 5 ./test8 "Rich Blum"
现在可以在使用参数前测试现有的参数个数:
#!/bin/bash # testing parameters if [ $# -ne 2 ]
then
echo Usage: test9 a b
else
total=$[ $1 + $2 ]
echo The total is $total
fi
./test9 ./test9 10 ./test9 10 15
./test9 10 15 20
${$#} #不能表示最后一个参数,这是一种错误的写法
#!/bin/bash # testing grabbing last parameter echo The last parameter war ${$#}
./badtest1 10 #理论上返回的是10,但实际上不是
如果想得到想要的结果,这里表明,不能在大括号中添加$符号,必须将$符号替换为!才行;
#!/bin/bash # Grabbing the last parameter params=$# echo The last parameter is $params echo The last parameter is ${!#}
./test10 1 2 3 4 5 The last parameter is 5 The last parameter is 5 ./test10 The last parameter is 0 The last parameter is ./test10
有时候,需要获取命令中所有参数,对这些参数进行循环。
$*和$@为所有参数提供了“一站式购物”服务,这两个变量都是在一个变量中包含所有的命令行参数。
$* 将多个变量视为一个单词处理。
$@将命令中提供的参数视为一个字符串中的多个单词处理;
#!/bin/bash # testing $* and $@ echo "Using the \$* method: $*" echo "Using the \$@ method: $@"
./test1 rich barbara katie jessica Using the $* method: rich barbara katie jessica Using the $@ method: rich barbara katie jessica
再看一个例子
#!/bin/bash # testing $* and $@ count=1 for param in "$*" do echo "\$* Parameter #$count = $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done count=1 for param in "#@" do echo "\$@ Parameter #$count = $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
./test12 rich barbara katie jessica
在使用for命令迭代特殊变量的时候,使用$*只进行一次。而$@则是将所有的变量都遍历一遍;
shift命令。bash shell提供了shift命令来对传参进行推进,改变命令行参数的位置。
没执行一次命令,则参数变量可以左移以为。于是$3就会变为$2。
#!/bin/bash # demonstrating the shift command count=1 while [ -n "$1" ] do echo "Parameter #$count = $1" count=$[ $count + 1 ] shift done
./test13 rich barbara katie jessica
脚本执行while循环,测试第一个参数的数值长度,当长度为0的时候,结束循环。
#!/bin/bash # demonstrating a multi-postion shift echo "The original parameters: $*" shift 2 echo "Here‘s the new first parameter: $1"
./test14 1 2 3 4 5
此时$1应该代表的是 3 ,因为之前执行了 shift 2 将参数向前移动了两位
选型就是脚本作为执行命令的时候,需要指定的特殊功能;这里我们需要自己来定义;
1、处理简单的选项
抽取每个参数时,使用case语句判断参数是否符合选项格式:
#!/bin/bash # extracting command line options as parameters while [ -n "$1" ] do case "$1" in -a) echo "Found the -a option";; -b) echo "Found the -b option";; -c) echo "Found the -c option";; *) echo "$1 is not an option";; esac shift done
case语句检查每个参数是否有效的选项。当找到一个选项时,就在case语句中运行适当的命令,以后,这些功能我们会以函数的形式写在下面,供这里来调用;
2、从参数中分离选项
命令中分离参数与选项
#!/bin/bash # extracting options and parameters while [ -n "$1" ] do case "$1" in -a) echo "Found the -a option";; -b) echo "Found the -b option";; -c) echo "Found the -c option";; --) shift #保证 -- 从参数变量中丢弃 break ;; *) echo "$1 is not an option";; esac shift done count=1 for param in $@ do echo "Parameter #$count: $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
./test16 -c -a -b test1 test2 test3 Found the -c option Found the -a option Found the -b option test1 is not an option test2 is not an option test3 is not an option
./test16 -c -a -b -- test1 test2 test3 Found the -c option Found the -a option Found the -b option Parameter #1: test1 Parameter #2: test2 Parameter #3: test3
3、处理带值的选项
有限选项需要附加参数值。这种情况下,命令形式与下面的格式类似;
./testing -a test1
例子:
#!/bin/bash # extracting command line options and values while [ -n "$1" ] do case "$1" in -a) echo "Found the -a option";; -b) param="$2" #这个有一个附加参数值,位于$2 echo "Found the -b option,with parameter value $param" shift 2;; -c) ehco "Found the -c option";; --) shift break;; *) echo "$1 is not an option";; esac shift done count=1 for param in "#@" do echo "Parameter #$count: $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
./test17 -b test1 -a -d
但是如果要将短选项合并呢, ./test17 -ac 则又会报错;
getopt用来处理命令行与选项之间的关系非常不错;
1、命令模式
getopt用法:getopt options optstring parameters
选项字符optsting是处理的关键。它定义了命令行中的有限选项字母。还定义了这些选项字母的相关参数;
getopt ab:cd -a -b test1 -cd test2 test3
如果使用命令不在getopt定义的选项字符串中,这样就会报错
getopt ab:cd -a -b test1 -cde test2 test3 getopt: invalid option -- e -a -b test1 -c -d -- test2 test3
如果先忽略这个错误 -q 就可以了;
2、在脚本中使用getopt
