标签:遍历 alt out ldb ESS 源码 同步队列 on() exception
一、ReentrantLock简介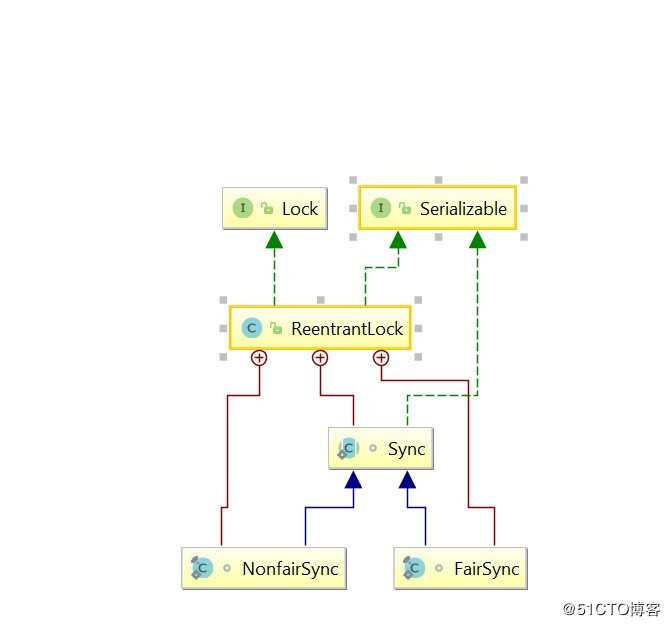
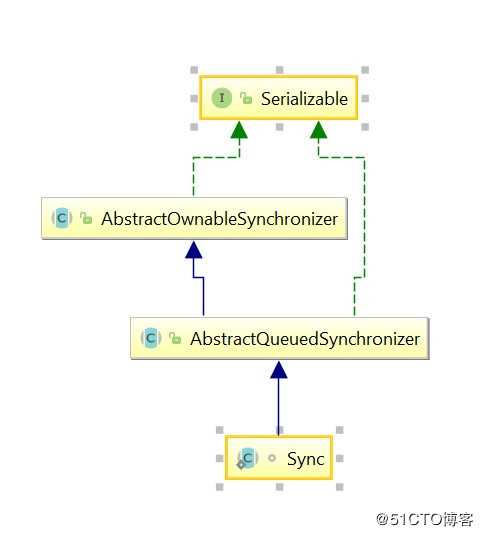
三、主要的方法
分析一些常用方法,不会介绍AQS,AQS的一些方法参考我的这一篇文章
①、构造方法,我们可以看出默认的无参是非公平锁,有参构造true表示公平,false表示非公平。
// 无参
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
// 有参
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}②、lock()获取锁,其实就是把state从0变成n(重入锁可以累加)。
实际调用的是sync的lock方法,分公平和非公平。
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}公平实现:FairSync,我们发现其实调用的是acquire,其实这个是AQS的acquire,然后aqs的acquire的方法里面又会调用tryAcquire方法,因为这个方法需要同步组件自己去实现,所以ReentrantLock里面重写了AQS的tryAcquire方法,所以我们获取到锁就会返回true,没有就会返回false;然后没有获取到锁的线程就交给AQS去处理。
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
/**
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don‘t grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 获取当前的线程
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取锁的状态
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// hasQueuedPredecessors 判断队列还有没有其它node,要保证公平
// 没有在用cas设置状态
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
// 设置获取锁的线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 判断当前线程有没有获取到锁
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// 获取过了就累加,因为可以重入
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// 重新设置锁的状态
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}非公平实现:NonfairSync,我们可以发现基本和公平一样,就没有hasQueuedPredecessors方法,没有遵循FIFO队列的模式,而是不管队列有没有node,自己都可以去获取锁,不需要排队
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}②、lockInterruptibly支持中断的获取锁,其实是调用了AQS的lockInterruptibly方法,在AQS方法里面又回去调用tryAcquire方法,这个方法在上面已经解释过了。
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}AQS的lockInterruptibly方法
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}③、tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit),支持中断,并且在这个基础上增加了超时设置,其实也是调用了AQS的tryAcquireNanos方法,我们发现其实他也是调用的tryAcquire方法。
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}AQS的tryAcquireNanos方法
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}④、unlock释放锁,其实就是把state从n(可能发生了锁的重入,需要多次释放)变成0,这个不区分公平与非公平,首先其实也是调用AQS的release方法,然后AQS在调用子类Sync的tryRelease方法。
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}调用Sync的tryRelease方法
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// 获取锁的状态
int c = getState() - releases;
// 获得锁的线程才能释放锁
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 直到锁的状态是0,说明锁释放成功,因为有重入锁
// 说明我们在一个线程里面调用几次lock,就要调用几次unlock,才能最终释放锁
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
// 释放线程的拥有者
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
// 设置锁的状态
setState(c);
return free;
}⑤、newCondition方法,创建一个newCondition。
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}⑥、getHoldCount方法,获取当前线程获得锁的个数。
public int getHoldCount() {
return sync.getHoldCount();
}
final int getHoldCount() {
// 当前线程是否获取到锁
return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;
}⑦、isHeldByCurrentThread方法,当前线程是否获取到锁。
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
// While we must in general read state before owner,
// we don‘t need to do so to check if current thread is owner
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}⑧、isLocked方法,是否有线程获取到了锁。
final boolean isLocked() {
return getState() != 0;
}⑨、getOwner方法,获取取得锁的线程。
⑩、getQueueLength方法,获取同步队列的数量。
public final int getQueueLength() {
// 从aqs的尾节点开始往前遍历,除去空节点(但是其实只有第一个节点是空节点),也就是thread != null
int n = 0;
for (Node p = tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.thread != null)
++n;
}
return n;
}四、总结
学习ReentrantLock,我们主要需要了解它,公平和非公平的实现,以及重入锁的获取与释放的流程,还有最重要的就是要了解AQS,这是实现重入锁的基础,因为ReentrantLock只是实现了AQS获取锁和释放锁制定的模板方法的语义,所以要理解ReentrantLock获取锁成功和失败具体都做了什么逻辑,和AQS的实现是离不开的。
可以参考我的这一篇AQS的文章。
参考 《Java 并发编程的艺术》
标签:遍历 alt out ldb ESS 源码 同步队列 on() exception
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/14220760/2391256