我们需要将现有的命令行选项和参数替换为getopt命令生成的格式化形式。方法是通过set命令来实现;
#!/bin/bash # extracting command line options and values with getopt set -- `getopt -q ab:c "$@"` while [ -n "$1" ] do case "$1" in -a) echo "Found the -a option";; -b) param="$2" echo "Found the -b option,with parameter value $param" shift;; -c) echo "Found the -c option" ;; --) shift break ;; *) echo "$1 is not an option" ;; esac shift done count=1 for param in "$@" do echo "Parameter #$count: $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
./test18 -ac ./test18 -a -b test1 -cd test2 test3 test4
./test18 -a -b test1 -cd "test2 test3" test #这样分别将 "test2 和 test3" 视为两个值了
getopt为命令行中找到的素有待处理选项和参数生成一个输出,而与getopt不同,getopts命令顺序对现有shell参数变量进行处理;
每调用一次getopts,它只处理在命令中检测到的参数中的一个。处理完所有参数后,以大于零的退出转态退出。因此,getopts非常适合用在循环中解析所有的命令行参数。
getopts用法:getopts optstring variable
#!/bin/bash # smiple demonstration of the getopts command while getopts :ab:c opt do case "$opt" in a) echo "Found the -a option" ;; b) echo "Found the -b option, with value $OPTARG" ;; c) echo "Found the -c option" ;; *) echo "Unknow option: $opt" ;; esac done
./test19 -ab test1 -c
./test19 -b "test1 test2" -a
getopts命令可以将正确的选项以及参数解析处理啊。getopts名里还可以将命令中找到的为定义的选项都绑定为一个符号输出--问号
./test19 -d
getopts每个处理选项,环境变量OPTIND的值会增加1.当达到getopts处理的末尾的时候,可以使用shift命令和OPTIND值进行操作来移动到参数:
#!/bin/bash # processing options and parameters wiht getopts while getopts :ab:cd opt do case "$opt" in a) echo "Found the -a option" ;; b) echo "Found the -b option, with value $OPTARG" ;; c) echo "Found the -c option" ;; d) echo "Found the -d option" ;; *) echo "Unknown option: $opt" ;; esac done shift $[ $OPTIND - 1 ] count=1 for param in "$@" do echo "Parameter $count: $param" count=$[ Parameter $count: $param] done
./test20 -a -b test1 -d test2 test3 test4
至此,就拥有了可以用于所有shell脚本的完整功能;
在Linux的世界里面,那些字母具有那些特定的意义呢?
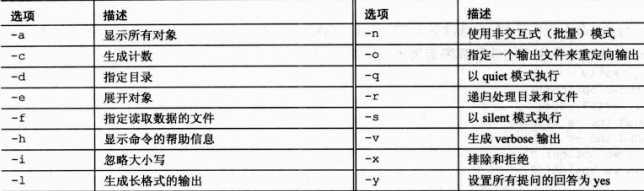
参数是一种输入数据的方式,有时候要进入交互式的方式进行输入选择,这时候就需要通过read的方式来实现;
#!/bin/bash # testing the read command echo -n "Enter your name: " #不换行 read name #读取name的值 echo "Hello $name, welcome to my program."
事实上不用这么麻烦,直接使用 -p 的参数就可以了
#!/bin/bash # testing the read -p option read -p "Please enter your age:" age days=$[ $age * 365 ] echo "That makes you over $days days old!"
直接使用 read -p 参数就避免的了使用echo -n 在加 read 的这种组合
事实上,read -p 后面同样可以添加多个变量值
#!/bin/bash # entering multiple variables read -p "Enter your name: " first last echo "Checking data for $last, $first ..."
这个例子中,first,last分别是read 后输入的两个变量值,在后面的代码中可以直接调用;
read也可以不用指定变量,那么read所接受到的环境变量值就会被默认放在REPLY中;
#!/bin/bash # testing the REPLY environment variable read -p "Enter a number: " factorial=1 for (( count=1; count <= $REPLY; count++ )) do factorial=$[ $factorial * $count ] done echo "The factorial of $REPLY is $factorial"
使用read存在着潜在的危险。会一直等待用户输入数据,这时候就可以使用 -t 参数指定在规定时间内输入数据,如果不输入就会执行下面的命令;
#!/bin/bash # timing the data entry if read -t 5 -p "Please enter your name: "name then echo "Hello $name, welcome to my script" else echo echo "Sorry, too slow!" fi
除了计时,还可以规定输入内容的字符数量
#!/bin/bash # getting just one character of input read -n1 -p "Do you want to contnue [Y/N]? " answer case $answer in Y | y) echo echo "fine, contnue on ... ";; N | n) echo echo OK, goodbye exit;; esac echo "This is the end of the script"
有时候,输入的内容不希望显示在显示器上,比如密码;
这时候,我们使用-s的参数来实现;
#!/bin/bash # hiding input data from the monitor read -s -p "Enter your password: " pass echo echo "Is your password really $pass?"
最后,我们可以使用read命令读取Linux系统上存储在文件中的数据。每调用一次read命令都会读取文件中的一行文本。当文件中没有可读的行时,read命令将以非零退出状态退出。
我通过cat命令将内容传输给read来读取;
#!/bin/bash # reading data from a file count=1 cat test | while read line #while命令使用read命令不断处理文件中的每一行,知道read命令以非零状态退出 do echo "Line $count: $line" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done echo "Finished processing the file"
标签:情况下 env 报错 好的 multi testing 执行命令 over 增加
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/BurnovBlog/p/10787631.html